oscarotero / folk
Universal CMS
Requires
- php: ^7.2|^8.0
- form-manager/form-manager: ^5.0
- gettext/gettext: ^5.0.0
- gettext/js-scanner: ^1.0.0
- gettext/json: ^1.0.0
- gettext/php-scanner: ^1.0.0
- gettext/robo: ^4.0.0
- gettext/translator: ^1.0.0
- imagecow/imagecow: ^2.1
- league/plates: ^3.1
- middlewares/aura-router: ^2.0
- middlewares/base-path: ^2.0
- middlewares/filesystem: ^2.0
- middlewares/method-override: ^2.0
- middlewares/negotiation: ^2.0
- middlewares/request-handler: ^2.0
- middlewares/trailing-slash: ^2.0
- middlewares/utils: ^3.0
- oscarotero/fol: ^1.0
- oscarotero/inline-svg: ^2.0
- oscarotero/middleland: ^1.0
- psr/http-server-middleware: ^1.0
Requires (Dev)
- consolidation/robo: ^2.0
- fly-crud/fly-crud: ^3.0
- friendsofphp/php-cs-fixer: ^2.15
- laminas/laminas-diactoros: ^2.1.3
- middlewares/emitter: ^1.0
- oscarotero/php-cs-fixer-config: ^1.0
- simple-crud/simple-crud: ^7.0
- symfony/yaml: ^4.0
- dev-master
- v3.7.4
- v3.7.3
- v3.7.2
- v3.7.1
- v3.7.0
- v3.6.3
- v3.6.2
- v3.6.1
- v3.6.0
- v3.5.1
- v3.5.0
- v3.4.1
- v3.4.0
- v3.3.0
- v3.2.1
- v3.2.0
- v3.1.0
- v3.0.4
- v3.0.3
- v3.0.2
- v3.0.1
- v3.0.0
- v2.5.0
- v2.4.1
- v2.4.0
- v2.3.0
- v2.2.4
- v2.2.3
- v2.2.2
- v2.2.1
- v2.2.0
- v2.1.0
- v2.0.0
- 1.x-dev
- v1.14.3
- v1.14.2
- v1.14.1
- v1.14.0
- v1.13.2
- v1.13.1
- v1.13.0
- v1.12.2
- v1.12.1
- v1.12.0
- v1.11.2
- v1.11.1
- 1.11.0
- v1.10.5
- v1.10.4
- v1.10.3
- v1.10.2
- v1.10.1
- v1.10.0
- 1.9.2
- v1.9.1
- v1.9.0
- v1.8.1
- 1.8.0
- v1.7.2
- v1.7.1
- v1.7.0
- v1.6.0
- v1.5.2
- v1.5.1
- v1.5.0
- v1.4.0
- v1.3.0
- v1.2.0
- v1.1.0
- v1.0.2
- v1.0.1
- v1.0.0
- dev-v4-dev
- dev-redesign
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-17 03:34:58 UTC
README
The universal CMS
This is a framework-agnostic CMS that you can use to edit the content of your site. It works with any kind of websites, no matter if the content is stored in a database, yml files, json, etc.
Demo: https://oscarotero.com/folk/demo/
Requirements
- PHP >= 7
- Composer
Installation
This package is installable and autoloadable via Composer as oscarotero/folk.
composer require oscarotero/folk
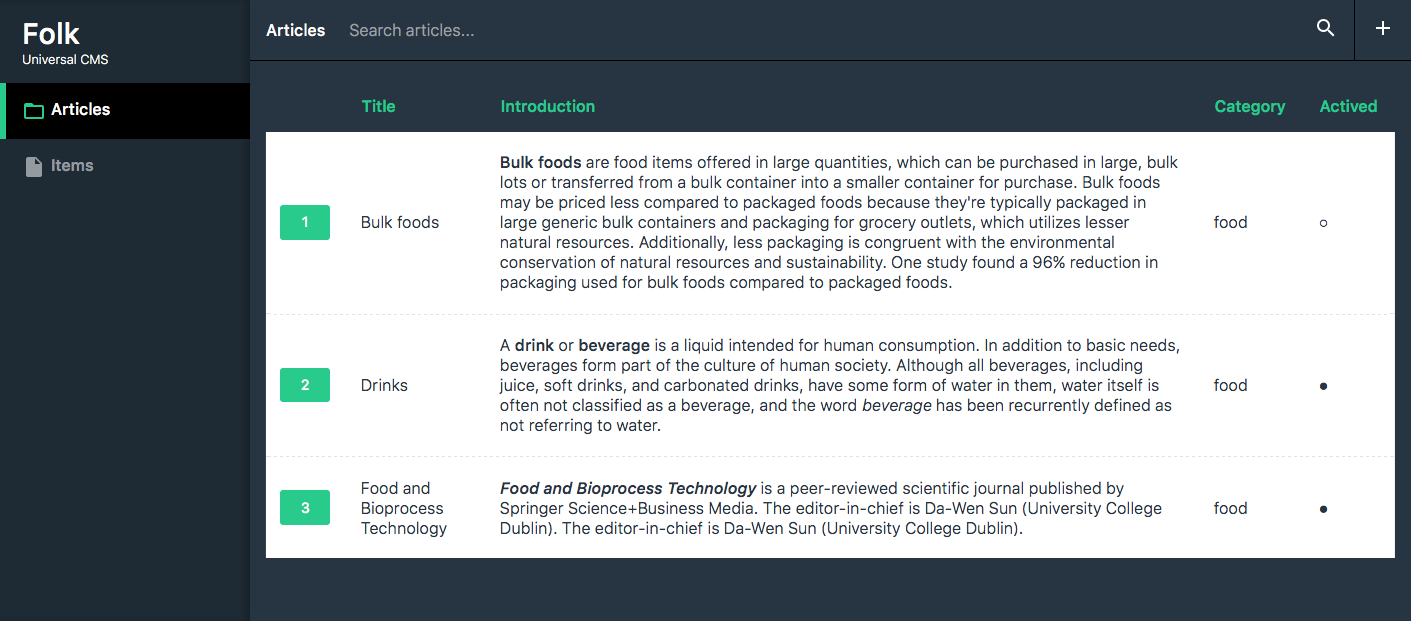
Entities
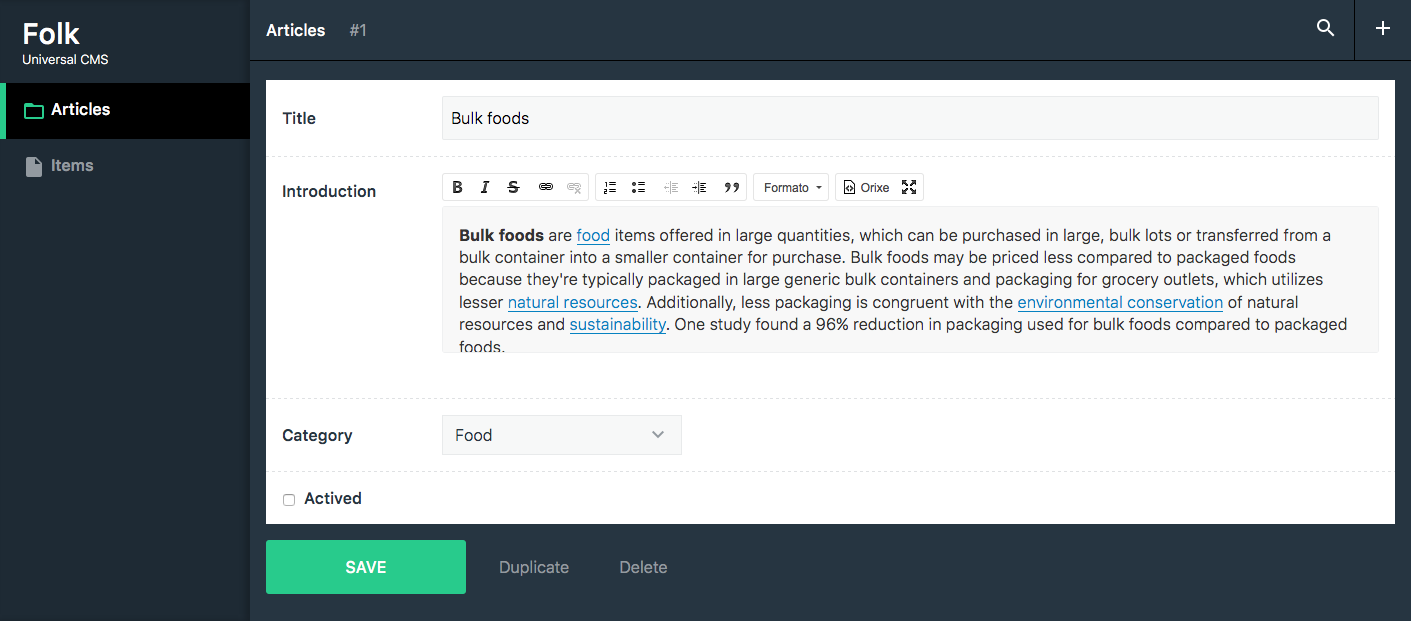
The entities are classes to manage "things". It can be a database table, a file, a directory with files, etc. They must implement Folk\Entities\EntityInterface (or extend Folk\Entities\AbstractEntity). Let's see an example of an entity using a database table.
namespace MyEntities; use Folk\SearchQuery; use Folk\Formats\FormatFactory; use Folk\Formats\Group; use Folk\Entities\AbstractEntity; /** * Entity to manage the posts */ class Posts extends AbstractEntity { public $title = 'Posts'; public $description = 'These are the posts of the blog'; /** * List the posts * * @return array [id => data, ...] */ public function search(SearchQuery $search): array { $query = 'SELECT * FROM posts'; if ($search->getPage() !== null) { $limit = $search->getLimit(); $offset = ($search->getPage() * $limit) - $limit; $query .= " LIMIT {$offset}, {$limit}"; } $pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo'); $result = $pdo->query($query); $data = []; while ($row = $result->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)) { $data[$row['id']] = $row; } return $data; } /** * Create a new post * * @return mixed The post id */ public function create(array $data) { $pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo'); $statement = $pdo->prepare('INSERT INTO posts (title, text) VALUES (:title, :text)'); $statement->execute([ ':title' => $data['title'], ':text' => $data['text'], ]); return $pdo->lastInsertId(); } /** * Read a post * * @return array */ public function read($id): array { $pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo'); $statement = $pdo->prepare('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = ? LIMIT 1'); $statement->execute([$id]); return $statement->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC); } /** * Update a post */ public function update($id, array $data) { $pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo'); $statement = $pdo->prepare('UPDATE posts SET title = :title, text = :text WHERE id = :id LIMIT 1'); $statement->execute([ ':title' => $data['title'], ':text' => $data['text'], ':id' => $data['id'], ]); } /** * Delete a post */ public function delete($id) { $pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo'); $statement = $pdo->prepare('DELETE FROM posts WHERE id = ? LIMIT 1'); $statement->execute([$id]); } /** * Returns the data scheme used by the posts. */ public function getScheme(FormatFactory $factory): Group { return $factory->group([ 'title' => $factory->text() ->maxlength(200) ->label('The post title'), 'text' => $factory->html() ->label('The body'), ]); } /** * Returns the label of a row. * (used in autocomplete searches, select, etc) */ public function getLabel($id, array $data): string { return sprintf('%s (%d)', $data['title'], $id); } }
Getting started
There's some predefined entities that you can extend and configure, for example to use with simplecrud, or to save the content in yaml or json files, etc.
Once your entities are created, let's make them to run:
use Folk\Admin; use Entities\Posts; //Create a Admin instance passing the root path and the http uri: $uri = new Zend\Diactoros\Uri('http://my-site.com/admin'); $admin = new Admin(__DIR__, $uri); //Set the pdo instance: $admin['pdo'] = new PDO('mysql:dbname=database;charset=UTF8'); //Add set your entities classes $admin->setEntities([ Posts::class ]); //Run the web (using PSR-7 request/responses) $request = Zend\Diactoros\ServerRequestFactory::fromGlobals(); $emitter = new Zend\Diactoros\Response\SapiEmitter(); $response = $admin($request); $emitter->emit($response);
As you can see, this is a simple example with a simple mysql table. But the interface is flexible enought to work with any kind of data.
To know how to work with the scheme, visit form-manager project.