aurorawebsoftware / arflow
ArFlow is a Laravel package that allows you to implement workflow management for your Laravel Eloquent models.
Installs: 2 901
Dependents: 2
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 23
Watchers: 1
Forks: 1
Open Issues: 2
pkg:composer/aurorawebsoftware/arflow
Requires
- php: ^8.2|^8.3|^8.4
- laravel/framework: ^12.0
- spatie/laravel-package-tools: ^1.14.0
Requires (Dev)
- larastan/larastan: ^v3
- laravel/pint: ^1.0
- nunomaduro/collision: ^8.0
- orchestra/testbench: ^10
- pestphp/pest: ^3.0
- pestphp/pest-plugin-arch: ^3.0
- pestphp/pest-plugin-laravel: ^3.0
- phpstan/extension-installer: ^1.1
- phpstan/phpstan-deprecation-rules: ^2.0
- phpstan/phpstan-phpunit: ^2.0
- dev-main
- 12.0.4
- 12.0.3
- 12.0.2
- 12.0.1
- 12.0.0
- 11.0.0
- 1.1.3
- 1.1.2
- 1.1.1
- 1.1.0
- 1.0.3
- 1.0.2
- 1.0.1
- 1.0.0
- dev-phpstan
- dev-cursor
- dev-laravel-12-update
- dev-laravel-11-update
- dev-has_state_fix
- dev-updated-successjob-parameter
- dev-add-get-last-updated-time
- dev-has-state-update
- dev-Facade-fonksiyonun-yazılması
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-01-25 17:11:16 UTC
README
Introduction
ArFlow is a Laravel package that allows you to implement workflow management for your Laravel Eloquent models. This documentation provides a comprehensive guide on how to use ArFlow effectively.
Key Concepts
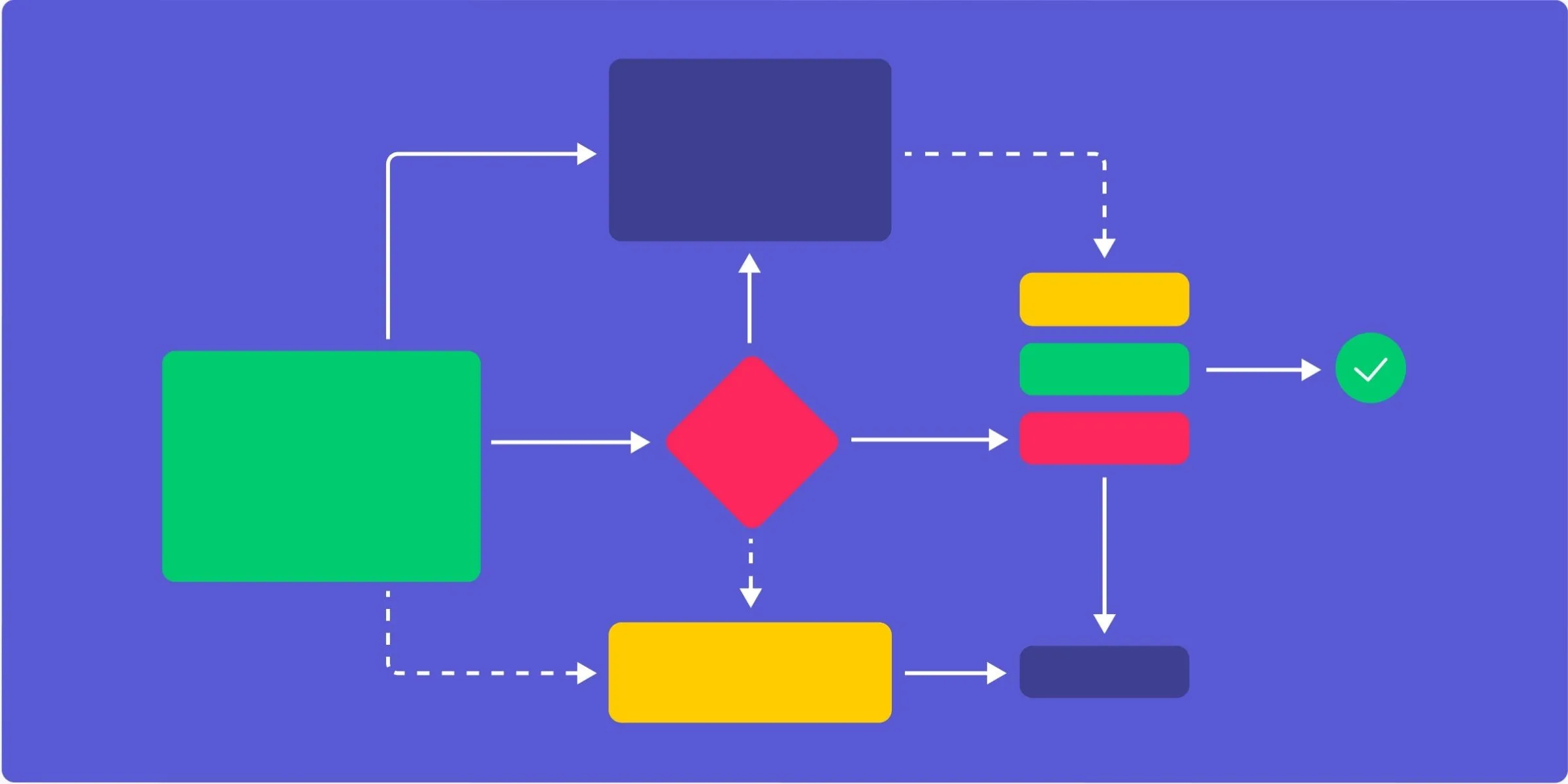
1. Workflows
A workflow represents a series of states and transitions that a model can go through. Key points about workflows:
- Each model can be associated with one or more workflows.
- Workflows define the possible states and transitions for a model.
2. States
States represent the different stages that a model can exist in within a workflow. Key points about states:
- Each workflow has a set of predefined states.
- Models can be in one of these states at any given time.
3. Transitions
Transitions define the rules and conditions for moving a model from one state to another within a workflow. Key points about transitions:
- Transitions specify which states a model can move from and to.
- They can have guards, actions, and success jobs associated with them.
4. Guards
Guards are conditions or checks that must be satisfied for a transition to occur. Key points about guards:
- Guards prevent transitions if their conditions are not met.
- They are defined as classes and can be customized to suit your application's logic.
5. Actions
Actions are tasks or operations that are executed during a transition. Key points about actions:
- Actions are executed when a transition occurs.
- They are defined as classes and can be customized to perform specific tasks.
6. Success Jobs
Success jobs are jobs or tasks that are dispatched after a successful transition. Key points about success jobs:
- They allow you to perform background tasks after a transition.
- Useful for logging, notifications, or other post-transition actions.
7. Initial State
Each workflow has an initial state that a model enters when the workflow is applied. Key points about the initial state:
- It's the starting point for models within a workflow.
- Models are in the initial state when the workflow is first applied.
Installation
You can install the ArFlow package via Composer. Run the following command:
composer require aurorawebsoftware/arflow
Next, you need to publish the package configuration and migration files:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag=arflow-config
don't forget to run the migration:
php artisan migrate
Model Setup
To use ArFlow in your model, follow these steps:
- Use the
HasStatetrait in your model class.
This trait provides functionality that allows a model to be a part of a workflow, fetch configurations, get initial states, and perform transitions.
use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Traits\HasState; class YourModel extends Model { use HasState; // Your model properties and methods }
- Implement the
StateableModelContractinterface in your model class.
This interface ensures your model has the required methods to function as a stateable entity. This includes setting workflow attributes, state attributes, and metadata attributes. You can also determine supported workflows, apply workflows, and make transitions. Below are sample usages:
use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Contacts\StateableModelContract; class YourModel extends Model implements StateableModelContract { use HasState; public static function supportedWorkflows(): array { return ['workflow1', 'workflow3']; } // Your model properties and methods }
- (Optional) Define the workflow-related attributes for your model in the model class if you want to change default values or skip this step:
class YourModel extends Model implements StateableModelContract { use HasState; public static function workflowAttribute(): string { return 'workflow'; } public static function stateAttribute(): string { return 'state'; } public static function stateMetadataAttribute(): string { return 'state_metadata'; } // Your model properties and methods }
Usage
Now that you've set up your model, you can apply workflows and perform transitions:
Applying a Workflow
To apply a workflow to a model instance, use the applyWorkflow method:
$model = YourModel::find($id); $model->applyWorkflow('workflow_name');
To get the current workflow of a model:
$currentWorkflow = $instance->currentWorkflow();
To get the current state of a model:
$currentState = $instance->currentState();
Checking Transition States
You can check if a transition to a specific state is allowed using the canTransitionTo method:
$model = YourModel::find($id); if ($model->canTransitionTo('new_state')) { // Transition is allowed } else { // Transition is not allowed }
Transitioning to a State
To transition a model to a new state, use the transitionTo method:
$model = YourModel::find($id); $model->transitionTo('new_state');
Getting Defined and Allowed Transition States
You can retrieve the defined and allowed transition states for a model:
// Defined transition states $definedStates = $model->definedTransitionStates(); // Allowed transition states $allowedStates = $model->allowedTransitionStates();
TransitionGuardResults
You can also get transition guard results using the transitionGuardResults method:
$results = $model->transitionGuardResults('new_state');
This method returns a collection of transition guard results, which can be used to check if guards allow the transition.
Configuration
You can configure your workflows in the config/arflow.php file. Define your workflows, states, transitions, guards, and actions there.
Sample Configuration
Here's a sample configuration for a workflow:
Blueprint Macro
To simplify adding state columns to your migrations, a Blueprint macro is provided:
This macro $table->arflow() will create three columns: workflow, state, and state_metadata.
// your_migration.php Schema::create('your_model', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->arflow(); $table->timestamps(); });
// config/arflow.php return [ 'workflows' => [ 'workflow_name' => [ 'states' => ['state1', 'state2', 'state3'], 'initial_state' => 'state1', 'transitions' => [ 'transition_name' => [ 'from' => ['state1'], 'to' => 'state2', 'guards' => [ [GuardClass::class, ['permission' => 'approval']], ], 'actions' => [ [ActionClass::class, ['param1' => 'value1']], ], 'success_metadata' => ['key' => 'value'], 'success_jobs' => [JobClass::class], ], // Define more transitions as needed ], ], // Define additional workflows ] ];
Creating Transition Guards
Sample Transition Guard Implementation.
namespace App\ArFlow\Guards; use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Contacts\StateableModelContract; use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Contacts\TransitionGuardContract; use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\DTOs\TransitionGuardResultDTO; class PermissionTransitionGuard implements TransitionGuardContract { private StateableModelContract $model; private string $from; private string $to; private array $parameters; public function __construct() {} public function boot(StateableModelContract &Model $model, string $from, string $to, array $parameters): void { $this->model = $model; $this->from = $from; $this->to = $to; $this->parameters = $parameters; // You can perform any initialization here. } public function handle(): TransitionGuardResultDTO { // Implement your logic to check permissions here. // For example, check if the user has the required role to make the transition. // If the permission check passes, allow the transition: return TransitionGuardResultDTO::build(TransitionGuardResultDTO::ALLOWED); // If the permission check fails, deny the transition: // return TransitionGuardResultDTO::build(TransitionGuardResultDTO::DENIED, 'Permission denied.'); } }
Creating Transition Action
Sample Transition Action
use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Contacts\TransitionActionContract; class SendNotificationAction implements TransitionActionContract { public function boot(StateableModelContract&Model $model, string $from, string $to, array $parameters = []): void {} public function handle(): void { // Send a notification when the transition is successful. } public function failed(): void { // Handle any cleanup or error logging here if the action fails. } }
Creating Transition Success Job
Sample Transition Job
namespace AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Tests\Jobs; use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Abstracts\AbstractTransitionSuccessJob; use AuroraWebSoftware\ArFlow\Contacts\StateableModelContract; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model; class TestTransitionSuccessJob extends AbstractTransitionSuccessJob { /** * Execute the job. * @param StateableModelContract&Model $model * @param string $from * @param string $to * @param array $parameters */ public function handle(StateableModelContract & Model $model, string $from, string $to, array $parameters = []): void { // Process } }
Contribution
- php 8.2+
docker-compose up -d
composer format
composer analyse
composer test
composer test-coverage
This documentation should help you get started with the ArFlow package in your Laravel application. Feel free to explore more features and configurations based on your project's requirements.
For more information, please refer to the package's GitHub repository or contact us for support.