snoke / symfony-websocket
Installs: 1 660
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 7
Watchers: 1
Forks: 4
Open Issues: 3
Type:symfony-bundle
pkg:composer/snoke/symfony-websocket
Requires
- php: ^8.1
- doctrine/collections: ^2.2
- psr/log: ^3.0
- react/event-loop: ^1.5
- react/socket: ^1.15
- symfony/console: ^7.1
- symfony/dependency-injection: ^7.1
- symfony/event-dispatcher: ^7.1
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-22 10:22:41 UTC
README
RFC 6455-compliant Websocket Server Bundle for Symfony 7
installation
checkout library
composer req snoke/symfony-websocket
modify config/packages/snoke_websocket.yaml:
snoke_websocket: context: tls: local_cert: 'path/to/server.pem' local_pk: 'path/to/private.key' allow_self_signed: true verify_peer: false
if you do not want to use TLS:
snoke_websocket: context: []
note that websockets without TLS only work on localhost (tho you can still use Stunnel to wrap them into a TLS Connection)
getting started
Starting the WebSocket Server
Use the Symfony console command to start the WebSocket server
php bin/console websocket:start
You can optionally specify the IP address and port:
php bin/console websocket:start --ip=127.0.0.1 --port=9000
testing the server
you can connect and send a message to your websocket server with following command:
php bin/console websocket:test
Registering Event Listeners
to react to WebSocket events, create your own listeners.
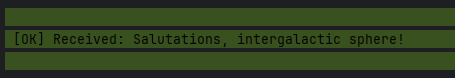
use Snoke\Websocket\Event\MessageReceived; use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\Attribute\AsEventListener; #[AsEventListener(event: MessageReceived::class, method: 'onRequestReceived')] final class MessageListener { public function onRequestReceived(MessageReceived $event): void { $connection = $event->getConnection(); $connection->send("Salutations, intergalactic sphere!"); } }
test again with php bin/console websocket:test
Mapping Users
the ConnectionWrapper contains getter and setter to match a connection with a Symfony UserInterface
namespace App\EventListener; use App\Security\Authenticator; use Snoke\Websocket\Event\RequestReceived; use Symfony\Component\Serializer\SerializerInterface; use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\Attribute\AsEventListener; #[AsEventListener(event: RequestReceived::class, method: 'onRequestReceived')] final class AuthListener { public function __construct( private readonly Authenticator, private readonly SerializerInterface ) {} public function onRequestReceived(RequestReceived $event): void { $request = $event->getFrame(); $connection = $event->getConnection(); if ($request['type'] === 'auth') { $payload = $request['payload']; $user = $this->authenticator->authenticate($payload['identifier'],$payload['password']); $connection->setUser($user); $connection->send($serializer->serialize($user, 'json')); } } }
Broadcasting
you can access all connections in the Listeners through the event
foreach($event->getConnections() as $connection) { $connection->send($message); }
Available Events
- ServerStarted: Triggered when the WebSocket server is started.
- ConnectionOpened: Triggered when a new WebSocket connection is established.
- ConnectionClosed: Triggered when a WebSocket connection is closed.
- Error: Triggered when an error occurs.
- MessageReceived: Triggered when a WebSocket message is received.
- TextFrame: Triggered after MessageReceived when a text message frame is received (WebSocketOpcode::TextFrame).
- BinaryFrame: Triggered after MessageReceived when a binary message frame is received (WebSocketOpcode::BinaryFrame).
- ContinuationFrame: Triggered after MessageReceived d when a continuation frame is received for a fragmented message (WebSocketOpcode::ContinuationFrame).
- ConnectionCloseFrame: Triggered after MessageReceived when a connection close frame is received (WebSocketOpcode::ConnectionCloseFrame).
- PingFrame: Triggered after DataReceived when a ping frame is received (WebSocketOpcode::PingFrame).
- PongFrame: Triggered after DataReceived when a pong frame is received (WebSocketOpcode::PongFrame).
Advanced
Message Fragmentation
The server handles fragmented messages using the following opcodes:
TextFrame (0x1)
BinaryFrame (0x2)
ContinuationFrame (0x0)
When a message is fragmented:
The first frame (Text or Binary Frame) starts with FIN set to 0.
Subsequent frames (Continuation Frames) continue the message with FIN set to 0 until the last frame.
The last frame of the message has FIN set to 1, indicating the end of the fragmented message.
Ensure your application handles fragmented messages correctly based on RFC 6455 specifications.