s-damian / laravel-man-pagination
Laravel Pagination library
Package info
github.com/s-damian/laravel-man-pagination
pkg:composer/s-damian/laravel-man-pagination
Requires
- php: ^8.0
Requires (Dev)
- laravel/framework: ^8.0 || ^9.0 || ^10.0 || ^11.0 || ^12.0
- laravel/pint: ^1.0
- orchestra/testbench: ^6
- phpstan/phpstan: ^1.11
- phpunit/phpunit: 9.5.*
README
Laravel Pagination for Manual SELECT Queries
Laravel Manual Pagination - Laravel Man Pagination
Introduction - Laravel Man Pagination
This package is particularly useful for implementing pagination with manual SELECT queries using DB::select().
Laravel Man Pagination is an Open Source PHP library of a simple manual pagination (compatible with Bootstrap 5).
With this pagination, you will have no limits in a Laravel project to manage paginations.
This pagination also allows you to generate a per page form. This will generate a form HTML tag with a select HTML tag and clickable options.
Key Features
- Simple Laravel library for pagination.
- Customizable per page options.
- Support for multiple languages.
- Compatible with Bootstrap 5.
Basic Example
Paginate easily without limits 🚀
<?php $pagination = new \SDamian\LaravelManPagination\Pagination(); $pagination->paginate($totalElements); // $totalElements: result of an SQL COUNT query $limit = $pagination->limit(); $offset = $pagination->offset(); // Here your manual SQL query with $limit and $offset // Then your listing of elements with a loop {!! $pagination->links() !!} {!! $pagination->perPageForm() !!}
Author
This package is developed by Stephen Damian.
Requirements
- PHP
8.0||8.1||8.2||8.3||8.4 - Laravel
8||9||10||11||12
Summary
- Installation
- Customization with "vendor:publish"
- Pagination instance methods
- Examples
- Instance Options
- Differences with Laravel integrated pagination
- Support
- License
Installation
Installation via Composer:
composer require s-damian/laravel-man-pagination
Customization With "vendor:publish"
Custom Config and Lang and CSS
After installing the package, you can run the vendor:publish command:
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="SDamian\LaravelManPagination\ManPaginationServiceProvider"
The vendor:publish command will generate these files:
config/man-pagination.phplang/vendor/man-pagination/{lang}/pagination.phppublic/vendor/man-pagination/css/pagination.css
You can of course customize these files.
"vendor:publish" With "--tag" Argument
Publish only config file:
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="SDamian\LaravelManPagination\ManPaginationServiceProvider" --tag=config
Publish only lang files:
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="SDamian\LaravelManPagination\ManPaginationServiceProvider" --tag=lang
Publish only CSS file:
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="SDamian\LaravelManPagination\ManPaginationServiceProvider" --tag=css
Pagination Instance Methods
| Return type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| void | __construct(array $options = []) | Constructor. |
| void | paginate(int $total) | (To use in the Controller) Activate the pagination. |
| null or int | limit() | (To use in the Controller) LIMIT: Number of items to retrieve. |
| null or int | offset() | (To use in the Controller) OFFSET: Starting point for the LIMIT. |
| int | total() | Determine the total number of matching items in the data store. |
| int | count() | Get the number of items for the current page. |
| int | firstItem() | Get the result number of the first item in the results. |
| int | lastItem() | Get the result number of the last item in the results. |
| int | currentPage() | Get the current page number. |
| int | lastPage() | Get the page number of the last available page (number of pages). |
| int | perPage() | The number of items to be shown per page. |
| bool | hasPages() | Determine if there are enough items to split into multiple pages. |
| bool | hasMorePages() | Determine if there are more items in the data store. |
| bool | onFirstPage() | Determine if the paginator is on the first page. |
| bool | onLastPage() | Determine if the paginator is on the last page. |
| bool | onPage(int $pageNb) | Determine if the paginator is on a given page number. |
| null or string | previousPageUrl() | Get the URL for the previous page. |
| null or string | nextPageUrl() | Get the URL for the next page. |
| string | firstPageUrl() | Get the URL for the first page. |
| string | lastPageUrl() | Get the URL for the last page. |
| string | url(int $pageNb) | Get the URL for a given page number. |
| string | getPageName() | Get the query string variable used to store the page. |
| string | getPerPageName() | Get the query string variable used to store the per page. |
| string | links() | (To use in the View) Make the rendering of the pagination in HTML format. |
| string | perPageForm(array $options = []) | (To use in the view) Make the rendering of the per page in HTML format. |
Examples
Concrete Example With a Manual SELECT Query "DB::select"
When doing "complex" SQL queries, sometimes you prefer to do it without Eloquent.
Here is an example of an SQL query where this library is really useful:
use SDamian\LaravelManPagination\Pagination; $pagination = new Pagination(); $pagination->paginate($total); $limit = $pagination->limit(); $offset = $pagination->offset(); $ordersAndInvoices = DB::select(' SELECT for_type AS type, for_reference AS reference, for_first_name AS first_name, for_last_name AS last_name, for_tel AS tel, for_email AS email, for_amount AS amount FROM ( ( SELECT "Order" AS for_type, orders.reference AS for_reference, customers.first_name AS for_first_name, customers.last_name AS for_last_name, customers.tel AS for_tel, customers.email AS for_email, baskets.amount AS for_amount FROM orders INNER JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id = customers.id INNER JOIN baskets ON orders.id = baskets.order_id LIMIT '.$limit.' OFFSET '.$offset.' ) UNION ALL ( SELECT "Invoice" AS for_type, invoices.reference AS for_reference, customers.first_name AS for_first_name, customers.last_name AS for_last_name, customers.tel AS for_tel, customers.email AS for_email, invoices.amount AS for_amount FROM invoices INNER JOIN customers ON invoices.customer_id = customers.id LIMIT '.$limit.' OFFSET '.$offset.' ) ) alias_ignored ORDER BY amount DESC LIMIT '.$limit.' OFFSET '.$offset );
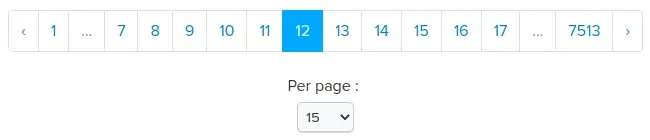
Example rendering of pagination:
Simple Example With a Manual SELECT Query "DB::select"
Here is a simple example, following the MVC pattern, of how to use this library:
Controller
<?php use SDamian\LaravelManPagination\Pagination; class CustomerController extends Controller { public function index() { $sqlForCount = DB::select(' SELECT COUNT(id) AS nb_customers FROM customers '); $total = $sqlForCount[0]->nb_customers; $pagination = new Pagination(); $pagination->paginate($total); $limit = $pagination->limit(); $offset = $pagination->offset(); $customers = DB::select(' SELECT * FROM customers ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT '.$limit.' OFFSET '.$offset.' '); return view('customer.index', [ 'customers' => $customers, 'pagination' => $pagination, ]); } }
View
<div style="text-align: center;"> @foreach ($customers as $customer) {{ $customer->id }} <br> @endforeach </div> <div style="text-align: center;"> {{-- Show the pagination --}} {!! $pagination->links() !!} {{-- Show the per page --}} {!! $pagination->perPageForm() !!} </div>
Simple Example of Controller With Eloquent
This is for example only. Concretely, using Eloquent, you don't need this library. Because You can use Eloquent's paginate method.
<?php use SDamian\LaravelManPagination\Pagination; class CustomerController extends Controller { public function index() { $total = Customer::count('id'); $pagination = new Pagination(); $pagination->paginate($total); $limit = $pagination->limit(); $offset = $pagination->offset(); $customers = Customer::skip($offset)->take($limit)->orderBy('id', 'desc')->get(); return view('customer.index', [ 'customers' => $customers, 'pagination' => $pagination, ]); } }
Instance Options
<?php use SDamian\LaravelManPagination\Pagination; // To change the number of elements per page: $pagination = new Pagination(['pp' => 50]); // Is 15 by default // To change number of links alongside the current page: $pagination = new Pagination(['number_links' => 10]); // Is 5 by default // To change the choice to select potentially generate with perPageForm(): $pagination = new Pagination(['options_select' => [5, 10, 50, 100, 500, 'all']]); // The value of 'options_select' must be an array. // Only integers and 'all' are permitted. // Options are [15, 30, 50, 100, 200, 300] by default. // To change the page name of the pagination in URL: $pagination = new Pagination(['page_name' => 'p']); // The page name is by default "page". // To change the "per page" name of the pagination in URL: $pagination = new Pagination(['per_page_name' => 'per_page']); // The "per page" name is by default "pp". // To change the CSS style of the pagination (to another CSS class as default): $pagination = new Pagination(['css_class_p' => 'name-css-class-of-pagination']); // The CSS class name is by default "pagination". // To change the CSS style of the pagination active (to another CSS class as default): $pagination = new Pagination(['css_class_link_active' => 'name-css-class-of-pagination']); // The active CSS class name is by default "active". // To change the CSS style of a per page (select) (to another id as default): $pagination = new Pagination(['css_id_pp' => 'name-css-id-of-per-page-form']); // The CSS ID name is by default "per-page-form".
Differences With Laravel Integrated Pagination
In this pagination, I tried to keep the conventions and the behavior of the pagination integrated in Laravel.
I Added Extra "Security":
If, for example, there are only 8 pages, and in the URL the visitor tries to go to page 9 (or to a page after page 9):
- The
onLastPage()method will returnfalse(whereas with the pagination integrated in Laravel, it returns true). - The
currentPage()method will return1(whereas with the pagination integrated in Laravel, it returns the page in the URL).
Support
If you discover a bug or a security vulnerability, please send a message to Stephen. Thank you.
All bugs and all security vulnerabilities will be promptly addressed.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.