rixbeck / reptor
PHP Spreadsheet Report Generator
Installs: 20
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 1
Watchers: 1
Forks: 0
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/rixbeck/reptor
Requires
- php: 8.1.*
- ext-json: *
- ext-pdo: *
- ext-sqlite3: *
- phpoffice/phpspreadsheet: ^1.29
- psr/event-dispatcher: *
- symfony/cache: ^6.3
- symfony/expression-language: ^6.3
- symfony/yaml: ^6.3
- uuf6429/expression-language-tplstring: ^2.0
Requires (Dev)
- friendsofphp/php-cs-fixer: ^v3.26.0
- phpstan/phpstan: ^1.8.5
- phpunit/phpunit: *
- rector/rector: ^0.15.0
- squizlabs/php_codesniffer: ^3.6
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-01-30 12:18:26 UTC
README
Reptor
PhpSpreadsheet based report generator
The PHPSpreadsheet Report Generator is a PHP-orientated solution curated to empower users to generate reports seamlessly. Embedded with the prevailing attributes of the PHP 8.1 enabled PHPSpreadsheet library, this project ensures the generation of dynamic XLSX reports using Excel-based template files.
The project aims to revolutionize report generation in the PHP world by converting raw data into comprehensive, digestible information punctuated with the expansive expressive ability of the Symfony Expression Language. Facilitating the inclusion of data sources or datasets makes it a versatile tool for diverse reporting needs.
Whether you are an individual aiming for personal data understanding or an enterprise seeking to streamline complex data analysis, the PHPSpreadsheet Report Generator serves to be an invaluable tool to garner insights, make strategic decisions or simply comprehend an array of information.
The project was highly inspired by alhimik1986 and his PHP Excel Templator library.
Key Features:
- Enhanced Report Generation: Create reports efficiently in XLSX, PDF, HTML and other formats.
- Symfony Expression Language: Harness the power of Symfony’s component to provide a simplified manipulation of your object graph.
- Data Sources or Datasets: Include a multitude of data end points or vast datasets to generate reports that match your preferences and requirements.
- Template Language Extensibility: The ability to extend the template language allows for more personalized and complex templates, accommodating a great degree of customization and functionality.
- Aggregator Functions: The ability to use aggregator functions like as
sum,avg, etc. the generation of reports with a greater degree of complexity and functionality. - Group By: The ability to group data by a specific column allows for the generation of reports that are more organized and structured.
- Flexible parameter declaration: Parameters or properties / like data sources, datasets, etc. - can be specified in the spreadsheet template itself or can be declared in runtime. This allows for greater flexibility and customization.
- Native PHP functions or objects in cell formulas: The ability to use native PHP functions or objects.
- Excel formulas in cell expressions: The ability to use Excel formulas in cell expressions and they can be combined with the Symfony Expression Language based extensions or native PHP functions.
- User defined cell ranges as base units of processing: Input data processing is controlled by interpreting the cell ranges as base units of processing.
Installation
Reptor can be acquired and installed through a Git clone, followed by a Composer installation. Please follow these steps:
-
If you haven't installed Git or Composer, start by downloading and installing them. Use the official download pages for Git and Composer.
-
Once Git and Composer are installed, clone Reptor repository into your local environment:
git clone https://github.com/rixbeck/reptor.git
-
Navigate to the cloned repository and install the dependencies:
cd reptor composer install
Make sure your PHP environment meets the requirements specified in the composer.json file, including enabled extensions like PDO, JSON, and SQLite3. After completing these steps, Reptor is ready for use in your project.
Use as a Composer Dependency
It is also possible to include Reptor in your PHP projects as a composer dependency rather than using it as a standalone project:
-
Navigate to your existing PHP project directory and open Terminal (or a command prompt)
cd /path/to/your/php/project -
Use the following composer command to add Reptor as a dependency in your project.
composer require rixbeck/reptor
That's it! You have now successfully added Reptor as a dependency to your PHP project.
Concept Behind Reptor: Templating vs. Scripting in Report Generation
When it comes to generating data-driven reports, there are fundamentally two approaches: scripting and templating.
Scripting
Scripting involves writing custom code to handle data and format the report. It offers flexibility but requires extensive programming, making it complex and time-consuming for users without coding expertise.
Templating
In contrast, templating, the approach chosen for Reptor, allows users to define report layouts and formatting directly within a familiar interface - an Excel file. This method is intuitive and user-friendly, significantly reducing the learning curve.
Why Templating with Excel?
- Familiarity: Excel is a widely-used tool with a familiar interface for many users, making it an ideal platform for designing report templates.
- Flexibility: Excel's native functionalities (like cells, formulas, and formatting options) offer significant flexibility in defining how data should be presented.
- Efficiency: By using Excel for templating, users can rapidly prototype and modify report designs without needing to delve into complex programming.
- Dynamic Reports: With Excel, we can create dynamic templates that automatically adjust and populate with data, offering a powerful way to generate customized reports.
Through Reptor, we bring the best of both worlds: the ease of templating through Excel and the power of PHP for processing and generating sophisticated reports.
Advanced Cell and Row Styling with Excel Templates
One of the most significant advantages of using Excel templates in Reptor is the extensive styling capabilities it offers:
-
Cell Styling: Users can leverage Excel's rich cell formatting options to define the appearance of individual cells. This includes font styles, colors, borders, and background fills, allowing for highly customized reports that are visually appealing and easy to read.
-
Row and Column Formatting: Beyond single cells, Reptor allows for the styling of entire rows and columns. This feature is crucial for maintaining consistency and clarity in reports, especially when dealing with large datasets.
-
Conditional Formatting: Excel's conditional formatting can be used to dynamically style cells based on the data they contain. This brings an added layer of interactivity to your reports, enabling users to quickly identify trends, anomalies, or key metrics at a glance.
-
Ease of Use: By harnessing the familiar interface of Excel, users can style their reports without any additional learning curve, making it accessible to both technical and non-technical users.
Through Reptor, these styling capabilities are seamlessly integrated into the report generation process, ensuring that the final output is not only informative but also aesthetically pleasing and tailored to specific presentation needs.
Utilizing Expression Language in Excel Cells
Reptor harnesses the power of Symfony Expression Language to enhance the dynamism of Excel templates:
-
Expression Language in Cells: Users can embed expressions directly into Excel cells. These expressions, based on Symfony's robust framework, can manipulate and present data dynamically, adding significant functionality to your reports.
-
Variable and Object Integration: A variety of user-defined or predefined objects and variables can be used within these expressions. These can be defined directly in the Excel document's custom properties or via an initializing boot script or in any pre-processing phase of the report generation.
-
Adaptors and Data Sources: Reptor supports various data sources through its adaptable interface, including PDO, Socket, Array, and more, as seen in the
Reptor/Adaptor/Datasourcenamespace. This flexibility allows for the integration of diverse data sets. -
Uniform Connection Strings: Data sources are connected using a uniform connection string, akin to Java or PHP DSN, simplifying the process of linking to and utilizing different datasets.
Through these features, Reptor allows for extensive customization and dynamic data processing, enabling users to create highly sophisticated and tailored reports directly from Excel.
Philosophy of Rendering: The Concept of Excel-Based Templating
Reptor introduces a unique approach to processing Excel templates, centered around the concept of 'Units':
-
Units - The Core of Templating: In Reptor, 'Units' are the basic units of expressions that belong together, crucial for understanding how expressions within the same row of a dataset interact.
-
Defining Units with Named Ranges: Users define these 'Units' using named ranges in Excel. This method organizes the template and prepares it for processing.
-
Sequential Processing and Evaluation: The template processing involves sequentially evaluating these Units. During this phase, evaluated expressions transform into objects.
-
Priority and Types of Units: Each object has a type, and these types have inherent priorities. The priority of an object determines the type of its corresponding Unit in the evaluation process.
-
Rendering Logic Driven by Unit Types: Once Units are classified, the rendering logic takes over, driven by the type of each Unit. This step ensures that the final output aligns with the intended structure and format of the template.
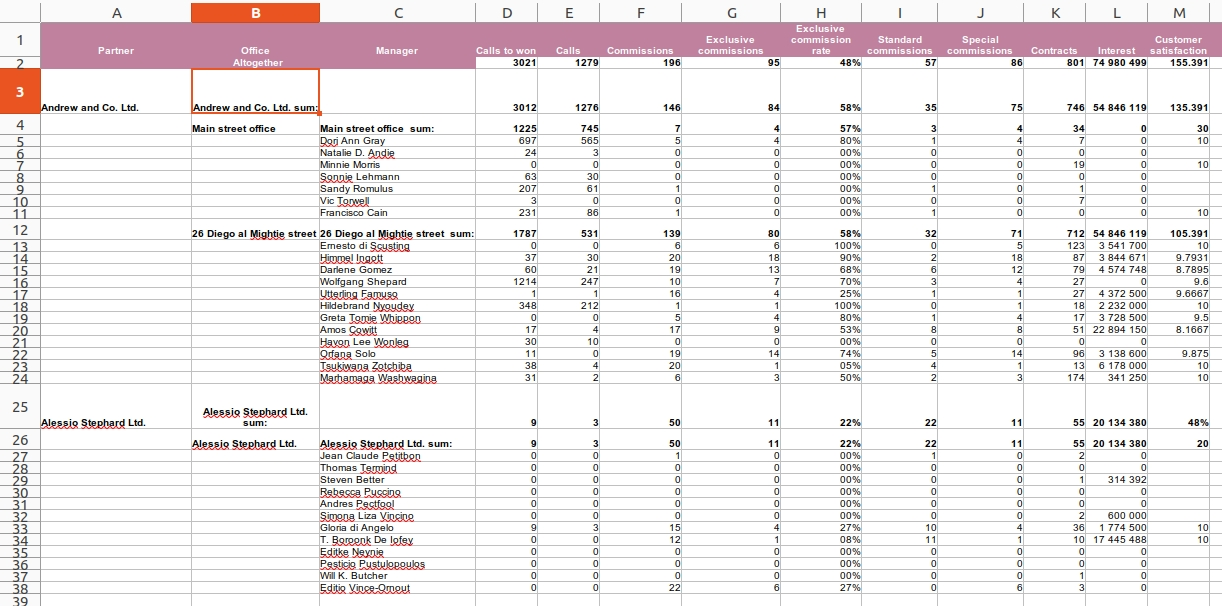
Understanding Units in Excel Templates
In the Reptor system, a 'Unit' encapsulates a collection of expressions that are logically related and processed together to produce a cohesive section of the report.
Here's how it works:
-
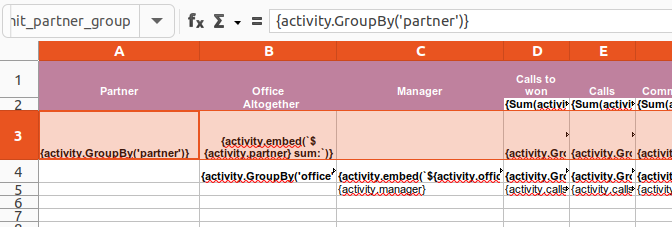
Binding Expressions: As demonstrated in the provided figure, expressions are bound within named ranges in Excel, forming a 'Unit'. This ensures that data belonging to the same conceptual group is processed in unison.
-
Named Ranges: The use of named ranges such as
unit_partner_grouphelps identify and process these Units efficiently, keeping the related expressions tied together. -
Multiple Units Handling: Users can define multiple Units within an Excel template, each representing a different section of the report or different data groupings.
-
Sequential Processing: Reptor iterates through these Units sequentially and processes their cells until reaches last one. After that emits event with the instruction of dataset iterators can fetch the next data row (if has). So the processing continues row by row this way, as long as there are remaining referred dataset rows in any units.
-
Expression Syntax: The syntax
{{activity.GroupBy('partner')}}within the cells is evaluated against the referred object provided to Reptor. This allows for dynamic content generation based on the data.
Understanding Expression Language based Templating in Cells
Reptor's templating system allows for sophisticated data manipulation directly within Excel cells using an expression language inspired by Symfony's. This system's flexibility stems from the ability to define properties, which are the base variables used within expressions for rendering.
The brix\Reptor\Bootstrap class sets up the Reptor environment, including:
-
Properties Initialization: These are the variables available to all expressions in the templating system. They can be default properties or extended via the
addPropertiesmethod. -
Expression Language Setup: The class initializes the ExpressionLanguage component, registering various extensions that enhance its functionality, such as
CoreExtension,DataExtension, andUtilityExtension. -
Data Source Integration: Through the
DataExtension, Reptor can connect to various data sources like databases, CSV, JSON, and arrays. It maps these data sources to readable objects for the templating engine. -
Template Processing: The
Templatorobject, once initialized, processes the Excel template, invoking the expressions and rendering the final output. -
Context Provisioning: The
ContextProvidermanages the context within which cell rendering occurs, ensuring that the appropriate properties are available during the rendering process. -
Unit Management:
UnitManagerhelps manage named ranges, referred to as 'Units', which group related expressions for coherent processing.
This initialization process is critical as it sets up the entire templating engine that powers the dynamic rendering of reports in Reptor, harnessing the power of the Symfony Expression Language to evaluate complex expressions within Excel cells.
In addition to setting up the Reptor environment, the project includes a bin/ directory, which houses scaffolding scripts to facilitate application initialization and configuration. This directory contains examples and boilerplate code that help users quickly set up their reporting projects:
-
Scaffolding Scripts: These are pre-written scripts in the
bin/folder that provide templates for common tasks, allowing users to scaffold their applications with ease. -
Quick Start Examples: New users can refer to these examples to understand how to bootstrap their Reptor application, configure data sources, and define properties.
-
Customization and Extensibility: While the examples offer a quick way to get started, they are also designed to be easily customizable, providing a starting point for users to tailor the application to their specific reporting needs.
This scaffolding approach aims to streamline the setup process, making it simple for users to jumpstart their report generation projects with Reptor.
About the status of the project
The provided content serves as a brief introduction to the Reptor project and its underlying structure. It is intended as a quickstart guide for users to get a glimpse of the system's capabilities, particularly the expression language-based templating in Excel cells. Full documentation, including detailed explanations, examples, and best practices, is currently in development and will be organized into chapters for easy navigation and comprehension. This initial overview is designed to help new users begin working with Reptor and understand its core concepts.
While the project is still in its early stages, it is fully functional and can be used to generate reports. The current version is 0.1.0-beta, and the project is under active development. We welcome feedback, issue reports and contributions from the community to help improve the project and make it more accessible to users.
What's Next?
We are currently working on the documentation mainly, and focusing on the following areas:
- Detailed Documentation: We are working on a comprehensive documentation that will cover all aspects of the project, including detailed explanations, examples, and best practices.
- Contribution Guidelines: We are also working on a contribution guide to help users contribute to the project and make it more accessible to the community.
- Release Schedule: We are planning to release the first stable version of the project in the coming months.
- Test automation: We are working on a test automation framework to ensure the stability and reliability of the project. Any help in this area would be greatly appreciated.
- Bug Fixes: We are actively working on fixing bugs and issues reported by the community. Please feel free to report any issues you encounter.
- Feature Requests: We are also open to feature requests and suggestions from the community. Please feel free to share your ideas with us.