oza75 / laravel-hubble
Create a beautiful laravel dashboard in no time
Installs: 295
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 1
Watchers: 0
Forks: 1
Open Issues: 1
pkg:composer/oza75/laravel-hubble
Requires
- php: ^7.1|^8.0
- ext-json: *
- maatwebsite/excel: ^3.1
Requires (Dev)
- orchestra/testbench: ^6.0
- phpunit/phpunit: ^9.0
- victorjonsson/markdowndocs: ^1.3
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-26 05:24:55 UTC
README
Build a beautiful dashboard with laravel in no time.
Requirements
- php : ^7.1
- Laravel : ^6.0
Installation
You can install the package via composer:
composer require oza75/laravel-hubble
Then install laravel-hubble
php artisan hubble:install
# Now Add App\Providers\HubbleServiceProvider into providers array in your config/app.php
Now go to : http://yourapp.tld/hubble (or http://localhost:8000/hubble if you use artisan serve)
Authentification
Hubble uses the default Laravel authorization gate to check if a user can access to the dashboard. By default, everyone
can access to hubble dashboard. You can restrict access by using authorizesAccess method
on App\Providers\HubbleServiceProvider.
// file: app/Providers/HubbleServiceProvider.php /** * Determines if a given user can access to hubble dashboard. * By default every user can access to hubble * * @param User $user * @return bool */ public function authorizesAccess(User $user): bool { return $user->isAdmin(); }
Usage
Resources
A hubble resource is a simple php class which aims to represent the resource you want to add, namely the different fields, actions, filters, etc. that it has.
Create resource
You can create a new resource by running hubble:resource command
php artisan hubble:resource UserResource
This will automatically create a new resource under app/Hubble folder
<?php namespace App\Hubble; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Action; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Field; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Filter; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Actions\DeleteAction; use App\Hubble\Resource; class UserResource extends Resource { /** * @var string The title will be used as your resource name in the ui */ protected $title = "Users"; /** * @var string[] */ protected $searchColumns = ['id']; /** * @var string used to show resource value in relationship */ protected $displayColumn = 'id'; /** * Get the fields displayed that the user resource * * @return Field[] array of fields */ public function fields() { return [ Field::make('id', 'ID'), Field::make('name', 'Name') ]; } /** * Register all actions that the user resource have * * @return Action[] array of actions */ public function actions() { return [ DeleteAction::make(), ]; } /** * Register all filters that the user resource have * * @return Filter[] array of filters */ public function filters() { return []; } /** * @return Builder */ public function baseQuery(): Builder { return \App\User::query(); } /** * Return this resource icon * * @return string|null */ public function icon() { return null; } }
After your resource is generated, you need to set the eloquent builder hubble should use to get your data. When
generating this resource we will try to obtain the eloquent builder according to the name of the resource passed
in php artisan hubble:resource command. You can modify this query builder to add some computed fields.
/** * @return Builder */ public function baseQuery(): Builder { return \App\User::query()->select('*')->selectRaw('age > 18 as is_adult'); }
fields method is used to return all fields your want to display. By default, hubble comes with some fields
like TextField, TextareaField, ImageField and more. But you can also create your own custom field.
/** * Get the fields displayed that the user resource * * @return Field[] array of fields */ public function fields() { return [ Field::make('id', 'ID'), TextField::make('name', 'Name')->sortable(), TextareaField::make('bio', 'Bio')->onlyOnDetails(), TextField::make('email', 'Email')->displayOnIndexUsing(function ($value) { return "<a href='mailto:$value'>$value</a>"; })->type('email')->sortable(), ]; }
Configure your resource
You can configure your resource by setting some properties on your resource class.
/** * @var string The title will be used as your resource name in the ui */ protected $title = "Users"; /** * @var string[] */ protected $searchColumns = ['id', 'name']; /** * @var string used to show resource value in relationship */ protected $displayColumn = 'name'; /** @var int Number of records per page */ protected $perPage = 38; /** @var bool Determines if a resource should be shown in sidebar */ protected $displayInSidebar = true; /** * @var bool Determines if a resource can be exported in excel format. */ protected $exportable = true;
If you want to customize the title that should be shown in each different screen (index page, edit page, details page etc...)
you may define configure method in your resource. For example:
// use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Configuration\Configuration; // use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Configuration\ScreenConfiguration; public function configure(Configuration $configuration) { $configuration->details(function (ScreenConfiguration $configuration, User $user) { $configuration->setTitle("User #". $user->id); }); }
Registering your resource
By default, hubble will automatically register all resources you have under app/Hubble folder.
Just go to http://yourapp.tld/hubble and you will see the new user resource that we add.
You can customize the folder within hubble must look for your resources in config file. The auto registration is very useful when developing your dashboard but you may disable it in production to gain a small performance.
In your app/Providers/HubbleServiceProvider.php :
<?php namespace App\Providers; use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\HubbleServiceProvider as BaseProvider; class HubbleServiceProvider extends BaseProvider { /** * Determines if hubble should detects automatically * resources under Hubble resource folder. This is useful when you are * developing but should be disable in production * * @var bool */ protected $autoRegistration = false; // set to false to disable auto registration /** * List of resource Hubble should register. Should be used * when you set autoRegistration = false. Optionally you can * define a resource method in this class to bypass this property. * * @var array */ protected $resources = [ // add your resources manually here UserResource::class, ]; /** * Determines if a given user can access to hubble dashboard. * By default every user can access to hubble * * @param User $user * @return bool */ public function authorizesAccess(User $user): bool { return parent::authorizesAccess($user); } }
Actions
Action is used to perform custom tasks on one or more Eloquent models. You can generate action using :
php artisan hubble:action ActiveUsers
This command will generate a new ActiveUsers class under app/Hubble/Actions
<?php namespace App\Hubble\Actions; use App\User; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model; use Illuminate\Support\LazyCollection; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Action; class ActiveUsers extends Action { /** * @var string the title of this action */ protected $title = 'ActiveUsers'; /** * @var string the confirmation message to warn user before running this action. Set to null to disable it */ protected $confirmationMessage = 'Do you really want to perform this action ?'; /** * Handle your action * * @param LazyCollection $collection * @param Builder $query * @return string */ public function handle(LazyCollection $collection, Builder $query) { $query = $query->newQuery(); $collection->each(function (User $user) use ($query) { $query->orWhere('id', $user->id); }); $query->update(['is_active' => true]); return "Utilisateurs activé avec succès !"; } /** * @param \Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User $user * @param Model|null $model * @return bool */ public function can(\Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User $user, ?Model $model = null): bool { return true; } protected function icon() { return asset('images/lock.svg'); } }
The title property contains the name of the action that will be shown on the User Interface
In the handle method you can perform your action. For our example, let's assume that our users table has an active
column which determine whether the user is active or not.
/** * Handle your action * * @param $ids * @return void */ public function handle($ids) { User::query()->whereIn('id', $ids)->update(['active' => true]); }
When you created your action you can add it in your resource.
/** * Register all actions that the user resource have * * @return Action[] array of actions */ public function actions() { return [ DeleteAction::make(), new ActiveUsers(), ]; }
Filters
As the name suggests, filters are used to filter your data and display only data that satisfy certain conditions. There are many ways to add filter into your resource :
- the first way (the easiest way ) :
/** * Register all filters that the user resource have * * @return Filter[] array of filters */ public function filters() { return [ Filter::make('is_active', 'Only Active Users', ['Yes' => 1, 'No' => 0]), ]; }
Filter::make take as is first argument, the column in the database. The second argument is the title and then the
third array of options.
The options' argument is an associative array where the key is the label and the value, the value of the option. You can
also pass an url where the options should be fetched or a custom array. for those cases you may set the valueKey and the
textKey using the setValueKey(string $key), and the setTextKey(string $key).
For example:
/** * Register all filters that the user resource have * * @return Filter[] array of filters */ public function filters() { return [ Filter::make('is_active', 'Users Status', [ ['name' => 'All', 'value' => null], ['name' => 'Active', 'value' => 1], ['name' => 'Non active', 'value' => 0] ])->setValueKey('value')->setTextKey('name'), ]; }
Another example:
/** * Register all filters that the user resource have * * @return Filter[] array of filters */ public function filters() { return [ Filter::make('state', 'Users State', "https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/all") ->setValueKey('alpha3Code') ->setTextKey('name') ->searchable('Start typing a state...'), ]; }
- the second way to define a filter (more powerful) :
/** * Register all filters that the user resource have * * @return Filter[] array of filters */ public function filters() { return [ Filter::make('state', 'Users State', "https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/all") ->setValueKey('alpha3Code') ->setTextKey('name') ->setHandler(function (Builder $builder, $value) { $builder->whereHas('state', function ($query) use ($value) { $query->where('code', $value); }); }), ]; }
With this way, you can use the setHandler method to pass a callable that takes the query builder as his first
argument and the value of the filter, you can add any where clause you want.
- The last way is to generate a new filter class.
php artisan hubble:filter MyCustomFilter
This command will generate a new filter class under app/Hubble/Filters.
<?php namespace App\Hubble\Filters; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Filter; class MyCustomFilter extends Filter { /** * @var string the title of your filter that will be shown on the ui. */ protected $title = 'My custom filter'; /** * @var string the VueJs component that will be used to display this filter */ protected $component = 'hubble-checkbox-filter'; /** * Apply your filter * * @param Builder $query * @param $value * @return void */ public function handle(Builder $query, $value) { // apply your filter here. return null; } /** * Return all options for this filter * * @return array */ public function options() { // first way return ['Option 1' => 1, 'Option 2' => 2]; // the key is the label and the value is the option value // second way return [ ['name' => 'Option 1', 'value' => 1], ['name' => 'Option 2', 'value' => 2], ]; // third way return "https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/all"; // do not forget to use `setValueKey(string $key)` and `setTextKey(string $key)` in the constructor of this class // or when instantiating this class to set the value key and the text key } }
You can also generate a filter with a custom VueJs components.
php artisan hubble:filter MyCustomFilter --custom
This will generate a VueJs component under resources/hubble/components/filters/my-custom-filter.vue
Fields
Fields are used to display your data. the base Field class can be used to create fields. Any types of fields extend
this class.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Field::make('column', 'title');
- sortable
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Field::make('column', 'title')->sortable(); // now this field can be used to sort your data
You can also tell to Hubble to sort your data by default using a certain field.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Field::make('column', 'title')->sortable(true, 'desc');
Custom Display
There are a few methods you can use to customize how you want to display the field value in the different sections of the dashboard.
- displayUsing
- displayOnIndexUsing
- displayOnDetailsUsing
- displayOnFormsUsing
- displayWhenEditingUsing
- displayWhenCreatingUsing
The displayUsing method customize the display in all sections of the dashboard.
All these methods as the same signature.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Field::make('fullname', 'Full Name')->displayUsing(function ($value, $resource) { return $resource->first_name . ' '. $resource->last_name; // in this case resource is a User model }); \Oza75\LaravelHubble\Field::make('email', 'Email')->displayOnIndexUsing(function ($value) { return "<a href='mailto:$value'>$value</a>"; });
Visibility
Field comes with some methods that you can use to tell when to display
- hide : will hide the field in all screen
- hideOnIndex
- hideOnForms
- hideOnDetails
- hideWhenCreating
- hideWhenEditing
- hideOnExport
- showOnIndex
- showOnDetails
- showOnForm
- showWhenCreating
- showWhenEditing
- showOnExport
- onlyOnIndex
- onlyOnDetails
- onlyOnForms
- onlyOnCreating
- onlyOnEditing
- onlyOnExport
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\TextField::make('email', 'Email')->hideOnIndex();
All of these methods can pass a closure that will be used to hide or display the field on a specific screen.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\PasswordField::make('password', 'Change the password')->onlyOnForms(function (User $user, ?\Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model $model = null) { return $user->isAdmin() || ($model && $model->id === $user->id); });
Hubble ships with many types of fields, but you can also create your own.
- TextField
- BooleanField
- NumberField
- TextareaField
- DateTimeField
- SelectField
- ColorField
- FileField
- ImageField
- BelongsToField (relation field)
- HasManyField (relation field)
TextField
Used to display a text Field.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\TextField::make('email', 'Email');
- text type
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\TextField::make('email', 'Email')->type('email');
this type will be used to display correct input type in forms.
- limit
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\TextField::make('bio', 'Bio')->limit(100);
limit the number of character that should be displayed in tables.
BooleanField
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\BooleanField::make('active', 'Active ?')->text('Yes', 'No');
the text method set the text to display when this field has true or false value.
NumberField
Used to display number values
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\NumberField::make('articles_count', 'Articles');
TextareaField
Used to display long text values
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\TextareaField::make('bio', 'Bio');
DateTimeField
Used to display dates values
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\DateTimeField::make('created_at', 'Created at');
- date format
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\DateTimeField::make('created_at', 'Created at')->format('Y-m-d at h:i');
- date locale
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\DateTimeField::make('created_at', 'Created at')->setLocale('fr')->format('Y-m-d at h:i');
SelectField
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\SelectField::make('user_type', 'Type')->options(['Pro' => 'pro', 'Normal' => 'normal']);
- display using label
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\SelectField::make('user_type', 'Type') ->options(['Pro' => 'pro', 'Normal' => 'normal']) ->displayUsingLabel();
ColorField
Used to display colors
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\ColorField::make('primary_color', 'Color');
- display using hex value
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\ColorField::make('primary_color', 'Color')->displayUsingHex();
FileField
Used to display and upload files
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\FileField::make('avatar', 'Avatar'),
- multiple
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\FileField::make('avatar', 'Avatar')->multiple(),
- max
Limit number of files
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\FileField::make('avatar', 'Avatar')->multiple()->max(5),
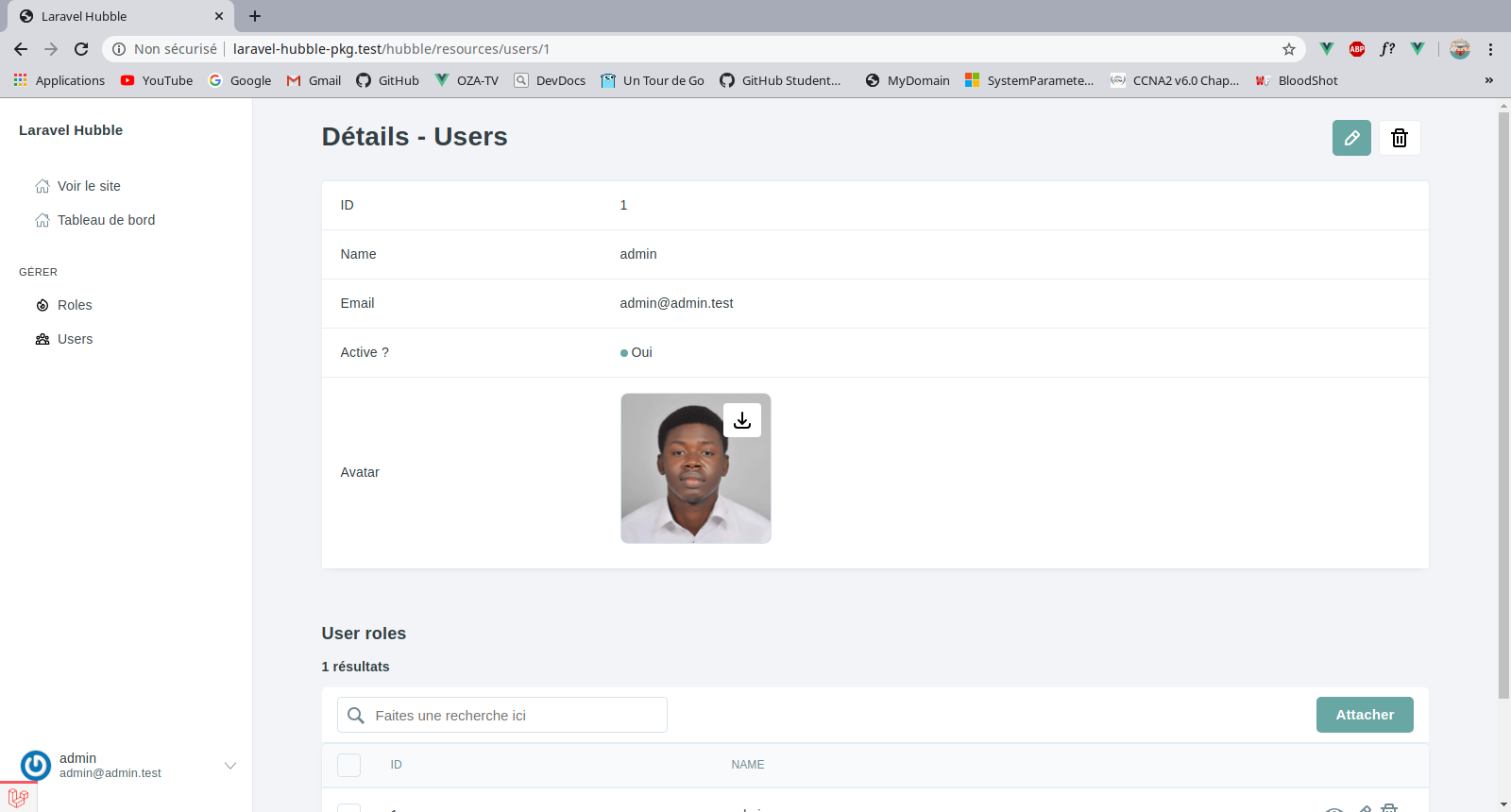
ImageField
Used to display image and upload images.
ImageField extends to FileField so it has all methods that FileField has, such as multiple or max.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\ImageField::make('avatar', 'Avatar'),
or
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\ImageField::make('avatar', 'Avatar')->multiple()->max(5),
BelongsToField
Used to display a related resource
- signature
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\BelongsToField::make('method_name', 'related_class', 'Title');
The first argument is the name relationship method. Let's assume we have in our User model a belongsTo method
to City Model.
/** * @return \Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\BelongsTo */ public function city() { return $this->belongsTo(City::class); }
Then to add this relationship in our resource
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\BelongsToField::make('city', CityResource::class);
HasManyField
Used to display related resources
- signature
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\BelongsToField::make('method_name', 'related_class', 'Title');
As the BelongsToField, the HasManyField takes the relationship method name as his first argument.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\HasManyField::make('roles', RoleResource::class, 'User Roles');
Create a custom field
You can create a custom field by using this command:
php artisan hubble:field ColorField
You can also generate a new field with custom components by using this command:
php artisan hubble:field ColorField --custom
This will create new VueJs components for your field under resources/hubble/components/fields/color
Use this command to build the newly components
npm run hubble:watch
or
npm run hubble:prod
php artisan hubble:field will generate a new Field Class under app/Hubble/Fields
<?php namespace App\Hubble\Fields; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\Field; use Oza75\LaravelHubble\HubbleResource; class ColorField extends Field { /** * Register your vuejs components */ protected function registerComponents() { parent::registerComponents(); $this->components = [ 'index' => 'index-text-field', 'editing' => 'edit-text-field', 'creating' => 'edit-text-field', 'details' => 'show-text-field' ]; } /** * This hook is called when the field is ready to work. * Basically it will just set the resource within your field is added. * So if you have some attributes to add or actions that depends on the resource * this is where you should do it. * * @param HubbleResource $resource */ public function prepare(HubbleResource $resource) { parent::boot($resource); // do action that depends on the resource within this field is added } }
Rules
You can automatically validate your forms data by setting rules on each field.
\Oza75\LaravelHubble\Fields\TextField::make('email', 'Email')->rules('required|email|max:255');
There are also rules methods for each creation and editing screen
rulesWhenUpdatingwill define the rules only when updatingrulesWhenCreatingwill define the rules only when creating
Warning: the rules' method cannot yet take a validation object (such as a rule class) or a closure but any
Pull Requestis welcoming.
For frontend interactivity, you may set a handler that can be used to validate automatically your field value under
resources/hubble/rules.js. If you don't, an ajax request will be sent to the backend to check if the value is valid
when user is filling the form.
// this method must return a boolean, a string or a promise (for validations that need to make ajax requests) export const string = function (value, fieldName) { if (typeof value !== "string") { // For localization purposes your laravel validation language file is injected into the javascript window, // then you can use the `window.trans` method to return a translated string return window.trans('validation.string', {attribute: fieldName}) } return true; }
Authorization
Authorization is used to restrict access of certain screen of your dashboard. Internally, it uses
mostly Laravel Authorization Gate.
You just need to create a Laravel Policy for your resource that will control which user can access or not to a specific screen.
For example, let's assume I have a Post model :
php artisan make:policy PostPolicy --model=Post
This will generate a new Laravel Policy under app/Policies.
<?php namespace App\Policies; use App\Post; use Illuminate\Auth\Access\HandlesAuthorization; class PostPolicy { use HandlesAuthorization; public function before(User $user) { // bypass all authorization check when user is admin if ($user->isAdmin()) { return true; } } /** * Determine whether the user can view any models. * * @param \App\User $user * @return mixed */ public function viewAny(User $user) { return true; // Anyone can see `the index table`. You can also return false to remove the hubble' PostResource in sidebar. } /** * Determine whether the user can view the model. * * @param \App\User $user * @param \App\Post $model * @return mixed */ public function view(User $user, Post $model) { return true; // anyone can see the details screen. } /** * Determine whether the user can create models. * * @param \App\User $user * @return mixed */ public function create(User $user) { return true; // anyone can create a new user } /** * Determine whether the user can update the model. * * @param \App\User $user * @param \App\Post $model * @return mixed */ public function update(User $user, Post $model) { return $user->id === $model->user_id; // only the owner of the post can edit this post } /** * Determine whether the user can delete the model. * * @param \App\User $user * @param \App\Post $model * @return mixed */ public function delete(User $user, Post $model) { return $user->id === $model->user_id; // only the owner of the post can delete this post } /** * Determine whether the user can restore the model. * * @param \App\User $user * @param \App\User $model * @return mixed */ public function restore(User $user, User $model) { return false; } /** * Determine whether the user can permanently delete the model. * * @param \App\User $user * @param \App\User $model * @return mixed */ public function forceDelete(User $user, User $model) { return false; } /** * Determines if the current user can attach users to post * when using a HasManyField */ public function attachUser(User $user) { return false; } /** * Determines if the current user can detach users to post * when using a HasManyField */ public function detachUser(User $user, Post $model) { return false; } }
Testing
composer test
Changelog
Please see CHANGELOG for more information what has changed recently.
Contributing
Please see CONTRIBUTING for details.
Security
If you discover any security related issues, please email abouba181@gmail.com instead of using the issue tracker.
Credits
License
The MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.
Laravel Package Boilerplate
This package was generated using the Laravel Package Boilerplate.