needle-project / laravel-rabbitmq
Simple rabbitmq integration for Laravel
Package info
github.com/needle-project/laravel-rabbitmq
pkg:composer/needle-project/laravel-rabbitmq
Requires
- php: 7.*|8.*
- php-amqplib/php-amqplib: >=2.7|3.*
Requires (Dev)
- laravel/framework: 7.*|8.*|9.*|10.*
- phpcompatibility/php-compatibility: ^9.3
- phpmd/phpmd: @stable
- phpstan/phpstan: ^1.10
- phpunit/phpunit: 9.*|10.*
- squizlabs/php_codesniffer: 3.7.*
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-03-01 00:55:39 UTC
README
Laravel RabbitMQ
A simple rabbitmq library for laravel based on Publish–Subscribe pattern where the subscriber is the Consumer.
Table of Contents
-
2.1. Connections
2.2. Queues
2.3. Exchanges
2.4. Publishers
2.5. Consumers
-
3.1. Publishing a message
3.2. Consuming a message
-
5.2 Required Help
1. Install
Run:
composer require needle-project/laravel-rabbitmq
For Laravel version 5.5 or higher the library should be automatically loaded via Package discovery.
For Laravel versions below 5.5 you need to add the service provider to app.php:
<?php return [ // ... 'providers' => [ // ... NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\Providers\ServiceProvider::class, ], // ... ];
2. Configure
- Create a new file called
laravel_rabbitmq.phpinside your Laravel's config directory. (Or useartisan vendor:publish- Read more here) - Fill out the config based on your needs.
The configuration files has 5 main nodes: connections, exchanges, queues, publishers, consumers.
They are used in the following mode:
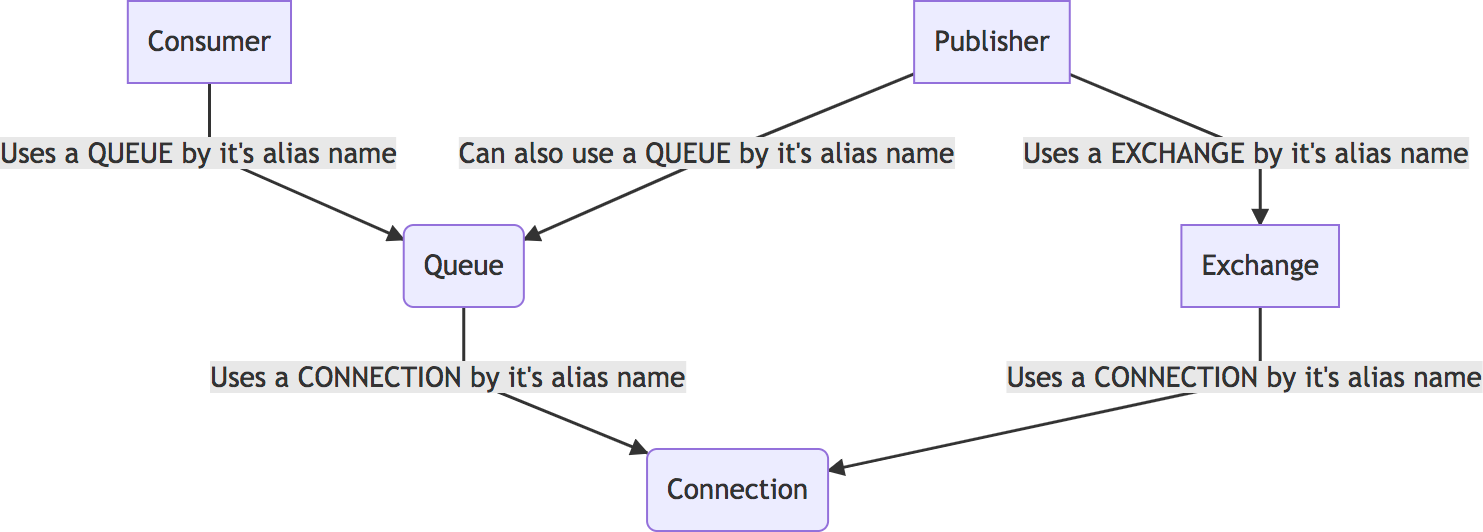
Example config:
return [ 'connections' => [ 'connectionA' => [/** Connection A attributes */], 'connectionB' => [/** Connection B attributes */], ], 'exchanges' => [ 'exchangeA' => [ // Tells that the exchange will use the connection A 'connection' => 'connectionA', /** Exchange A Attributes */ ], 'exchangeB' => [ // Tells that the exchange will use the connection B 'connection' => 'connectionB', /** Exchange B Attributes */ ] ], 'queues' => [ 'queueA' => [ // Tells that the queue will use the connection alias A 'connection' => 'connectionA', /** Queue A Attributes */ ] ], 'publishers' => [ 'aPublisherName' => /** will publish to exchange defined by alias */ 'exchangeA' ], 'consumers' => [ 'aConsumerName' => [ // will read messages from 'queue' => 'queueA', // and will send the for processing to an "NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\Processor\MessageProcessorInterface" 'message_processor' => \NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\Processor\CliOutputProcessor::class ] ] ]
2.1. Connections
Connection attributes:
- All attributes are optional, if not defined the defaults will be used.
| Attribute | Type | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| hostname | string | 127.0.0.1 | The host for the RabbitMQ instance |
| port | integer | 5672 | The port for the RabbitMQ instance |
| username | string | guest | Default's RabbiqMQ username |
| password | string | guest | Default's RabbiqMQ username |
| vhost | string | / | RabbitMQ Virtual Host. Read more here. |
| lazy | boolean | true | Setting it lazy will only make the connection when an action that needs the connection willl be called |
| read_write_timeout | integer | 3 | TTL for read/write operations. |
| connect_timeout | integer | 3 | TTL for the connection |
| heartbeat | integer | 0 | Whether to check the socket connection periodically. Read more here. |
| keep_alive | boolean | false | Whether to use system's keep alive property. Read more here. |
2.2. Queues
Queue main nodes:
| Node key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connection | string | The reference to the connection that should be used. |
| name | string | The actual name of the queue on RabbitMQ |
| attributes | array | Optional attributes for the queue |
Queue attributes
| Attribute key | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| passive | boolean | false | This is an AMQP attribute. Read about [here] (https://www.rabbitmq.com/amqp-0-9-1-reference.html) |
| durable | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| exclusive | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| auto_delete | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| internal | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| nowait | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| auto_create | boolean | false | Whether should try to create (and bind) the queue when queried. |
| throw_exception_on_redeclare | boolean | true | Throw exception when re-declare of the queue fails |
| throw_exception_on_bind_fail | boolean | true | Throw exception when cannot create the bindings |
| bind | array | empty | Whether should bind to an exchange: See Example 1. |
Example 1:
[ ['exchange' => 'first.exchange', 'routing_key' => '*'], ['exchange' => 'second.exchange', 'routing_key' => 'foo_bar'], ]
2.3. Exchanges
Exchange main nodes:
| Node key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connection | string | The reference to the connection that should be used. |
| name | string | The actual name of the queue on RabbitMQ |
| attributes | array | Optional attributes for the exchange |
Exchange attributes
| Attribute key | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| exchange_type | string | - | Mandatory The type of the exchange (direct / fanout / topic / headers). View description [here] (https://www.rabbitmq.com/tutorials/amqp-concepts.html) |
| passive | boolean | false | This is an AMQP attribute. Read about [here] (https://www.rabbitmq.com/amqp-0-9-1-reference.html) |
| durable | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| auto_delete | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| internal | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| nowait | boolean | false | Same as passive attribute |
| auto_create | boolean | false | Whether should try to create (and bind) the queue when queried. |
| throw_exception_on_redeclare | boolean | true | Throw exception when re-declare of the queue fails |
| throw_exception_on_bind_fail | boolean | true | Throw exception when cannot create the bindings |
| bind | array | empty | Whether should bind to an exchange: See Example 2. |
Example 2:
[ ['queue' => 'first.exchange', 'routing_key' => '*'], ['queue' => 'second.exchange', 'routing_key' => 'foo_bar'], ]
2.4. Publishers
A publisher push a message on an exchange (but it can also push it on a queue). Defining a publishers:
'publishers' => [ 'myFirstPublisher' => 'echangeAliasName', 'mySecondPublisher' => 'queueAliasName' // and many as you need ]
2.5. Consumers
A consumer will always get message from a queue. Define a consumer:
'consumers' => [ 'myConsumerName' => [ 'queue' => 'queueAliasName', 'prefetch_count' => 1, 'message_processor' => \NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\Processor\CliOutputProcessor::class ] ]
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| queue | string | Reference of the defined queue block. |
| prefetch_count | int | Default: 1. The number of the message that a cosumer will grab without ack. Read more here |
| global_prefetch | boolean | Default: true. Setting if the prefetch should be set globally on the channel. Read more here |
| passive | boolean | false |
| durable | boolean | false |
| auto_delete | boolean | false |
| internal | boolean | false |
| nowait | boolean | false |
| auto_create | boolean | false |
| throw_exception_on_redeclare | boolean | true |
| throw_exception_on_bind_fail | boolean | true |
| bind | array | empty |
3. Usage
After configuring, you should end up with a configuration file laravel_rabbitmq.php similar to this one:
return [ 'connections' => [ 'connectionA' => [], ], 'exchanges' => [ 'exchangeA' => [ 'connection' => 'connectionA', 'name' => 'foo_bar', 'attributes' => [ 'exchange_type' => 'topic' ] ] ], 'queues' => [ 'queueB' => [ 'connection' => 'connectionA', 'name' => 'foo_bar_listener', 'attributes' => [ 'bind' => [ ['exchange' => 'foo_bar', 'routing_key' => '*'] ] ] ] ], 'publishers' => [ 'aPublisherName' => 'exchangeA' ], 'consumers' => [ 'aConsumerName' => [ 'queue' => 'queueB', 'message_processor' => \NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\Processor\CliOutputProcessor::class ] ] ]
3.1. Publishing a message
Example of usage in code:
<?php /** * @var $app \Illuminate\Contracts\Container\Container * @var $publisher \NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\PublisherInterface */ $publisher = $app->makeWith(PublisherInterface::class, ['aPublisherName']); $message = [ 'title' => 'Hello world', 'body' => 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.', ]; $routingKey = '*'; $publisher->publish(json_encode($message), /* optional */$routingKey);
Optional, there is a command that can be used to publish a message.
php artisan rabbitmq:publish aPublisherName MyMessage
Note: At the moment, routing key in CLI is not supported.
3.2. Consuming a message
Consuming message should be done by running a command in deamon mode. While PHP is not intended to do that, you can use supervisor for that.
The flow of the consumer is rather simple:
CLI Consumers -> Get message -> Passes it to the message_processor key from configuration.
A message processor is a class that implements NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\Processor interface. If you do no want to handle acknowledgement you can extend \NeedleProject\LaravelRabbitMq\Processor\AbstractMessageProcessor which require implementation of processMessage(AMQPMessage $message): bool method.
You message_processor key is runned by laravel's app command for build of the class.
Start the message consumer/listener:
php artisan rabbitmq:consume aConsumerName
Running consumers with limit (it will stop when one of the limits are reached)
php artisan rabbitmq:consume aConsumerName --time=60 --messages=100 --memory=64
This tells the consumer to stop if it run for 1 minute or consumer 100 messages or has reached 64MB of memory usage.
3.3. Available commands
When running php artisan a new namespace will be present:
| Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| rabbitmq:consume | Consummer command | php artisan rabbitmq:consume [consumer-name] --time=60 --messages=100 --memory=64 Where --time/messages/memory are optional. Default values are 60 seconds, 100 messages and 64MB of RAM usage |
| rabbitmq:delete-all | Delete all queues, exchanges and binds that are defined in entities AND referenced to either a publisher or a consumer | |
| rabbitmq:list | List all entities by type: publishers | consumers |
| rabbitmq:publish | Publish one message using a consumer | php artisan rabbitmq:publish [publisher-name] message |
| rabbitmq:setup | Creates all queues and exchanges | php artisan rabbitmq:setup or php artisan rabbitmq:setup --force. NOTE When using force, all queues and exchanges will be deleted first and then re-created. |
3.4. Custom Message Processor
At the current moment there is the possibility to either implement the MessageProcessorInterface class or extend the AbstractMessageProcessor.
When using the AbstractMessageProcessor, you will have access to extra API than can be used in your processMessage():
protected function ack(AMQPMessage $message); protected function nack(AMQPMessage $message, bool $redeliver = true);
5. Contribute
You are free to contribute by submitting pull request or reporting any issue in Github. At the current stage of the project, no contribution procedure is defined.
5.1 Local Development
Run composer install (with ignore-platform-reqs to avoid missing extensions):
docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/app jitesoft/phpunit:8.1 composer install --ignore-platform-req=ext-sockets
Run unit tests via Docker:
docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/app jitesoft/phpunit:8.1 phpunit --configuration phpunit.xml
5.2. Required Help
There are multiple topics for which the library needs help
- CI Pipeline: There is a need for a configuration of scrutinizer (or any other tool) that can cover running tests for all supported PHP Versions and Laravel Framework versions
- Documentation: Any improvement to easy the use of the library it's welcome
- Examples: A section of examples that proves the library's different real-world scenario examples
6. Special "Thank you"
Special "Thank you" goes out to the library contributors.
