inerba / filament-db-config
A Filament plugin for database-backed application settings and editable content, with caching and easy page generation.
Installs: 7 458
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 29
Watchers: 0
Forks: 1
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/inerba/filament-db-config
Requires
- php: ^8.2
- filament/filament: ^4.0|^5.0
- spatie/laravel-package-tools: ^1.15.0
Requires (Dev)
- laravel/pint: ^1.14
- orchestra/testbench: ^10.0
- pestphp/pest: ^4.0
- phpstan/phpstan: ^2.1
README
DB Config – Lightweight settings & content manager for Filament
⭐ Star this repo if it helps you - it truly motivates us to do more. 🙏😊
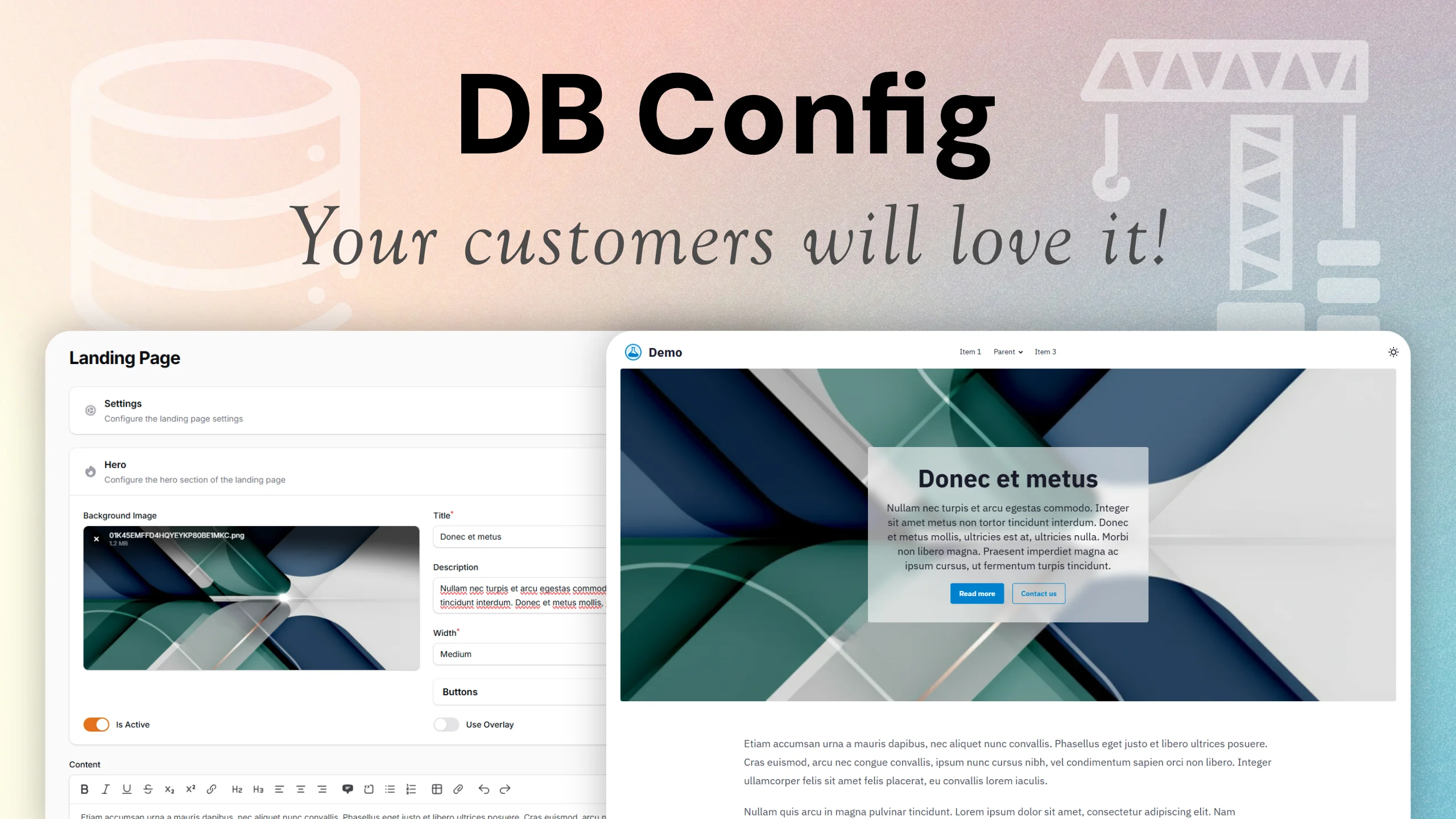
DB Config is a Filament plugin that provides a simple, database-backed key/value store for application settings and editable content.
It’s ideal both for storing configuration (like site name, contact info, labels) and for managing page sections (homepage hero, landing blocks, about text, etc.) without the need for a full CMS.
- 🔑 Store application settings in a simple key/value table
- 📝 Manage editable content (homepages, landing pages, about sections)
- ⚡ Use any Filament form fields or layouts — including third-party ones
- 🗄️ Transparent caching, no extra boilerplate, zero external deps
It provides a clean set of simple helpers for reading and writing values, with transparent caching under the hood, and persists data as JSON in a dedicated table.
It is framework-friendly and requires no custom Eloquent models in your app.
- DB Config – Lightweight settings & content manager for Filament
Requirements
- PHP version supported by your Laravel installation
- Laravel 12
- A database engine with JSON support (MySQL 5.7+, MariaDB 10.2.7+, PostgreSQL, SQLite recent versions)
- Filament 4 or Filament 5
Installation
-
Install the package via Composer:
composer require inerba/filament-db-config
-
Publish the assets (Configuration and Migration):
php artisan vendor:publish --tag="db-config-migrations" -
Run the migration:
php artisan migrate
This command executes the migration file that you just published, creating the
db_configtable (or the custom table name you defined in the config file) in your database. Your package is now ready to use!
Tip
If you want to use a custom table name instead of db_config, edit the configuration file config/db-config.php before running the migration. See the Configuration section for details.
🚀 Getting Started
Get up and running in just a few steps:
-
Generate Your First Settings Page
php artisan make:db-config Website
This command creates a new Filament page (e.g., App/Filament/Pages/WebsiteSettings.php). You can repeat this step for more pages as needed.
Note
The generator will automatically add the “Settings” suffix to the page name for consistency (e.g., WebsiteSettings), but you can use any group name you wish.
-
Define Your Fields
Open the generated page and customize the form() method with your desired fields:
public function form(Form $form): Form { return $form ->components([ TextInput::make('site_name')->label('Site Name'), TextInput::make('contact_email')->label('Contact Email'), Toggle::make('maintenance_mode')->label('Maintenance Mode'), ]) ->statePath('data'); }
Note
You may use any Filament form fields or layout components - including third-party ones - to build your settings and content pages, giving you full flexibility in how data is structured and edited.
-
Save and Edit Settings from the Admin Panel
You can now edit these settings directly in your Filament admin panel—no extra boilerplate needed.
-
Use Your Settings Anywhere
Retrieve your configuration values easily:
-
In PHP:
$siteName = db_config('website.site_name', 'Default Site Name');
-
In Blade:
<h1>{{ db_config('website.site_name', 'Default Site Name') }}</h1> <!-- or --> <h1>@db_config('website.site_name', 'Default Site Name')</h1>
-
That’s it! 🎉
Define your fields, save from the admin panel, and access your settings anywhere in your Laravel app.
Configuration
You can customize the behavior of the package by publishing the configuration file:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag="db-config-config"
Details
Table Name: By default, settings are stored in the db_config table. You can change this by modifying the table_name value. This is useful to avoid collisions or to follow a specific naming convention.
'table_name' => 'db_config',
Cache Behavior: The package uses caching to minimize database queries. You can fine-tune the cache settings.
-
prefix: All cache keys generated by the package will use this prefix. Changing this can prevent collisions with other cache keys in your application.
-
ttl: Defines the cache lifetime in minutes. By default, it's null, which means settings are cached forever. You can specify a number of minutes to have the cache expire periodically.
'cache' => [ 'prefix' => 'my-app-settings', 'ttl' => 60, // Cache for 1 hour ],
Advanced Usage
Generate a settings page
DB Config ships with an Artisan generator and an abstract Page class to quickly scaffold Filament settings pages.
php artisan make:db-config
Details
Arguments can be omitted: if you don’t provide them, the command will enter interactive mode and prompt you for the group name (name) and, optionally, the panel (panel). You can also pass them on the command line to avoid interactive prompts.
Parameters:
name: the settings group name (e.g.website). It is used to generate the view name and the class name (singular, capitalized).panel(optional): the Filament panel to create the page in (e.g.Admin). If omitted the default panel is used.
Examples:
php artisan make:db-config website # default panel php artisan make:db-config website admin # specific panel (e.g. Admin)
What is generated:
- A Page class at
app/Filament/{Panel}/Pages/{Name}Settings.php(the class name is the singular form of{name}+Settings, e.g.WebsiteSettings.php). - A Blade view at
resources/views/filament/config-pages/{slug-name}-settings.blade.php(the view name is a slugified version of thenamewith a-settingssuffix).
Behavior:
- The command does not overwrite existing files: if the class or the view already exist it will warn and leave the files intact.
- Names are normalized: the class uses the singular form of the provided name, the view is slugified (spaces and special characters are converted).
Note: the generated class extends Inerba\DbConfig\AbstractPageSettings and the view is placed under resources/views/filament/config-pages/.
Page lifecycle and saving:
- On
mount(), the page loads all settings for the given group (defined bysettingName()) viaDbConfig::getGroup()and fills the page content state. - A built-in header action “Save” persists the current state by calling
DbConfig::set("{group}.{key}", $value)for each top-level key present in the page content.
Defining the page content:
- Implement
protected function settingName(): stringto define the group name (e.g.website). - Implement
public function content(Schema $schema): Schemaand return your content schema. - Set
->statePath('data')so the page state is bound to the$dataproperty and saved correctly.
Example page content (Filament schema):
use Filament\Forms\Components\TextInput; use Filament\Schemas\Schema; public function content(Schema $schema): Schema { return $schema ->components([ TextInput::make('site_name')->required(), // ... other inputs ]) ->statePath('data'); }
Creating a widget 🆕
Create a custom widget as per the Filament instructions
and extend it as shown in the example:
namespace App\Filament\Resources\Post\Widgets; // depending on your app structure use Filament\Schemas\Schema; use Inerba\DbConfig\AbstractWidgetSettings; class BlogSettings extends AbstractWidgetSettings { /** * Get the name of the setting. * * @return string The name of the setting. */ protected function settingName(): string { return 'blog-settings'; } /** * Provide default values for the settings. * * @return array<string, mixed> The default data for the settings. */ public function getDefaultData(): array { return []; } /** * Define the form schema for the settings page. * * @param Schema $schema The schema instance. * @return Schema The modified schema with components. */ public function form(Schema $schema): Schema { return $schema ->components([ // Form components go here ]) ->statePath('data'); } }
Read & write values
The simplest way to manage values is through the Filament pages scaffolded by DB Config:
you can define the fields you need (text inputs, toggles, repeaters, rich text, even third-party components) and edit them directly in the admin panel.
All changes are saved automatically in the db_config table and cached for fast access.
For programmatic access, the package also provides simple helpers and static methods:
Read a value (helper)
db_config('website.site_name', 'Default Name');
Read a value safely (with exception handling)
For scenarios where database access might fail (e.g., during migrations, maintenance, or bootstrapping), use the safe_db_config() helper. It catches any exceptions and returns the default value instead of crashing your application:
safe_db_config('website.site_name', 'Default Name');
This is particularly useful in:
- Service providers or middleware that run before the database is fully initialized
- Fallback scenarios where you want graceful degradation
- Development or CI environments where the database might not always be available
Tip
Use safe_db_config() in critical paths where a configuration failure should not interrupt the application flow.
Blade directive
You can also access values directly inside Blade templates:
@db_config('website.site_name', 'Default Name')
Read a value (class)
\Inerba\DbConfig\DbConfig::get('website.site_name', 'Default Name');
Write a value
\Inerba\DbConfig\DbConfig::set('website.site_name', 'Acme Inc.');
Read an entire group as associative array
\Inerba\DbConfig\DbConfig::getGroup('website'); // => [ 'site_name' => 'Acme Inc.', 'contact' => ['email' => 'info@acme.test'] ]
Facade (optional)
\Inerba\DbConfig\Facades\DbConfig::get('website.site_name');
Note
these values are not part of Laravel’s config() cache.
Always use db_config() or @db_config instead of config(). The db_config() helper is auto-registered by the package and is the recommended way to read values in application code.
Set Default Values
You can provide default values for your settings page. This is useful for pre-filling the form with sensible defaults when it's accessed for the first time. It guides the user by showing recommended settings, which they can then adjust or save directly to establish a working configuration without manual setup.
To define default values, simply override the getDefaultData() method in your settings page class and return an array of key-value pairs.
Example:
use Filament\Forms\Components\TextInput; use Filament\Forms\Components\Toggle; use Filament\Schemas\Schema; /** * Set the default values to pre-fill the form. * * @return array<string,mixed> */ public function getDefaultData(): array { return [ 'posts_per_page' => 10, 'allow_comments' => true, ]; } public function form(Schema $schema): Schema { return $schema ->components([ TextInput::make('posts_per_page')->required(), Toggle::make('allow_comments'), ]) ->statePath('data'); } }
When the settings page is loaded, the getDefaultData() method provides the initial values to populate the form fields. These defaults are only used if no value for a given field has been previously saved to the database.
It's important to note that these default values are not persistent until the user explicitly clicks the "Save" button.
Working with nested values
DB Config uses a group.setting format for keys, with optional nested sub-keys resolved from JSON.
- The first segment is the group
- The second is the top-level key
- Any remaining segments are treated as nested paths inside the JSON value
Example:
// Store a nested structure \Inerba\DbConfig\DbConfig::set('profile.preferences', [ 'theme' => 'dark', 'notifications' => ['email' => true, 'sms' => false], ]); // Read a nested value with default db_config('profile.preferences.theme', 'light'); // 'dark' // Read a missing nested value db_config('profile.preferences.timezone', 'UTC'); // 'UTC'
How it works
Settings are organized by a two-part key: group.setting, with optional nested sub-keys (e.g. group.setting.nested.key).
Under the hood:
- Database Storage: Settings are stored in a database table (by default
db_config), with one row per(group, key). The actual settings are stored as a JSON payload in thesettingscolumn. - Intelligent Caching: Reads are cached to ensure high performance. By default, they are cached forever, but you can configure a specific TTL (Time To Live) in the config file.
- Configurable Cache Keys: The cache key is generated using a configurable prefix (
db-configby default) followed by the group and setting (e.g.,db-config.website.site_name). - Automatic Cache Invalidation: Writes automatically clear the corresponding cache entry, ensuring that data always stays fresh.
Database
The db_config table contains:
id(bigint, primary key)group(string)key(string)settings(json, nullable)created_at,updated_at(timestamps)
There is a unique index on (group, key). Timestamps are present but not used by the package logic and may remain null depending on your database defaults.
This package stores settings as JSON. Ensure your chosen database supports JSON columns. For SQLite (common in tests), JSON is stored as text and works transparently for typical use cases.
Caching behavior
To minimize database traffic, DB Config comes with a powerful caching layer. Here’s how it works:
- Default Behavior: By default, settings are cached forever. The first time a setting is read, it's fetched from the database and stored in the cache. All subsequent reads will hit the cache directly, making them incredibly fast.
- Automatic Cache Invalidation: When you use
DbConfig::set()or the "Save" action on a settings page, the cache for the affected(group, setting)pair is automatically cleared. This ensures that the next read will fetch the fresh value from the database. - Configurable TTL: You can change the default behavior by setting a
ttl(Time To Live) in minutes in theconfig/db-config.phpfile. If a TTL is set, the package will use a temporary cache that expires after the specified duration. - Manual Cache Clearing: When debugging, you can clear the entire framework cache using
php artisan cache:clearto reset all cached settings.
Return values and defaults
- If a value or nested path does not exist, the provided default is returned.
- If the stored JSON value is
null, the default is returned. getGroup()returns an associative array of all settings for the group, or an empty array if none exist.
Why use DB Config when Spatie Settings already exists?
Both DB Config and the official Spatie Laravel Settings Plugin solve a similar problem - managing application settings in Laravel + Filament - but they take very different approaches.
Spatie Settings focuses on strict typing, validation, and integration with your domain logic, while DB Config is designed to be lightweight, flexible, and quick to set up, even for editable content blocks.
Show comparison table between DB Config and Spatie Settings
The table below highlights the key differences so you can choose the right tool for your project:
| Feature | DB Config | Spatie Laravel Settings Plugin |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Ready to use, no extra classes or migrations | Requires a dedicated Settings class for each group, plus migration to register it |
| Data storage | Single db_config table with JSON values |
Each group stored as its own settings record (linked to its Settings class) |
| Boilerplate | None required | A new PHP class must be created for every settings group |
| Access | Dot notation, supports nested keys in JSON | Strongly typed properties defined in the Settings class |
| Cache | Built-in, refreshed automatically on write | Built-in, but usually configured explicitly |
| Ideal for | Application settings and editable page content (homepage, blocks, texts) | Strictly typed, validated settings tightly bound to app logic |
| Content usage | Can store full page sections (homepage, landing, about, etc.) | Not designed for CMS-like use |
| Dependencies | No external deps | Requires spatie/laravel-settings |
Choose DB Config if you want:
- A lightweight key/value system for both settings and content.
- Minimal setup, no boilerplate code.
- Flexibility to manage simple settings and even page content directly in Filament.
Choose Spatie Laravel Settings Plugin if you need strict typing, validation, and DTOs as part of your domain logic.
Security considerations
Caution
DB Config is a place for values you want admins to edit safely at runtime, not for infrastructure secrets (API keys, DB credentials).
Values are not encrypted by default. If you need encryption, apply it before using the package’s helpers to read or write values.
Testing
This package comes with a full test suite powered by Pest. To run the tests, first install the development dependencies:
composer install
Then, run the test suite from the root of the project:
./vendor/bin/pest
The package also uses GitHub Actions to automatically run tests on every push and pull request, ensuring that the code remains stable and reliable.
Plugin Skill: filament-db-config
This package includes a Boost Agent Skill (resources/boost/skills/filament-db-config/SKILL.md) that provides guidance and strict conventions for creating database-backed settings pages with the db-config / filament-db-config workflows.
To use it, you must have Laravel Boost installed and run the command php artisan boost:install.
Versioning
This package follows semantic versioning. Use a version constraint compatible with your Laravel version as shown in the installation section.
License
The MIT License (MIT). See the LICENSE file for more details.