code-rhapsodie / ibexa-dataflow-bundle
Import / export bundle for Ibexa Content based on Code Rhapsodie Dataflow framework
Package info
github.com/code-rhapsodie/ibexa-dataflow-bundle
Type:symfony-bundle
pkg:composer/code-rhapsodie/ibexa-dataflow-bundle
Requires
- php: ^8.3
- ext-json: *
- code-rhapsodie/dataflow-bundle: ^5.0
- guzzlehttp/promises: ^2.2
- http-interop/http-factory-guzzle: ^1.2
- ibexa/admin-ui: ^5.0
- ibexa/core: ^5.0
Requires (Dev)
- doctrine/dbal: ^3.0
- phpunit/phpunit: ^12.0
- rector/rector: ^2.0
Replaces
README
Ibexa DataflowBundle is a bundle integrating Code Rhapsodie Dataflow bundle into Ibexa 4.0+. Dataflows can be piloted from an interface integrated into the Ibexa backoffice. Ibexa Dataflow bundle is intended to manage content imports from external data sources.
Note: before using this bundle, please read the Code Rhapsodie Dataflow bundle documentation.
Command line notice: When you use Dataflow commands, use
--siteaccessinstead of--connectionexcept forcode-rhapsodie:dataflow:dump-schemacommand.
| Ibexa Dataflow Version | Ibexa Content Version | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 5.x | 4.x | ✅ Maintained |
User Interface (UI)
The UI lets you create workflow processes from any defined DataflowTypes, and set options to each.
Processes can be set to run either:
- only once, at a given date and time
- regularly, by defining the first run date and time, and the interval between subsequent runs
Installation
Step 1: Install the bundle via composer
$ composer require code-rhapsodie/ibexa-dataflow-bundle
Step 2: Enable the bundle
Note: The loading order between the Dataflow bundle and Ibexa Dataflow bundle is important. Dataflow must be loaded first.
Add those two lines in the config/bundles.php file:
<?php return [ // ... CodeRhapsodie\DataflowBundle\CodeRhapsodieDataflowBundle::class => ['all' => true], CodeRhapsodie\IbexaDataflowBundle\CodeRhapsodieIbexaDataflowBundle::class => ['all' => true], // ... ];
Step 3: Import bundle routing file
# config/routing/ibexa_dataflow.yaml _cr.ibexa_dataflow: resource: '@CodeRhapsodieIbexaDataflowBundle/Resources/config/routing.yaml'
Step 4: Update the database schema
Please refer to the Code-Rhapsodie Dataflow Bundle installation guide.
Step 5: Schedule the job runner
Please refer to the Code-Rhapsodie Dataflow Bundle Queue section.
Configuration
By default, the ContentWriter will publish contents using the admin user. If you want to use another user (with
sufficient permissions), you can configure it like this:
# config/packages/code_rhapsodie_ibexa_dataflow.yaml code_rhapsodie_ibexa_dataflow: # Integer values are assumed to be user ids, non-integer values are assumed to be user logins admin_login_or_id: webmaster
Define your Dataflow
Before using the admin UI to manage your dataflows, you need to define them. Please refer to Code-Rhapsodie Dataflow type documentation.
Use the ContentWriter
To add or update Ibexa contents, you can use the CodeRhapsodie\IbexaDataflowBundle\Writer\ContentWriter writer.
Step 1: Inject the dependencies and add the writer
Inject the ContentWriter service into the constructor of your DataflowType and add the content writer into the writer
list like this:
// In your DataflowType use CodeRhapsodie\IbexaDataflowBundle\Writer\ContentWriter; use CodeRhapsodie\DataflowBundle\DataflowType\AbstractDataflowType; [...] class MyDataflowType extends AbstractDataflowType { //[...] public function __construct(private readonly ContentWriter $contentWriter) { } //[...] protected function buildDataflow(DataflowBuilder $builder, array $options): void { //[...] $builder->addWriter($this->contentWriter); } }
Step 2: Add a step for prepare the content
To process Ibexa contents into your Dataflow, you need to transform the data into ContentCreateStructure
or ContentUpdateStructure objects.
in order to respectively create or update contents.
But, in order to determine if the content already exists or not, you first need to look up for it.
One way is to use the remote id to search for the content.
In the following example, the remote id pattern is article-<id> with the <id> replaced by the data id provided by
the reader.
To check if the content exists or not, I use the service ContentService provided by Ibexa.
The step is added as an anonymous function and has 3 types of return values:
- When the step returns
false, the data is dropped. - When the step returns a
ContentCreateStructure, the data will be saved into a new Ibexa content. - When the step returns a
ContentUpdateStructure, the existing Ibexa content will be updated by overwriting all defined fields in the data.
For the new content, you must provide one or more "parent location id" as the 3rd argument of
the ContentCreateStructure constructor.
In this example, I have added a new folder to store all articles.
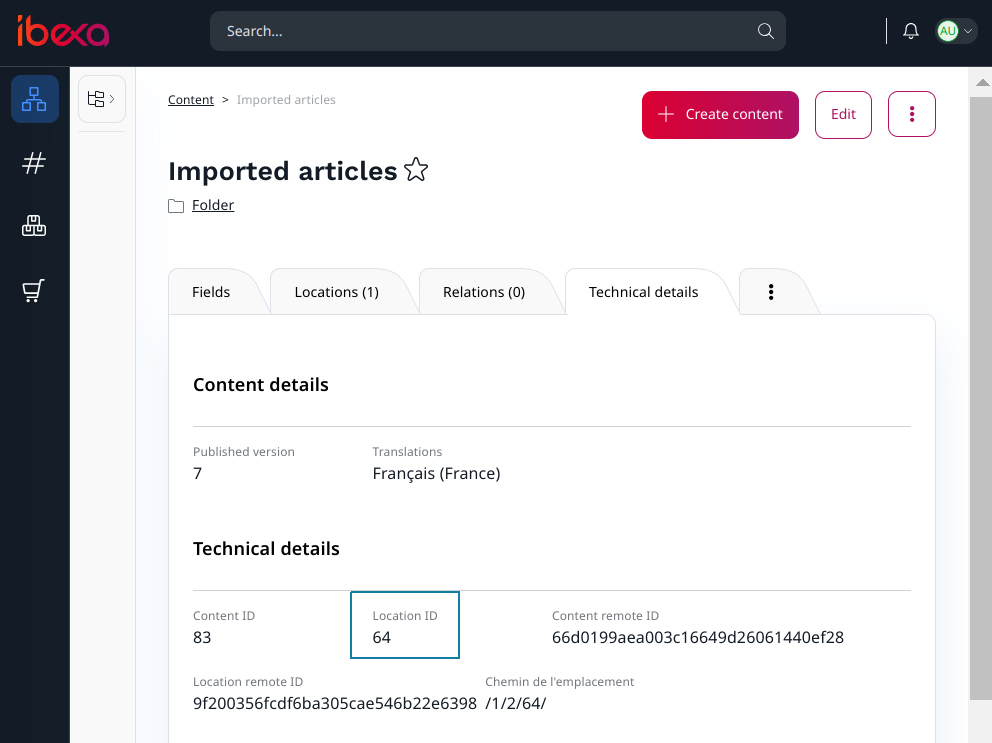
To get the location id of the parent Ibexa content, go to the admin UI and select the future parent content, click on the details tabs, and read the "Location id" like this:
Note: the best practice is to define this parent id in your
parameters.yamlfile or your.env.localfile for each execution environment.
// In your DataflowType use CodeRhapsodie\IbexaDataflowBundle\Factory\ContentStructureFactory; use CodeRhapsodie\IbexaDataflowBundle\Writer\ContentWriter; use CodeRhapsodie\DataflowBundle\DataflowType\AbstractDataflowType; [...] class MyDataflowType extends AbstractDataflowType { //[...] public function __construct( private readonly ContentWriter $contentWriter, private readonly ContentStructureFactory $contentStructureFactory ) { } //[...] protected function buildDataflow(DataflowBuilder $builder, array $options): void { //[...] $builder->addStep(function ($data) { if (!isset($data['id'])) { return false; } $remoteId = sprintf('article-%d', $data['id']); unset($data['id']); return $this->contentStructureFactory->transform( $data, $remoteId, 'eng-GB', 'article2', 54, //Parent location id ContentStructureFactoryInterface::MODE_INSERT_OR_UPDATE //Optional value. Other choice : ContentStructureFactoryInterface::MODE_INSERT_ONLY or ContentStructureFactoryInterface::MODE_UPDATE_ONLY ); }); // If you want the writer log $this->contentWriter->setLogger($this->logger); $builder->addWriter($this->contentWriter); } }
This example uses ContentStructureFactory to check if the content exists and returns the adequate ContentStrucure to
pass to the content writer.
Use the NotModifiedContentFilter
When updating contents, you might want to ignore contents where the update would not result in any actual changes in
fields values. In that case, you can add the NotModifiedContentFilter as one of your steps.
// In your DataflowType public function __construct(NotModifiedContentFilter $notModifiedContentFilter) { $this->notModifiedContentFilter = $notModifiedContentFilter; } //[...] protected function buildDataflow(DataflowBuilder $builder, array $options): void { //[...] // If you want the filter log $this->notModifiedContentFilter->setLogger($this->logger); $builder->addStep($this->notModifiedContentFilter); //[...] }
This filter compares each field value in the ContentUpdateStructure received to the fields values in the existing
content object. If all values are identical, this filter will return false, otherwise, the ContentUpdateStructure
will be returned as is.
Not all field types are supported by this filter. Il a field type is not supported, values will be assumed different. If
your dataflow is dealing with content types containing unsupported field types, it is better to simply not use
the NotModifiedContentFilter to prevent unnecessary overhead.
Supported field types
- ezstring
- ezauthor
- ezboolean
- ezcountry
- ezdate
- ezdatetime
- ezemail
- ezfloat
- ezisbn
- ezobjectrelation
- ezobjectrelationlist
- ezkeyword
- ezselection
- eztext
- eztime
- eztags
- novaseometas
- ezurl
- ezmatrix
- ezgmaplocation
- ezrichtext
Add custom field comparator
If you want to add support for a field type, simply create your own comparator.
<?php use CodeRhapsodie\IbexaDataflowBundle\Core\FieldComparator\AbstractFieldComparator; use Ibexa\Core\FieldType\Value; //[...] class MyFieldComparator extends AbstractFieldComparator { //[...] protected function compareValues(Value $currentValue, Value $newValue): bool { // Return true if values are identical, false if values are different. } }
# Service declaration App\FieldComparator\MyFieldComparator: parent: 'CodeRhapsodie\IbexaDataflowBundle\Core\FieldComparator\AbstractFieldComparator' tags: - { name: 'coderhapsodie.ibexa_dataflow.field_comparator', fieldType: 'my_field_type_identifier' }
Admin UI
Access to the Ibexa Dataflow UI
You can access the Ibexa Dataflow administration UI from your Ibexa admin back-office.
- Click to "Admin"
- Click to "Ibexa Dataflow"
Scheduled dataflow list
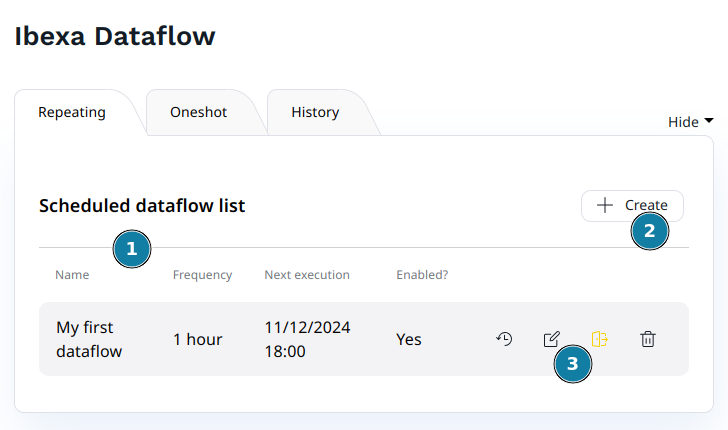
When you access to the Ibexa Dataflow administration UI, you arrive on the scheduled dataflow list page:
- Scheduled dataflow list
- Button to add a new scheduled dataflow
- Tools available for each scheduled dataflow. In order from left to right :
- Display the history for this dataflow schedule
- Edit this dataflow schedule
- Enable/Disable this dataflow schedule
- Delete this dataflow schedule
Note: You can define more than one schedule for any given dataflow.
Add a new schedule
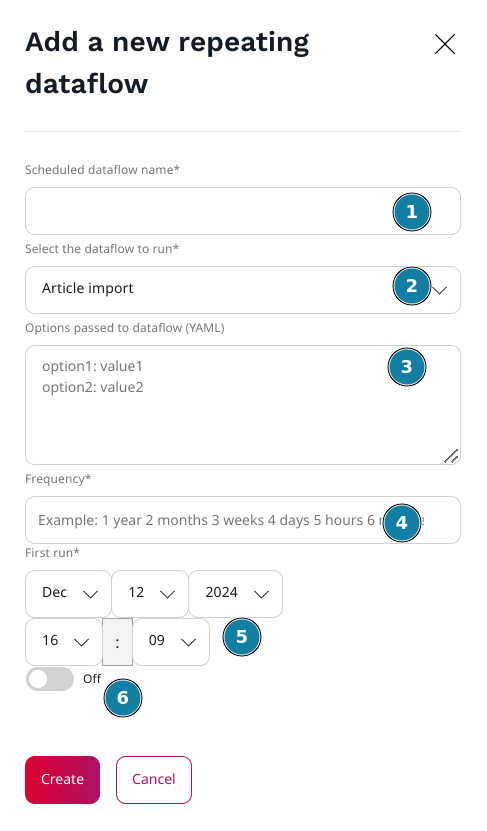
Go to the Ibexa Dataflow admin, and click on the "+" orange button.
In the new popin, fill in the fields:
- Type the Dataflow schedule name
- Select the Dataflow type. The list is automatically generated from the list of Symfony services with the
tags
coderhapsodie.dataflow.type. If your dataflow type is not present, check the configuration - Type here the Dataflow options. Basic expected format: one option per line and option name and value separated
with
:. For more complex options, the whole YAML format is supported. - Type here the frequency. The value must be compatible with the the PHP strtotime function.
- Choose the date and time of the first job.
- Check if you want to run this Dataflow.
Finally, click on the "Create" button.
Read the history
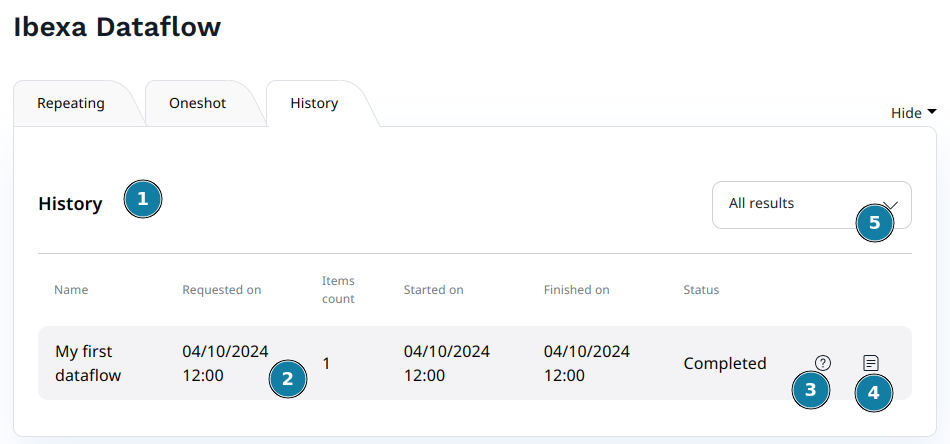
When you click on the "History" tab in the Ibexa Dataflow admin UI, the job history for all Dataflow configured and executed is displayed.
- The history list
- A summary of each job dates and number of items processed.
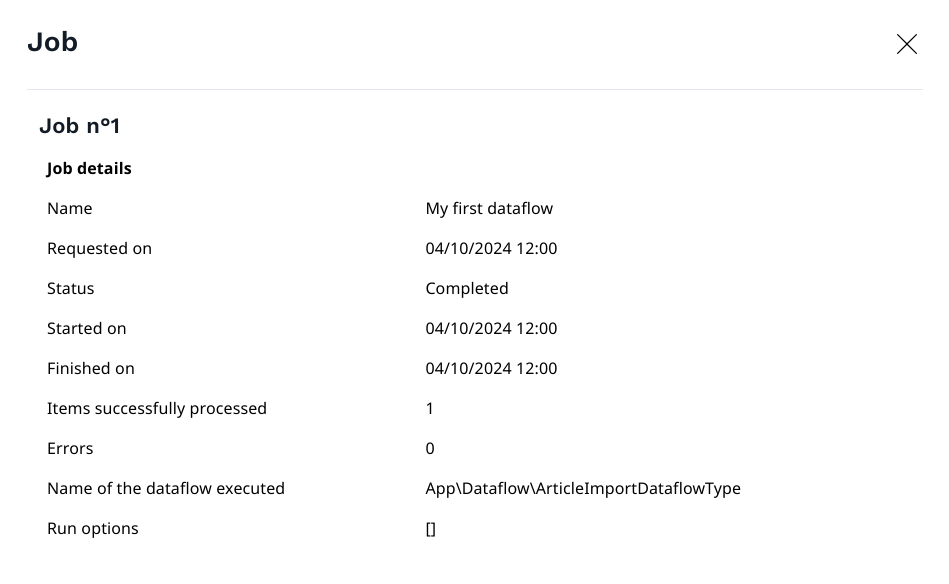
- Click on the question mark icon to display the job details.
- Click on the text icon to display the job exception log.
- Switch between displaying all jobs, or only non-empty jobs (at least 1 item was processed)
Details of one scheduled job:
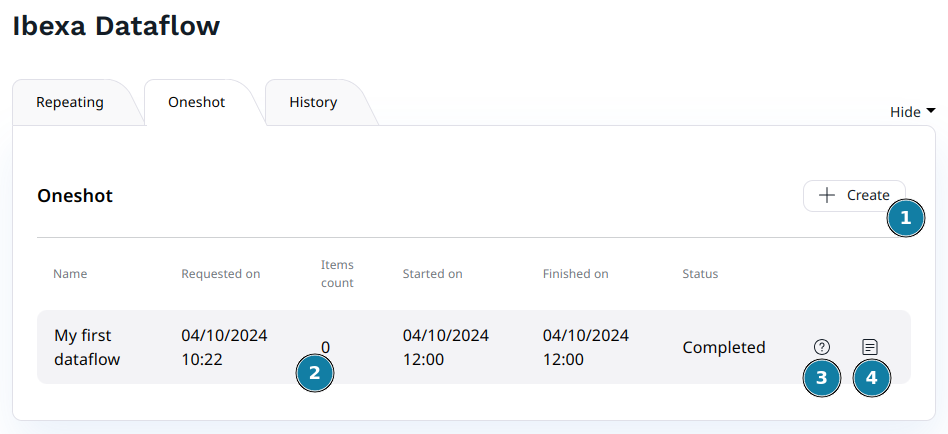
One-shot job
If you don't want to run a Dataflow periodically, you can add a single execution at the time and date that you want.
Go to the Ibexa Dataflow admin UI and click on the "Oneshot" tab.
- This button allows you to create a new one-shot job (see below).
- A summary of each job dates and number of items processed.
- Click on the question mark icon to display the job details.
- Click on the text icon to display the job exception log.
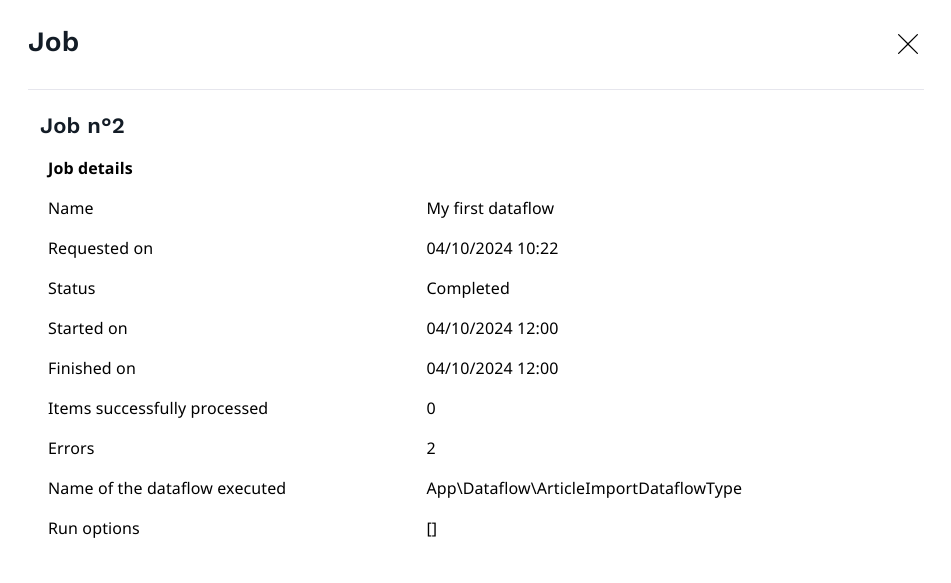
Details of one-shot job:
Here the job has fail.
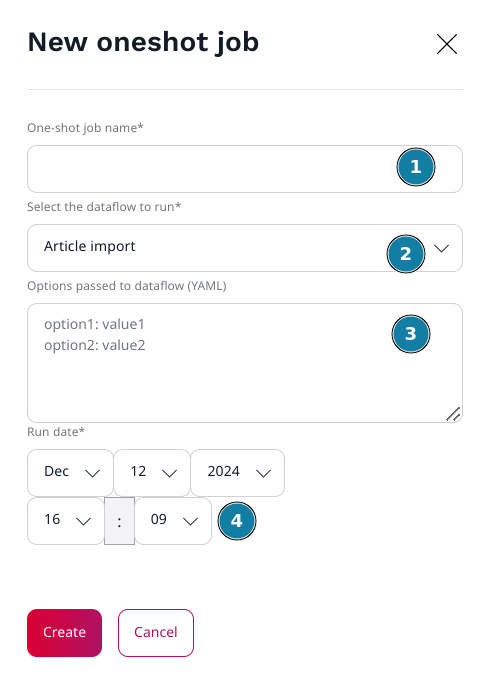
Add a one-shot job
Go to the Ibexa Dataflow admin UI and click on the "Oneshot" tab. Click on the "+ Create" button to open the add popin.
- Type the Dataflow job name
- Select the Dataflow type. The list is automatically generated from the list of Symfony services with the
tags
coderhapsodie.dataflow.type. If your dataflow type is not present, check the configuration - Type here the Dataflow options. Basic expected format: one option per line and option name and value separated
with
:. For more complex options, the whole YAML format is supported. - Choose the date and time of the first job.
Finally, click on the "Create" button.
Rights
If a non-administrator user needs read-only access to the dataflow interface, add the Setup / Administrate
and Ibexa Dataflow / View policies in one of their roles.
Issues and feature requests
Please report issues and request features at https://github.com/code-rhapsodie/ibexa-dataflow-bundle/issues.
Contributing
Contributions are very welcome. Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for details. Thanks to everyone who has contributed already.
License
This package is licensed under the MIT license.