tamedevelopers / database
Lightweight PHP ORM Database Model.
Installs: 111
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 6
Watchers: 1
Forks: 1
Open Issues: 1
Type:composer-plugin
pkg:composer/tamedevelopers/database
Requires
- php: >=8.0
- composer-plugin-api: ^2.0
- tamedevelopers/support: ^5.0
- dev-main
- 6.0.14
- 6.0.13
- 6.0.12
- 6.0.11
- 6.0.10
- 6.0.9
- 6.0.8
- 6.0.7
- 6.0.6
- 6.0.5
- 6.0.4
- 6.0.3
- 6.0.2
- 6.0.1
- 5.0.10
- 5.0.9
- 5.0.8
- 5.0.7
- 5.0.6
- 5.0.5
- 5.0.4
- 5.0.3
- 5.0.2
- 5.0.1
- 5.0.0
- 4.3.9
- 4.3.8
- 4.3.7
- 4.3.6
- 4.3.5
- 4.3.4
- 4.3.3
- 4.3.2
- 4.3.1
- 4.3.0
- 4.2.1
- 4.2.0
- 4.1.9
- 4.1.8
- 4.1.7
- 4.1.6
- 4.1.5
- 4.1.3
- 4.1.2
- 4.1.1
- 4.0.1
- 3.1.9
- 3.1.8
- 3.1.7
- 3.1.6
- 3.1.5
- 3.1.4
- 3.1.3
- 3.1.2
- 3.1.1
- 3.0.1
- 2.2.9
- 2.1.1
- 1.0.5
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-05 06:56:47 UTC
README
Inspiration
Having been introduced to learning Laravel Framework; Over the past yr(s), Coming back to vanilla PHP,
was pretty tough. So i decided to create a much more easier way of communicating with Database, using native PHP PDO:: Driver.
Documentation
- Requirements
- Installation
- Instantiate
- Init php
- Tame Cli
- BootLoader
- Database Connection
- Database Disconnect
- App Debug ENV
- Usage
- Database Connection Keys
- Fetching Data
- Collections
- Auth
- Pagination
- Clause
- query
- select
- selectRaw
- orderBy
- orderByRaw
- orderByDesc
- orderByAsc
- latest
- oldest
- inRandomOrder
- random
- limit
- take
- offset
- join
- joinWhere
- leftJoin
- leftJoinWhere
- rightJoin
- rightJoinWhere
- crossJoin
- where
- orWhere
- whereNot
- orWhereNot
- whereRaw
- whereColumn
- orWhereColumn
- whereNull
- orWhereNull
- whereNotNull
- orWhereNotNull
- whereBetween
- orWhereBetween
- whereNotBetween
- orWhereNotBetween
- whereBetweenColumns
- orWhereBetweenColumns
- whereNotBetweenColumns
- orWhereNotBetweenColumns
- whereDate
- orWhereDate
- whereTime
- orWhereTime
- whereDay
- orWhereDay
- whereMonth
- orWhereMonth
- whereYear
- orWhereYear
- having
- orHaving
- havingNull
- orHavingNull
- havingNotNull
- orHavingNotNull
- havingBetween
- havingRaw
- whereIn
- orWhereIn
- whereNotIn
- orWhereNotIn
- orHavingRaw
- groupBy
- groupByRaw
- Database Migration
- Get Database Config
- Get Database Connection
- Get Database Name
- Get Database PDO
- Get Database TablePrefix
- Database Import
- Update Env Variable
- Autoload Register
- Collation And Charset
- Extend Model Class
- Helpers Functions
- Error Dump
- Error Status
- Useful links
Requirements
>= php 8.0+
Installation
Prior to installing database package get the Composer dependency manager for PHP because it'll simplify installation.
composer require tamedevelopers/database
Instantiate
Step 1 — Require composer autoload:
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
Step 2 — [optional] If you want the Package scalfolding
- This will auto setup your entire application on a
go!- It's helper class can be called, using --
autoloader_start()
- It's helper class can be called, using --
| Description |
|---|
| It's important to install vendor in your project root, As we use this to get your root [dir] |
| By default you don't need to define any path again |
| Files you'll see after you reload browser: |
.env .env.example .gitignore .htaccess .user.ini init.php |
use Tamedevelopers\Database\AutoLoader; AutoLoader::start(); // then reload your browser to allow the system scalfold for you
init php
- [optional] This will extends the
composer autoloadand other setup- If you used the package
Package scalfoldingthis file will be automatically generated, that you can include at the beginning of your project.
- If you used the package
Tame Cli
- Custom commands support for CLI
php tame list
tame-cli-scaffold
- Scalffold the database files, instead of running
AutoLoader::start()in browser.- The
-f|--forceflag is needed if you're inside a framework or if on production server. - This doesn't alter nor replace any files that exists and safe.
- The
php tame scaffold:run --force
tame-artisan-call
- Using the CLI from within php, without the CMD interface.
use Tamedevelopers\Support\Capsule\Artisan; Artisan::call('db:wipe --force');
BootLoader
- [optional] from
version ^6.0.3If you do not want to include or use theinit.phpfile- You can as well call the bootloader, to start the database life-circle.
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Capsule\AppManager; AppManager::bootLoader(); // app_manager()->bootLoader();
Database Connection
- Take two param as
[$name|$options]- Mandatory
$nameas string of connection name - [optional]
$optionsand an array, if no connection data is found - First navigate to [config/database.php] file and add connection configuration or use .env
- Mandatory
DB::connection('connName', $options);
Database Disconnect
- If you want to connect to already connected database, You first need to disconnect
- Takes one param as
string
- Takes one param as
DB::disconnect('connName');
Database Reconnect
- same as
Database Connection
DB::reconnect('connName', $options);
App Debug Env
- The
.envfile contains a key calledAPP_DEBUG- It's mandatory to set to false on Production environment
- This helps to secure your applicaiton and exit with error 404
- instead of displaying entire server errors.
| key | Type | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| APP_DEBUG | boolean | true |
Database Connection Keys
- All available connection keys
- The DB_CONNECTION uses only
mysql - No other connection type is supported for now.
- The DB_CONNECTION uses only
| key | Type | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| driver | string | mysql |
| host | string | localhost |
| port | int | 3306 |
| database | string | |
| username | string | |
| password | string | |
| charset | string | utf8mb4 |
| collation | string | utf8mb4_unicode_ci |
| prefix | string | |
| prefix_indexes | bool | false |
Usage
- All Methods of usage
- Without calling the
DB::connection()and passing the driver name you want. It will automatically be using the default connection driver, you've in your setup'
- Without calling the
Table
- Takes a parameter as
stringtable_name
$db = DB::connection(); $db->table('users');
Insert
- Takes one parameter as assoc array
column_name => value- It returns an object on success or error
DB::table('users')->insert([ 'user_id' => 10000001, 'first_name' => 'Alfred', 'last_name' => 'Pete', 'wallet_bal' => 0.00, 'registered' => strtotime('now'), ]); -- To see data, you need to save into a variable
Insert Or Ignore
- Same as
insert()method- It returns an object of created data or
falseon error
- It returns an object of created data or
DB::table('users')->insertOrIgnore([ 'user_id' => 10000001, 'first_name' => 'Alfred', ]);
Update
- Takes one parameter as assoc array
column_name => value- Returns an
intnumbers of affected rows or error
- Returns an
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->update([ 'first_name' => 'Alfred C.', ]);
Update Or Ignore
- Same as
update()method- Returns an
intnumbers of affected rows or0on error
- Returns an
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->updateOrIgnore([ 'first_name' => 'Alfred C.', ]);
delete
- Returns an
int
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->delete();
destroy
- Take two param as
[value|column]- Mandatory
valueas mixed value - [optional]
columnas Default isid - Returns an
int
- Mandatory
DB::table('posts')->destroy(1); // Query: delete from `posts` where `id` = ? DB::table('posts')->destroy(10, 'post_id'); // Query: delete from `posts` where `post_id` = ?
Increment
- Takes three parameter
- Only the first param is required
| param | Data types |
|---|---|
column required |
string |
count or [] |
int | array |
| param | array |
1 By default if the the second param not passed, this will increment by 1
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->increment('wallet_bal');
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->increment('wallet_bal', 10);
- You can also pass in a second or third parameter to update additional columns
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->increment('wallet_bal', 100.23, [ 'first_name' => 'F. Peterson', 'status' => 1, ]);
- You can ommit the second param and it'll be automatically seen as update param (If an array)
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->increment('wallet_bal', [ 'first_name' => 'F. Peterson', 'status' => 1, ]);
Decrement
- Same as Increment
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->decrement('wallet_bal', [ 'first_name' => 'F. Peterson', 'status' => 1, ]);
min
- Take one param as
Expression|string
DB::table('blog')->min('amount');
max
- Same as min
DB::table('blog')->max('amount');
sum
- Take one param as
Expression|string
DB::table('blog')->sum('amount');
avg
- Take one param as
Expression|string
DB::table('blog')->avg('amount'); DB::table('blog')->average('amount');
Fetching Data
| object name | Returns |
|---|---|
| get() | array of objects |
| find() | object | null |
| first() | object | null |
| FirstOrIgnore() | object | null |
| FirstOrCreate() | object |
| firstOrFail() | object or exit with 404 status |
| count() | int |
| paginate() | array of objects |
| exists() | boolean true | false |
| tableExists() | boolean true | false |
GET
DB::table('users')->get();
First
DB::table('users')->first();
First or Create
-
Take two param as an
array- Mandatory
$conditionsparam asarray - [optional]
$dataparam asarray
- Mandatory
-
First it checks if codition to retrieve data. If fails, then it merge the
$conditionsto$datavalue to create new records
DB::table('users')->firstOrCreate( ['email' => 'example.com'] );
- or --
Example 2
DB::table('users')->firstOrCreate( ['email' => 'example.com'], [ 'country' => 'Nigeria', 'age' => 18, 'dob' => 2001, ] );
First or Fail
- Same as
first()method but exit with error code 404, if data not found
DB::table('users')->firstOrFail();
Count
DB::table('users')->count();
Paginate
- Takes param as
int$per_page- By default if no param is given, then it displays 10 per page
$users = DB::table('users') ->paginate(40); $users // this will return the data objects $users->links() // this will return the paginations links view $users->showing() // Display items of total results
Exists
- Returns boolean
true \| false
DB::table('users') ->where('email', 'email@gmail.com') ->orWhere('name', 'Mandison') ->exists();
Table Exists
- Takes param as
string$table_name
DB::tableExists('users');
Collections
- You can directly use
methodsofCollections Instanceon any of the below - All the below
methodsare received by Collectionclass- get()
- find()
- first()
- firstOrIgnore()
- firstOrCreate()
- firstOrFail()
- insert()
- insertOrIgnore()
Collection Methods
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| getAttributes() | array Returns an array of data |
| getOriginal() | object Returns an object of data |
| isEmpty() | boolean true | false If data is empty |
| isNotEmpty() | opposite of ->isEmpty() |
| count() | int count data in items collection |
| toArray() | array Convert items to array |
| toObject() | object Convert items to object |
| toJson() | string Convert items to json |
Collection Usage
- Colections are called automatically on all Database Fetch Request
- With this you can access data as an
object\|arraykey property - If no data found then it returns null on
->first()method only
- With this you can access data as an
$user = DB::tableExists('users') ->first(); if($user){ $user->first_name $user['first_name'] } $user->toArray() $user->getAttributes()
- Example two(2)
->get() \| ->paginate()Request
$users = DB::tableExists('users') ->where('is_active', 1), ->random(), ->get(); if($users->isNotEmpty()){ foreach($users as $user){ $user->first_name $user['first_name'] $user->toArray() $user->getAttributes() } }
Auth
- Lightweight guard-based authentication similar to Laravel.
- attempt() only validates and sets in-memory user; call login() to persist to session.
| method name | Description |
|---|---|
| guard() | Create a guard bound to a table and [optional] connection. |
| attempt() | Validate credentials, set in-memory user on success; does not persist to session. |
| login() | Persist the current user (or provided array) to session. If userData is not an array, it’s ignored. |
| user() | Get the in-memory user or rehydrate from session if available. |
| id() | Get the authenticated user’s id (or custom key). |
| logout() | Clear in-memory user and remove from session. |
auth-guard
- Set the authentication guard (Takes two param)
- Mandatory
$tableparam asstring - [optional]
$connectionparam asstring | nulldatabase connection name.
- Mandatory
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Auth; $admin = Auth::guard('admins');
Auth Usage
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Auth; // Create guards $admin = (new Auth)->guard('tb_admin'); $user = (new Auth)->guard('tb_user', 'woocommerce'); // Credentials (password is required in attempt) $credentials = [ 'email' => 'peter.blosom@gmail.com', 'status' => '1', 'password' => 'tagged', ]; // 1) Validate credentials only (no session persistence) if ($user->attempt($credentials)) { // In-memory user available $user->check(); // true $user->id(); // e.g., 123 $user->user(); // full user array } // 2) Persist explicitly (similar to Laravel Auth::login()) $user->login($user->user()); // stores sanitized user in session (no password) // 3) Retrieve later in another request $another = (new Auth)->guard('tb_user', 'woocommerce'); $another->user(); // rehydrated from session $another->check(); // true if session had user // 4) Logout $another->logout(); // clears in-memory and session
Pagination
- Configuring Pagination
- It's helper class can be called, using --
config_pagination()
- It's helper class can be called, using --
| key | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allow | true | false |
Default false Setting to true will allow the system use this settings across app |
| class | string | Css selector For pagination ul tag in the browser |
| span | string | Default .page-span Css selector For pagination Showing Span tags in the browser |
| view | bootstrap | cursor | loading | onloading |
Default simple - For pagination design |
| first | string | Change the letter First |
| last | string | Change the letter Last |
| next | string | Change the letter Next |
| prev | string | Change the letter Prev |
| showing | string | Change the letter Showing |
| of | string | Change the letter of |
| results | string | Change the letter results |
| buttons | int | Numbers of pagination links to generate. Default is 5 and limit is 20 |
Global Configuration
- 1 Setup global pagination on ENV autostart
most preferredmethod
AutoLoader::configPagination([ 'allow' => true, 'prev' => 'Prev Page', 'last' => 'Last Page', 'next' => 'Next Page', 'view' => 'bootstrap', 'class' => 'Custom-Class-Css-Selector', ]);
Pagination Query
$users = DB::table('users')->paginate(40);
Pagination Data
$users // This will return `Collections` of pagination data
Pagination Links
$users->links(); // This will return pagination links view
Pagination Links Config
Read more...
- You can directly configure pagination links
- It'll override the global settings
$users->links([ 'first' => 'First Page', 'last' => 'Last Page', 'prev' => 'Previous Page', 'next' => 'Next Page', 'no_content' => 'All videos has been loaded', ])
Pagination Showing
$users->showing(); // This will create a span html element with text <span class='page-span'> Showing 0-40 of 500 results </span>
Pagination Showing Config
Read more...
- You can configure showing text directly as well
$users->showing([ 'showing' => 'Showing', 'of' => 'out of', 'results' => 'Results', 'span' => 'css-selector', ])
Pagination Foreach Numbers
- Page numbering
starts counting from 1- This will format all pagination items collections
- On each page, it starts counting from last pagination item number
$users = DB::table('users')->paginate(20); foreach($users as $user){ echo $user->numbers(); }
Pagination Ajax Loading
- When the view is either
loading||onloading|cursor|bootstrap- This can automatically fetched data without page load
- You need to give your DOM-element
data-pagination-contentanddata-pagination-append
$users = DB::table('users')->paginate(20);
<div data-pagination-content> <div class="wallet-container" data-pagination-append> <?php foreach($users as $user) {?> <!-- Content to be loaded structure --> <?php }?> </div> </div> or <div data-pagination-content data-pagination-append> <!-- Content to be loaded structure --> </div> <!-- pagination links --> <div> <?= $users->links([ 'no_content' => 'All users have been loaded.' ]); ?> </div>
Get Pagination
- Returns pagination informations
| key | Description |
|---|---|
| limit | Pagination limit int |
| offset | Pagination offset int |
| page | Pagination Current page int |
| pageCount | Pagination Total page count int |
| perPage | Pagination per page count int |
| totalCount | Pagination total items count int |
$users = DB::table('users')->paginate(20); $users->getPagination();
Clause
- Multiple clause
Query
- Allows the use direct sql query
SQL query syntax- Or direct query exec()
- [important] you cannot use paginate on
query()method
DB::query("SHOW COLUMNS FROM users") ->limit(10) ->get(); DB::query("ALTER TABLE `langs` ADD COLUMN es TEXT; UPDATE `langs` SET es = en;") ->exec();
Select
- Used to select needed columns from database
DB::table('users') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->select(['first_name', 'email']) ->select('email', 'name') ->first();
orderBy
- Takes two param
$columnand$direction- By default
$directionparam is set toASC
- By default
DB::table('wallet') ->orderBy('date', 'DESC') ->get();
orderByRaw
- Takes one param
$query
DB::table('wallet') ->orderByRaw('CAST(`amount` AS UNSIGNED) DESC') ->get();
Latest
- Takes one param
$columnby default the column used isid
DB::table('wallet') ->latest('date') ->get();
Oldest
- Takes one param
$columnby default the column used isid
DB::table('wallet') ->oldest() ->get();
inRandomOrder
DB::table('wallet') ->inRandomOrder() ->get();
random
Read more...
- Same as
inRandomOrder()
DB::table('wallet') ->random() ->get();
limit
- Takes one param
$limitas int. By default value is1
DB::table('wallet') ->limit(10) ->get();
offset
Read more...
- Takes one param
$offsetas int. By default value is0
DB::table('wallet') ->limit(3) ->offset(2) ->get();
- Example 2 (Providing only offset will return as LIMIT without error)
DB::table('wallet') ->offset(2) ->get();
join
- Includes
join|leftJoin|rightJoin|crossJoin
| Params | Description |
|---|---|
| table | table |
| foreignColumn | table.column |
| operator | operator sign |
| localColumn | local_table.column |
DB::table('wallet') ->join('users', 'users.user_id', '=', 'wallet.user_id') ->get();
- or
DB::table('wallet') ->join('users', 'users.user_id', '=', 'wallet.user_id') ->where('wallet.email', 'example.com') ->orWhere('wallet.user_id', 10000001) ->paginate(10);
leftJoin
- Same as
join
DB::table('wallet') ->leftJoin('users', 'users.user_id', '=', 'wallet.user_id') ->where('wallet.email', 'example.com') ->get();
where
- Takes three parameter
- Only the first param is required
| param | Data types |
|---|---|
| column | string |
| operator | string |
| value | string |
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->where('amount', '>', 10) ->where('balance', '>=', 100) ->get();
orWhere
Read more...
- Same as Where clause
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->where('amount', '>', 10) ->orWhere('first_name', 'like', '%Peterson%') ->where('amount', '<=', 10) ->get();
whereRaw
- Allows you to use direct raw
SQL query syntax
$date = strtotime('next week'); DB::table("tb_wallet") ->whereRaw("NOW() > created_at") ->whereRaw("date >= ?", [$date]) ->where(DB::raw("YEAR(created_at) = 2022")) ->where('email', 'email@gmail.com') ->limit(10) ->random() ->get();
whereColumn
- Takes three parameter
columnoperatorcolumn2
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->whereColumn('amount', 'tax') ->whereColumn('amount', '<=', 'balance') ->get();
whereNull
- Takes one parameter
column
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->whereNull('email_status') ->get();
whereNotNull
Read more...
- Takes one parameter
column
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->whereNotNull('email_status') ->get();
whereBetween
- Takes two parameter
columnas stringparamas array- Doesn't support float value
| param | Data types | Value |
|---|---|---|
| column | string | column_name |
| param | array | [10, 100] |
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->whereBetween('amount', [0, 100]) ->get();
whereNotBetween
Read more...
- Same as
whereBetween()method
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->whereNotBetween('amount', [0, 100]) ->get();
whereIn
- Takes two parameter
columnas stringparamas array- Doesn't support float value
| param | Data types | Value |
|---|---|---|
| column | string | column_name |
| param | array | [0, 20, 80] |
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->whereIn('amount', [10, 20, 40, 100]) ->get();
whereNotIn
Read more...
Same as whereIn() method
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->whereNotIn('amount', [10, 20, 40, 100]) ->get();
groupBy
- Takes one param
$column
DB::table('wallet') ->where('user_id', 10000001) ->groupBy('amount') ->get();
Database Migration
- Similar to Laravel DB Migration
Just to make database table creation more easier
| method name | Returns |
|---|---|
| create() | Create table schema |
| run() | Begin migration |
| drop() | Drop migration tables |
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Migrations\Migration;
Create Table Schema
- Takes param as string
$table- [optional] Second parameter
stringjobs|sessionsIf passed will create a dummyjobs|sessionstable schema - It's helper class can be called, using --
migration()
- [optional] Second parameter
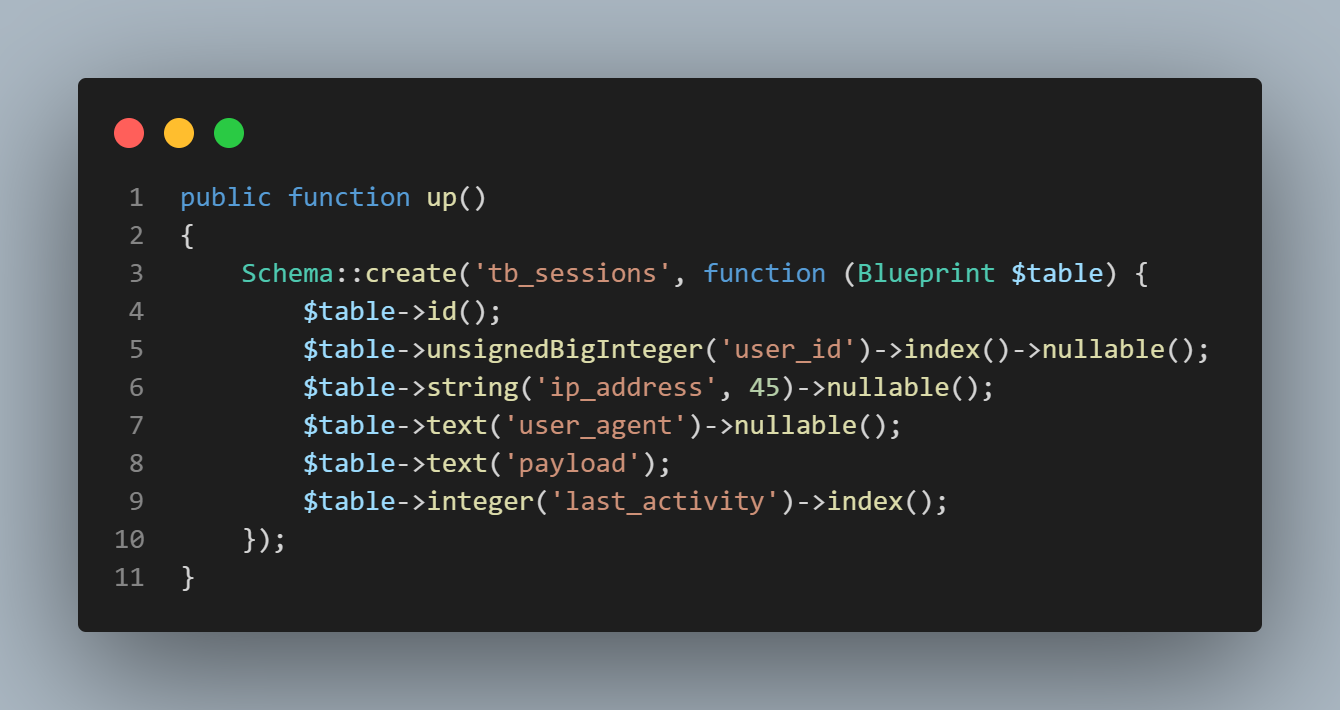
Migration::create('users'); Migration::create('users_wallet'); Migration::create('tb_jobs', 'jobs'); Migration::create('tb_sessions', 'sessions'); // migration()->create('users'); // Table `2023_04_19_1681860618_user` has been created successfully // Table `2023_04_19_1681860618_user_wallet` has been created successfully // Table `2023_04_19_1681860618_tb_jobs` has been created successfully // Table `2023_04_19_1681860618_tb_sessions` has been created successfully
Default String Length
- In some cases you may want to setup default string legnth to all Migration Tables
- It's helper class can be called, using --
schema()
- It's helper class can be called, using --
| Description |
|---|
The Default Set is 255 But you can override by setting custom value |
According to MySql v:5.0.0 Maximum allowed legnth is 4096 chars |
| If provided length is more than that, then we'll revert to default as the above |
This affects only VACHAR |
| You must define this before start using the migrations |
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Migrations\Schema; Schema::defaultStringLength(200); // schema()->defaultStringLength(2000);
Update Column Default Value
- In some cases you may want to update the default column value
- Yes! It's very much possible with the help of Schema. Takes three (3) params
$tablenameas string$column_nameas string$valuesas mixed dataNULLNOT NULL\|NoneSTRINGcurrent_timestamp()
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Migrations\Schema; Schema::updateColumnDefaultValue('users_table', 'email_column', 'NOT NULL'); Schema::updateColumnDefaultValue('users_table', 'gender_column', []); // or // schema()->updateColumnDefaultValue('users_table', 'gender_column', []);
Run Migration
- This will execute and run migrations using files located at [root/database/migrations]
Migration::run(); or migration()->run(); // Migration runned successfully on `2023_04_19_1681860618_user` // Migration runned successfully on `2023_04_19_1681860618_user_wallet`
Drop Migration
Read more...
- Be careful as this will execute and drop all files table
located in the migration - [optional param]
boolto force delete of tables
Migration::drop(); or migration()->drop(true);
Drop Table
Read more...
- Takes one param as
string$table_name
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Migrations\Schema; Schema::dropTable('table_name'); or schema()->dropTable('table_name');
Drop Column
Read more...
- To Drop Column
takes two param- This will drop the column available
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Migrations\Schema; Schema::dropColumn('table_name', 'column_name'); or schema()->dropColumn('table_name', 'column_name');
Get Database Config
$db->getConfig()
Get Database Connection
- It's helper class can be called, using --
db_connection()
$db->dbConnection()
Get Database Name
$db->getDatabaseName()
Get Database PDO
$db->getPDO()
Get Database TablePrefix
$db->getTablePrefix()
Database Import
- You can use this class to import
.sqlinto a database programatically- Take two param as
[$path|$connection] - Mandatory
$pathas string of path to .sql file - [optional]
$connectiondefine the connection of database you want to run
- Take two param as
use Tamedevelopers\Database\DBImport; $database = new DBImport('path_to/orm.sql', 'connName'); // new DBImport(base_path('path_to/orm.sql')) // run the method $status = $database->run(); // - Status code // ->status == 404 (Failed to read file or File does'nt exists // ->status == 400 (Query to database error // ->status == 200 (Success importing to database
Update Env Variable
- You can use this class to import .sql into a database programatically
| Params | Description |
|---|---|
| key | ENV key |
| value | ENV value |
| allow_quote | true | false - Default is true (Allow quotes within value) |
| allow_space | true | false - Default is false (Allow space between key and value) |
use Tamedevelopers\Support\Env; Env::updateENV('DB_PASSWORD', 'newPassword'); Env::updateENV('APP_DEBUG', false); Env::updateENV('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8', false); // env_update('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8', false); // Returns - Boolean // true|false
Collation And Charset
- Collation and Charset Data
listing
Collation
- utf8_bin
- utf8_general_ci
- utf8mb4_bin
- utf8mb4_unicode_ci
- utf8mb4_general_ci
- latin1_bin
- latin1_general_ci
Charset
- utf8
- utf8mb4
- latin1
Extend Model Class
Read more...
- You can as well extends the DB Model class directly from other class
use Tamedevelopers\Database\Model; class Post extends Model{ // define your custom model table name protected $table = 'posts'; // -- You now have access to the DB public instances public function getPost(){ return $this->select(['images', 'title', 'description'])->get(); } }
Helpers Functions
| function name | Description |
|---|---|
| db() | Return instance of new DB($options) class |
| db_connection() | Same as $db->dbConnection() |
| config_pagination() | Same as $db->configPagination() or AutoLoader::configPagination |
| autoloader_start() | Same as AutoLoader::start() |
| env_update() | Same as Env::updateENV method |
| app_manager() | Return instance of (new AppManager) class |
| import() | Return instance of (new DBImport)->import() method |
| migration() | Return instance of (new Migration) class |
| schema() | Return instance of (new Schema) class |
Error Dump
| function | Description |
|---|---|
| dump | Dump Data |
| dd | Dump and Die |
Error Status
- On error returns
404status code - On success returns
200status code
Useful Links
- @author Fredrick Peterson (Tame Developers)
- If you love this PHP Library, you can Buy Tame Developers a coffee
- Lightweight - PHP ORM Database
- Support - Library