eftec / validationone
It's a php library for fetch and validate fields
Requires
- php: ^7.4 || ^8.0
- ext-ctype: *
- ext-fileinfo: *
- ext-json: *
- eftec/messagecontainer: ^2.9
Requires (Dev)
- phpunit/phpunit: ^8.5.13
Suggests
- eftec/formone: Allows to create form and integrates with the validation
README
It's a PHP library for fetches and validate fields and store messages in different containers(including error, warning, info , and success) depending on the conditions.
The ideology behind this library is simple: 3 classes, a simple dependencies and runs in PHP 7.1 and higher, so it could run in practically any PHP project, including WordPress, Laravel, core PHP project, etc.
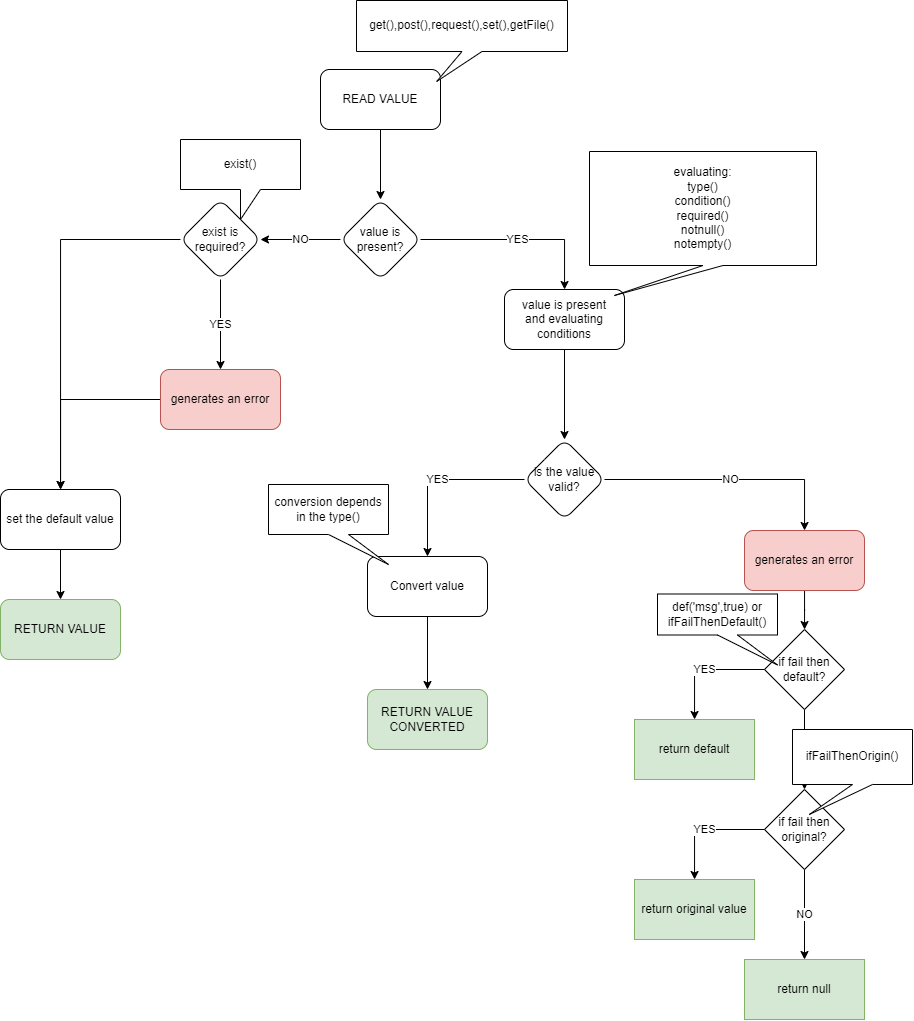
Full Diagram
Table of contents
- ValidationOne
Examples
Tutorial Form and Table with PHP
It is an example of functionality. A typical example is more complex, even if it's only a few lines of code.
Concept
Let's say we want to validate a value an input value (get) called "id", we could do the next things:
- The default value is the text "ERROR"
- the type of the value is an integer, so it just returns an integer. It also could be an integer, decimal, string, date,datestring and boolean
- we add a condition, the value must be equals (eq) to 10. If it fails, then it returns a message (as error)
- we add another condition if the value must be equals (eq) to 30. If it fails, then it returns an info (not an error)
- If the operation fails, then it returns the default value.
- And finally, we obtain the "id" from $_GET (parameter URL).
use eftec\ValidationOne; $val=new ValidationOne(); $r = $val->def('ERROR') ->type('integer') ->ifMissingThenDefault() ->condition("eq", "It's not equals to 10", 10) ->condition("eq", "It's not equals to 30 (info)", 30, 'info') ->ifFailThenDefault() ->get('id'); // <-- end of the chain
But where is the error?. The messages are stored in messageList
var_dump($val->messageList->allArray()); // here we show all messages of any kind of type. var_dump($val->messageList->errorCount); // returns the number of errors. var_dump($val->errorcount()); // returns the number of errors (alternative) var_dump($val->hasError()); // returns true if there is an error.
However, we could also show a message by type (error, warning..) and only message by a specific identifier.
var_dump($val->messageList->get('id')->allErrorOrWarning()); // All error or warning contained in the key "id".
Why the messages are store in some structure?. Is it not easy to simply return the error?
An answer is a form. Let's say we have a form with three fields. If one of them fails, then the error must be visible for each field separately. Also, the whole form could have its own message.
Starting the chain
The start of the chain usually it is written at the end of the code.
The methods allowed are:
- get(): it reads a value from $_GET
- post(): it reads a value from $_POST
- request(): It reads a value from $_REQUEST
- getFile(). It reads a value from$_FILES
- set(): it reads a value entered manually (a variable or constant)
Example:
$val=new ValidationOne(); $id = $val->type('integer')->get('id'); $id = $val->type('integer')->post('id'); $id = $val->type('integer')->request('id'); $id = $val->type('integer')->set('123','id'); $val=new ValidationOne(); $id = $val->type('integer')->get('id'); // $_GET['id'] $val=new ValidationOne('frm'); // we set a prefix for every reading. $id = $val->type('integer')->get('id'); // $_GET['frm_id']
Adding a new condition
condition ($condition, $message = "", $conditionValue = null, $level = 'error', $key = null)
It adds a condition that it depends on the type of the input.
-
@param string $condition
number:req,eq,ne,gt,lt,gte,lte,between,null,notnull
string:req,eq,ne,minlen,maxlen,betweenlen,null,notnull,contain,notcontain ,alpha,alphanum,text,regexp,email,url,domain
date:req,eq,ne,gt,lt,gte,lte,between
datestring:req,eq,ne,gt,lt,gte,lte,between
boolean:req,eq,ne,true,false
file:minsize,maxsize,req,image,doc,compression,architecture,ext
function:
fn.static.Class.methodstatic
fn.global.function
fn.object.Class.method where object is a global $object
fn.class.Class.method
fn.class.\namespace\Class.method -
@param string $message
Message could use the next variables '%field','%realfield','%value','%comp','%first','%second'
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| %field | name of the field, it could be the friendid or the actual name | CustomerID |
| %realfield | name of the field (not the friendid) | Customer Identifier |
| %value | current value of the field | John |
| %comp | value to compare (if any) | |
| %first | first value to compare (if the compare value is an array) | |
| %second | second value to compare (if the compare value is an array) | |
| %key | key used (for input array) |
-
@param null $conditionValue
-
@param string $level (error,warning,info,success). The level of the error. See MessageContainer for further information
-
@param string $key If the key is not null then it is used to add more than one condition by key
-
@return ValidationOne
Note: if the value is null and isNullValid() is true, then the conditions are ignored. If the value is missing and isMissingValid() is true, then the conditions are ignored. If the value is empty ('') and isEmptyValid() is true, then the conditions are ignored. If the value is empty ('') or null and isNullOrEmptyValid() is true, then the conditions are ignored. isNullValid(),isMissingValid(),isNullOrEmptyValid() and isEmptyValid() are useful when we want to validate a value only if it exists or if the value is set.
Example:
$validation->def(null) ->type('integer') ->condition('eq','%field %value is not equal to %comp ',50) ->condition('eq','%field %value is not equal to %comp ',60) ->set('aaa','variable2');
types
| type | description |
|---|---|
| integer | (numeric) it allows a number without decimal |
| unixtime | (numeric) it allows a number without decimal |
| boolean | (boolean) it stores true or false. The input could vary (empty, zero or null = false, otherwise true) |
| decimal | (numeric) it allows a number with decimal |
| float | (numeric) it allows a number with decimal |
| varchar | (string) it allows any input |
| string | (string) it allows any input |
| date | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as an object DateTime |
| datetime | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as an object DateTime |
| datestring | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as a string |
| datetimestring | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as a string |
| file | (file) the input is a string, and it's store as a string, but it adds special validation |
Type of conditions per type of input.
| Input type | Condition | |
|---|---|---|
| number | gt,lt,gte,lte,between | |
| string | minlen,maxlen,betweenlen,contain ,notcontain,alpha,alphanum,text,regexp,email,url,domain |
|
| date | gt,lt,gte,lte,between | |
| datestring | gt,lt,gte,lte,between | |
| boolean | true,false | |
| file | minsize,maxsize,req,image,doc,compression,architecture,ext | |
| * (it applies for any type) | req,eq,ne,null,notnull,empty,notempty | |
| * | function | |
| * | fn.static.Class.methodstatic | |
| * | fn.global.function | |
| * | fn.object.Class.method where object is a global $object | |
| * | fn.class.Class.method | |
| * | fn.class.\namespace\Class.method |
Types of Conditions.
| Condition | Description | Value Example |
|---|---|---|
| architecture | The extension of the file must be an architecture file (dwg, etc.) | |
| between | The number must be between two values | [0,20] |
| betweenlen | The length of the text must be between two values | [0,20] |
| compression | The extension of the file must be an compression file | |
| contain | The text must contain a value | "text" |
| doc | The extension of the file must be a document file | |
| eq (it could be an array or value) / == | The value must be equals to The value must be contained in a array |
"text",["text","text2"] |
| exist | The file or value must exist (it could be null/empty) | |
| missing / notexist | The file or value must not exists or be null/empty | |
| required (or req) | The value must not be null or empty | |
| ext | The extension (file) must be in the list of extensions | ["ext1","ext2","ext3"] |
| false | The value must be false (===false) | |
| fn.class.\namespace\Class.method | The method of a class must returns true | |
| fn.class.Class.method | The method of a class must returns true | |
| fn.global.function | The global function must returns true | |
| fn.object.Class.method where object is a global $object | The method of a global object must returns true | |
| fn.static.Class.methodstatic | The static method of a class must returns true | |
| function | The function must returns true | |
| gt / > | The value must be greater than | 123 |
| gte / >= | The value must be greater or equal than | 123 |
| image | The extension of the file must be an image file | |
| lt / < | The value must be less than | 123 |
| lte / <= | The value must be less or equal than | 123 |
| maxlen | The maximum length of a string | 123 |
| maxsize | The maximum size of a file | 123 |
| minlen | The minimum length of a string | 123 |
| minsize | The minimum size of a file | 123 |
| mime (the value to compare could be an string or array) | The mime type of a file | "application/msword" or ["application/msword","image/gif"] |
| mimetype | The mime type (without subtype) of a file | "application" or ["application,"image"] |
| ne / != (the value to compare could be an single value or array) | The value must not be equals. Or the value must not be contained in a array |
123,[123,345],["aa","bb"] |
| notcontain | The value must not contain a value | "text" |
| notnull | The value must not be null | |
| null | The value must be null | |
| empty | The value must be empty (i.e. "",0,null) | |
| notempty | The value must not be empty (i.e. not equals to "",0,null) | |
| req | The value must exists | |
| true | The value must be true (===true) |
Examples:
$validation->def(null) ->type('integer') ->condition('eq','%field %value is not equal to %comp ',50) ->condition('between','%field %value must be between 1 and 50 ',[1,50]) ->condition('eq','%field %value is not equal to %comp ',60) ->condition('eq','%field %value is not equal to %comp ',[60,200]) // eq allows a single or array ->condition('fn.static.Example.customval','the function does not work') ->condition('req') ->condition('lt',"es muy grande",2000,'warning') ->condition('eq','%field %value is not equal to %comp',50) ->condition('fn.static.Example.fnstatic','the static function does not work') ->condition('fn.static.\somespace\Someclass.methodStatic',null) ->condition('fn.global.customval','The global function does not work') ->condition('fn.object.example.fnnostatic','the function object does not work') ->condition('fn.class.\somespace\Someclass.method','The function some class does not work') ->condition('fn.class.Example.fnnostatic','la funcion class no funciona'); // ->condition('fn.static.Example.customval','la funcion no funciona') function customval($value,$compareValue) { return true; }
Calling a custom function
Sometimes we need to use a custom condition. We could create a global variable, a static function, or even a method
inside a class.
Every method or function created must have two parameters (with any name):
- $value The value to evaluate.
- $compareValue The value to compare (it could be optional)
For example, what if we need to evaluate if some id does not exist in the Database?
$validation->condition('fn.global.idExist','The id already exist!')->get("id"); function idExist($id,$compare=null) { // select count(*) c from table where id=$id if($c>0) { return true; } else { return false; } }
Note: if we need to specify a namespace, then we could use the notation: \namespace\SomeClass
$validation->condition('fn.global.customfn'); // global $validation->condition('fn.static.SomeClass.staticfn'); // calling a static method inside the class SomeClass. $validation->condition('fn.class.SomeClass.noStaticFn'); // method inside a class,it creates an instance of an object then it calls the method $validation->condition('fn.object.myObject.noStaticFn'); // method inside a class, it uses an instance called $myObject // global function function customfn($value,$compareValue) { // returns true or false } // static function $myObject=new SomeClass(); class SomeClass { public static function staticfn($value,$compareValue) { // returns true or false } public function noStaticFn($value,$compareValue) { // returns true or false } }
Getting the messages
When we validate an object, it could store the information inside the Message Container (also called Message List).
MessageContainer (EFTEC/MessageContainer) contains a list messages in a hierarchy way:
⭐ Container (usually only 1 for all the project) ⭐ Lockers (from zero to many) ⭐ Messages (from zero to many and grouped by level) $container->get('locker20')->firstError(); // it returns the first message of error in the locker20 that is part of the container.
Messages are leveled as follows
| id | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| error | The message is an error, and it must be solved. It is our show stopper. | Database is down |
| warning | The message is a warning that maybe it could be ignored. However, the class MessageContainer allows to group Error and Warning as the same. | The registry was stored but with warnings |
| info | The message is information. For example, to log or debug an operation. | Log is stored |
| success | The message is a successful operation | Order Accepted |
How to manage to the messages?
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| addMessage($idLocker, $message, $level = 'error') | It adds a message inside a locker. Usually, it is done automatically by the library but you can add messages manually via code. |
$this->addMessage('pwd','the password is required','error'); |
| getMessage($withWarning = false) | It gets the first error message or empty if none | $this->getMessage(); |
| getMessages($withWarning = false) | It gets all the error messages or empty if none | $this->getMessages(); |
| getMessageId($idLocker) | It gets a MessageLocker object (see EFTEC/MessageContainer for more information) | $obj=$this->getMessageId('pwd'); |
| errorCount(includeWarning=false) | It gets the error count | $count=$this->errorCount(); |
| hasError($includeWarning=false) | It returns true if there is an error | $fail=$this->hasError(); |
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| $messageList | It gets all the container. It returns an object of the type MessageContainer | $container=$this->messageList; |
You can see more information about MessageContainer in EFTEC/MessageContainer
Example:
$validation->addMessage('idlocker','this field is required','error'); // it adds a message inside a locker. $validation->messageList->get('idlocker')->allError(); // it gets all errors from the locker idlocker $validation->getMessages(true); // it gets all messages of error or warning from all the lockers.
Working with dates
We also could work with dates. There are several types of date formats.
| type | description |
|---|---|
| date | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as an object DateTime |
| datetime | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as an object DateTime |
| datestring | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as a string using the field $dateOutputString |
| datetimestring | (date) the input could be a DateTime or a string. The value is stored as a string using the field $dateLongOutputString |
There are two ways to specify the format of dates, short (Date only) and long (date and time). And we could specify the format as input and output.
| Name Field | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| $dateShort | It is the (expected) input format for date (short) | d/m/Y |
| $dateLong | It is the (expected) input format (with date and time) | d/m/Y H:i:s |
| $dateOutputString | It is the output format (for datestring) | Y-m-d |
| $dateLongOutputString | It is the output format (for datetimestring) | Y-m-d\TH:i:s\Z |
$r=getVal()->type('datestring')->set('31-12-2019'); // 2019-12-31 note: the default input value is d/m/Y, not m/d/Y
We can change the date format by changing the fields or calling the next functions
setDateFormat
Setting the format of the dates (input short, input long, output short and output long)
$validation->setDateFormat('m/d/Y', 'm/d/Y H:i:s', 'Y-m-d', 'Y-m-d\TH:i:s\Z')
setDateFormatDefault
We set the format of the dates to the default configuration
$validation->setDateFormatDefault();
setDateFormatEnglish
We set the format to the dates to :
| Name | Format |
|---|---|
| input short | m/d/Y |
| input long | m/d/Y H:i:s |
| output short | Y-m-d |
| output long | Y-m-d\TH:i:s\Z |
$validation->setDateFormatEnglish()
Generating exceptions
By default, this library does not generate exceptions. However, it is possible to generate exceptions if the message is of the type ERROR and/or WARNING.
throwOnError()
With this method, if the container generates an error, then it is stored also generates a new exception.
Note: By default, most messages are of the type ERROR.
Note: When the operator is throw, then the value is not assigned and the stack is deleted, i.e. if we throw an exception, all the information is lost.
try { $validation->type('integer') ->throwOnError() // for errors only ->set('hello', 'field1'); // or you could use: $validation->type('integer') ->throwOnError(true,true) // for errors and warnings ->set('hello', 'field1'); $this->fail('this value means the throw failed'); } catch(\Exception $ex) { $this->assertEquals('field1 is not numeric',$ex->getMessage()); }
Dealing with missing or empty values
There are four different ways to deal with empty values in this library.
exist
- A value exist if the field or file exists, no matter the value or if it is null or empty.
- if exist() is set and the value is missing, then it raise an error.
$validation->exist()->set(null); // is valid. $validation->exist()->set(''); // is valid. $validation->exist()->get('field'); // is valid only if $_GET['field'] exist (even if it is null)
required
- A value is required if the field is not null or empty. Required is equals that null and empty at the same time
$validation->required()->set(null); // is not valid. $validation->required()->set(""); // is not valid. $validation->required()->set('hi'); // is valid.
notnull
- A value is not null if the field is not null, but it could be empty ("").
$validation->notnull()->set(null); // is not valid. $validation->notnull()->set(""); // is valid. $validation->notnull()->set('hi'); // is valid.
notempty
- A value is not empty if the field is not '' (string with length 0), but it could be null.
$validation->notempty()->set(null); // is valid. $validation->notempty()->set(""); // is not valid. $validation->notempty()->set('hi'); // is valid.
Allowing missing or empty values
Also, there are 4 ways to accept missing values, null or empty, bypassing any condition.
$validation->isNullValid()->condition(....)->set(null); // is valid no matter the condition. $validation->isNullorEmptyValid()->condition(....)->set(null); // is valid no matter the condition. $validation->isEmptyValid()->condition(....)->set(''); // is valid no matter the condition. $validation->isMissingValid()->condition(....)->get('field'); // If the field is missing, then is valid no matter the condition
It is used when we need to validate when an input has some value unless the value is missing, empty or null.
isNullorEmptyValid() is equals than to call: isEmptyValid()->isNullValid()
Also, those operators could be stacked.
$validation ->isNullorEmptyValid() ->isMissingValid() ->condition(....) ->set(....); // this expression is valid if the value is null, empty(''), the value is missing, no matter the conditions.
Processing the result
def()
We could set a default value. This value could be as fallback when there is an error. The default value is never converted or processed.
$validation ->def(-1) ->type('integer') ->ifFailThenDefault() ->set(...); // if the operation fails, then it returns -1
trim()
Trim the result. By default, the result is not trimmed. You can trim the left, right or both sides. It uses the method convert() to do the operation.
$validation->trim()->set(....); // trim both sided $validation->trim('trim','.,')->set(....); // trim . and , $validation->trim('ltrim')->set(....); // trim left sided $validation->trim('rtrim')->set(....); // trim right sided
alwaysTrim()
Sometimes, we always want to trim the results. So we could use this method to always trim the result. It stacks at the end of the conversion.
$validation->alwaysTrim(); // always trim the next characters " \t\n\r\0\x0B" $validation->alwaysTrim(true,",."); // always trim , and . // ... $validation->alwaysTrim(false); // we disable the always trim.
isArray()
If we want to fetch an array, then we could use the next method
$array=$validation->isArray()->request('id');
It also validates every value. However, it stores the messages in a single container.
If we want to store every message separately, then we could use:
$array=$validation->isArray(true)->request('id');
Example of array
<form> <input type='text' name='field[col1][0]' value="cocacola" /> <input type='text' name='field[col2][0]' value="123" /><br> <input type='text' name='field[col1][1]' value="fanta" /> <input type='text' name='field[col2][1]' value="123" /><br> <input type="submit"><br> </form>
Note: You could also define the fields as 'field[0][col1]' so you won't need to invert the array
$values=getVal()->isArray(true)->request('field'); // ['col1'=>['cocacola','fanta'],'col2'=>[123,123]] ValidationOne::invertArray($values); // // [['col1'=>'cocacola','col2'=>123],['col1'=>'fanta','col2'=>123]]
invertArray()
If the value is an array but the indexes of the columns are inverted with the columns, then you can invert the order
example:
$arr=['col1'=>['cocacola','fanta'],'col2'=>[1,2]]; ValidationOne::invertArray($arr); // [['col1'=>'cocacola','col2'=>1],['col1'=>'fanta','col2'=>2]] ''' ### convert() It converts the end result after it is validated. Depending on the type of conversion, it allows up to 2 arguments. The conversion could be stacked so the order could matter. If the value is missing, or it is used the default value, then it is not converted. | Type | | Description | Example | |-------------------|-----|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | upper | | Converts the value in uppercase | $this->conversion('upper')->set('Hello World'); // HELLO WORLD | | lower | | Converts the value in lowercase | $this->conversion('lower')->set('Hello World'); // hello world | | ucfirst | | Converts the first character in uppercase | $this->conversion('ucfirst')->set('hello world'); // Hello world | | ucwords | | Converts the first character in a word in uppercase | $this->conversion('ucwords')->set('hello world'); // Hello World | | replace | | Replace a string by other | $this->conversion('replace','hello','world')->set('hello hello'); // world world | | sanitizer | | Sanitizer the result. It uses filter_var() | $this->conversion('sanitizer',FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL)->set('//aaa@bb.com'); // aaa@bb.com<br />$this->conversion('sanitizer',FILTER_SANITIZE_SPECIAL_CHARS,FILTER_FLAG_STRIP_HIGH) | | alphanumeric | | Sanitize the result by keeping the alphanumeric characters plus underscore : | this->conversion('alphanumeric')->set('HELLO world_-123'); // HELLOworld_123 | | alphanumericminus | | Sanitize the result by keeping the alphanumeric characters plus underscore and minus symbol | this->conversion('alphanumericminus')->set('HELLO world_-123'); // HELLOworld_-123 | | regexp | | It calls preg_replace to replace a text | this->conversion('regexp','/[/^0-9]/','')->set('hello123'); // 123 | | rtrim | | Trim the right characters | $this->conversion('rtrim') | | ltrim | | Trim the left characters | $this->conversion('ltrim') | | trim | | Trim the right and left. It is equivalent to $this->trim() | $this->conversion('trim')->set(' hello '); // hello<br />$this->conversion('trim'," \t\n\r\0\x0B") | | htmlencode | | Encode to html content. It uses htmlentities() | $this->conversion('htmlencode')->set('\<b>dog\</b>'); //\<b\>dog\< | | htmldecode | | Decode from a html. It uses html_entity_decode() | $this->conversion('htmldecode')->set('\<b\>dog\<'); // \<b>dog\</b> | ```php $validation ->convert('replace','hello','world') // world world ->convert('upper') // WORLD WORLD ->set('hello hello'); // stacking an operator. $validation->convert('upper')->set(....); $validation->convert('lower')->set(....); $validation->convert('ucfirst')->set(....); $validation->convert('ucwords')->set(....); $validation->convert('replace','hello','world')->set(....); // trim right sided $validation->convert('sanitizer',FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL)->set(....); $validation->convert('rtrim')->set(....); $validation->convert('ltrim')->set(....); $validation->convert('trim')->set(....); $validation->convert('htmlencode')->set(....); $validation->convert('htmldecode')->set(....);
Version list
- 2024-12-31 2.10
- Updated to PHP 8.4
- 2024-03-02 2.9
- Updating dependency to PHP 7.4. The extended support of PHP 7.2 ended 3 years ago.
- Added more type hinting in the code.
- 2023-11-13 2.8
- some maintenance code.
- 2023-02-26 2.7
- added a new argument for isArray()
- added the static method invertArray()
- 2023-01-26 2.6
- Some small cleanups.
- 2022-08-27 2.5
- [update] added the validation of arguments for most of the functions of the library.
- 2022-03-11 2.4
- [update] added condition alphanumunder (alphanumeric or underscore).
- 2022-02-05 2.3
- [update] update dependency to MessageContainer 2.3. Now MessageContainer is injected as singleton.
- [update] ValidationOne methods now has type hinting (return values).
- [fix] inputDate() method has some wrong operations. Now, they were removed.
- 2022-02-04 2.2
- [new] support to PHP 8.1. PHP 8.1 is quite tricky, it deprecated a lot of arguments for several functions.
- [new] This library support PHP 7.2 or higher. If you need older functionality, then you can use an old version.
- 2022-01-29 2.1
- [new] method throwOnError()
- 2022-01-29 2.0.2
- fixed a problem when the condition is "gte".
- 2022-01-15 2.0.1
- Update dependency
- 2022-01-15 2.0
- PHP 7.1 and higher.
- [core] Lots of cleanups
- 2021-03-18 1.30.1
- Updated dependency in composer.json
- 2021-03-17 1.30
- We split the library in two, one for the validation (this library) and other for the messages, called eftec/MessageContainer.
- 2021-02-13 1.29
- Added the methods trim(), alwaysTrim(), convert(), errorCount() and hasError() .
- 2021-02-10 1.28
- Added new method isNullOrEmptyValid()
- 2021-02-10 1.27
- Added new methods isMissingValid(), isEmptyValid() and isNulLValid()
- 2021-02-09 1.26
- New validations and methods.
- exist() where the value must exist (but it could be null or empty)
- required() now it validates if the value is not null or empty only. It does not validate if the value exists.
- notempty()
- 2021-01-07 1.25
- PHP 8.0 discontinued the constants INPUT_GET, INPUT_POST and INPUT_REQUEST, so we will use instead the numbers
- INPUT_POST = 0
- INPUT_GET = 1
- INPUT_REQUEST = 99 So, if you are using INPUT_GET,INPUT_POST OR INPUT_REQUEST, then they will still work.
- PHP 8.0 discontinued the constants INPUT_GET, INPUT_POST and INPUT_REQUEST, so we will use instead the numbers
- 2020-10-01 1.24.3
- A small cleanup.
- 2020-05-21 1.24.2
- Fixed a problem with conditions and array (when it is initiated).
- 2020-05-21 1.24.1
- Fixed a problem with conditions and array.
- 2020-05-21 1.24
- Cleanups
- 2020-04-07 1.23.2
- Solved a problem with datetimestring and a defnatural
- 2020-04-07 1.23.1
- Solved a problem with validation and input. It failed to validate.
- Solved a problem where the default value is a string and the type is a datetimestring.
- 2020-02-01 1.23
- Solved a problem in endConversion() when the default value is "" or null (or not a DateTime object), the type is "datetimestring", and the value is missing.
- Practically all methods were tested.
- resetValidation() now allows to delete all messages.
- Fixed the validation "ne"
- 2020-01-04 1.22
- New conditions 'mime','minetype','exist','notexist',etc.
- Condition 'eq' and 'ne' allows a simple or an array of values.
- 2020-01-03 1.21
- ValidationOne::runConditions() now allows (for file type), conditions architecture and compression
- ValidationOne::getFileExtension() now could return the extension as mime
- ValidationOne::getFileMime() new method that returns the mime-type of a file.
- 2019-11-27 1.20
- Fixed the name countErrorOrWaring->countErrorOrWarning
- 2019-11-27 1.19
- Added new field MessageContainer.errorOrWarning
- Added new method MessageLocker.countErrorOrWaring()
- 2019-10.01 1.18 Added compatibility for phpunit/phpunit 5.7 and 6.5
- 2019-10-01 1.17 Fixed a bug. If the input is zero, then it is considered as null.
- 2019-08-10 1.16 Solved a problem with the datestring/datetimestring.
- 2019-08-07 1.15
-
- Added the type datestring and datetimestring. It reads a string, and it converts into another string (as date or datetime)
-
- Code formatted
- 2019-03-08 1.14 Added getFile() to upload a file.
- 2018-12-15 1.13 Added phpunit and travis.
- 2018-10-29 1.12 getFile now it's available via ValidationOne()
- 2018-10-22 1.11 Some fixes. Now isEmpty is called isMissing
- 2018-10-22 1.10 New Features
-
- Added ValidationInputOne, now the fetchs are done by this class (SRP principle)
-
- Added a fix with the input, when the value expected is an array, but it's returned a single value
- 2018-10-15 1.9 Added some extra features
- 2018-10-15 1.8 Some fixes and phpdocs, a new example
- 2018-10-15 1.7 Added method addMessage() in ValidationOne. Now ErrorItem/ErrorList is called MessageLocker and MessageContainer
- 2018-10-06 1.5 added method first() in MessageLocker
- 2018-10-03 1.4 added defaultNatural()
- 2018-10-02 1.3 basicvalidation() was deleted. It was restored.
- 2018-10-02 1.2 array() is now isArray()
- 2018-09-30 1.1 Some fixes
- 2018-09-29 1.0 first version
todo
- More examples
- Documentation
Note
It's distributed as dual license, as LGPL-v3 and commercial.
You can use it freely in your close source project. However, if you change this library, then the changes must be disclosed.