devtools-marvellous / postman-documentation
Package description
Installs: 53
Dependents: 6
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 0
Watchers: 2
Forks: 0
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/devtools-marvellous/postman-documentation
Requires
- laravel/framework: ^10.0
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-11 20:11:07 UTC
README
This package implements powerful postman json exporter in 2.1.1 json version.
Package integrated with amondar/rest-actions right of the box.
NOTE!!! Please, don't use this exporter for none API routes, that will cause problems with session management during exporting.
Installation
To install this package:
- Add to your
composer.json:
{
"repositories": [
{"type": "composer", "url": "https://repo.packagist.com/attractgroup/"}
]
}
- Authenticate your composer to work with private
attractgrouprepo.
composer config --global --auth http-basic.repo.packagist.com ${USER} ${AUTH_TOKEN}
- Then execute:
composer require attract-cores/postman-documentation
After that you can run artisan command:
php artisan export:postman
All created json docs will be saved at /storage/app/public/postman/* directory inside your project.
Configuration
| Setting | Explanation |
|---|---|
filename |
Default file pattern is - {timestamp}_{app}_collection.json. You can change it into what ever you want. Replacement engine can work with: {timestamp}, {app} |
structured |
This flag determine, that json output routes tree should be structured by name\url segments separated via dot(.) |
oauth_route |
Name of the oauth token issuing route. Works in pair with auth_type setting. If your project don't have this kind of route, then set it to NULL |
auth_type |
Type of routes authentication. Works in pair with auth_middleware. Accept: oauth2, token, none. For More information read docs below |
token_placement |
"Add To" postman option value. Can be only header or query. Works only via auth_type=token |
auth_middleware |
The name of auth middleware. If route has this middleware, then exporter apply selected auth_type setting blocks into route json |
client_auth_middleware |
The name of client auth middleware. If route has this middleware, then exporter apply client_credentials grant authorization |
auth_clients |
Array of settings that applied into password or client_credentials grant type authorization |
scopes |
Array of route patterns to determine which scopes should be applied in oauth2 type |
start-user |
Credentials of given user will be used for password grant authorization. After exporting, end user can change this credentials for his user |
headers |
Headers pack, that required for each route |
enable_formdata |
Enable or disable form data generation for each route. Works in pair with factories_path. For More information read docs below |
factories_path |
Path to request form data factories classes |
include_middleware |
Array of base middlewares, that should be added into export. By default, only api middleware used |
disk |
Disk of storage that should be used for json result file store. By default, public driver used |
Authorization types and tricks
Package support several authentication types:
oauth2tokennone
When none type used, result routes will be created with empty auth blocks. That option preferable on old projects with custom authentication system.
When token type used, result routes will be created with simple Api Key authorization option. In that case, end user, after import should place api_key into each route manually.
When oauth2 type used, result routes will be created with OAuth 2.0 authorization option. Depends on middleware settings auth_middleware or client_auth_middleware
will be user password or client_credentials grant types. On some projects can be implemented anonymous authorization.
In at case you can run command with configured auth_type=oauth2 and add --personal-access option.
php artinsan export:postman --personal-access={{user_access_token}}
In that case will be added Bearer Token authorization option to each route.
That trick can be used on old projects, that used passport, but doesn't have opened token route. Just run command as described above without changing.
Form data from form factories
If command ran with enable_formdata=true then you can specify form factory for each route for each request type: POST, PUT, PATCH, GET, DELETE.
By default, all factories should be placed in ./app/Postman directory.
Each factory should be named by a pattern below and extends core factory class, just like a standard model factories in laravel:
${FULL_REQUEST_NAME}Factory.php #For example UserProfileRequestFactory.php
All factories loaded into memory each time, when command dispatched.
Example of factory class looks like below:
<?php namespace App\Postman; use AttractCores\LaravelCoreKit\Http\Requests\UserProfileRequest; use AttractCores\PostmanDocumentation\Factory\FormRequestFactory; use Database\Factories\UserFactory; /** * Class UserProfileRequestFactory * * @package App\Postman * Date: 01.12.2021 * Version: 1.0 */ class UserProfileRequestFactory extends FormRequestFactory { /** * The name of the factory's corresponding form request. * @note Value of the $request property can be request class name or route name, * so you can generate name of the factory as you want. * Example - api.v1.profile.update * Example - UserProfileRequest::class * * @var string|null */ protected ?string $request = UserProfileRequest::class; /** * Define the model's default state. * * @return array */ public function definition() : array { return [ 'email' => $this->faker->email, 'password' => UserFactory::DEFAULT_PASSWORD, 'password_confirmation' => UserFactory::DEFAULT_PASSWORD, 'firebase_token' => NULL, 'name' => $this->faker->name, ]; } }
Each factory has initialized $this->faker instance, just like model factory in laravel.
If you need dedicated form for each type of REST standard request, then you can add, for example,
public function postDefinition() function and add different from default definition() form body.
Route documentation
Package add several hook methods and classed that can help you generate docs for your routes right in Postman Markdown. You can export postman collection without any of below tricks, but to make full documentation for your project you need a little more explanations and descriptions.
Route tricks
| Hook | Explanation |
|---|---|
->aliasedName('My name') |
Works as ->name() function on route, but add humanized name description for the route in Postman |
->getAliasedName() |
Return aliased name of the route. This macro function used in the core of the package. Return NULL if not set. |
->structureDepth(3) |
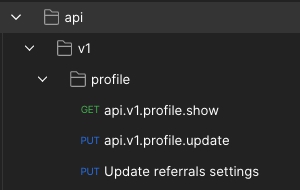
This macro function will set structure depth for given route. For example, you have this routes: api.v1.profile.show, api.v1.profile.update and api.v1.profile.referral-settings.update. If we run export as is, then last route will be added into separate group in structure, cuz it base segments count longer then other profile route. We can use described marco to say tree builder which depth of three on given route we want. In example case it will be ->structureDepth(3) and tree builder will use api.v1.profile as structure base. |
->getStructureDepth() |
Return depth that was set or NULL |
->expands() |
Set documentation block based on Sextant or Filter packages implemented in given model class expands. For example, ->expands(App\Models\User::class, [ 'roles' => [ '*Roles expand for the user*', '*First Example* - ?expand=roles' ], 'zipCode' => 'Zip code expand. Each time requested on referral return distance from current user zip.' ]). As you can see you can add text description for each expand as string or as array if you need nested list |
->scopes() |
Set documentation block based on Sextant or Filter packages implemented in given model class scopes. Can be used same as expands - ->scopes($modelClass, array of descriptions) |
->description() |
Set documentation block based on coder needs. This function accept one parameter: Markdown facade class instance. |
->docPattern() |
Set route documentation pattern. By default this patter set to ->docPattern('description|expands|scopes'). You can change ordering of doc blocks as you wish |
->compileDocs() |
Return compiled Markdown string of route docs. |
Example of usage:
<?php use AttractCores\PostmanDocumentation\PostmanAction; Route::put('profile/referrals-settings', 'Api\ReferralsSettingsController@update') ->name('profile.referrals-settings.update') ->aliasedName('Update referrals settings') ->structureDepth(3) ->expands(App\Models\User::class, [ 'roles' => [ '*Roles expand for the user*', '*First Example* - `?expand=roles`', ], 'zipCode' => 'Zip code expand. Each time requested on referral return distance from current user zip.', ]) ->scopes(App\Models\User::class) ->description( \AttractCores\PostmanDocumentation\Facade\Markdown::heading('Here the new heading') ->line('Some explanation line') ); // OR via resource Route::apiResource('users', 'UserController') ->postman([ 'index' => PostmanAction::fresh() ->aliasedName('Get list of users') ->expands(CoreUserContract::class), 'show' => PostmanAction::fresh() ->aliasedName('Get one user resource') ->expands(CoreUserContract::class), 'store' => PostmanAction::fresh() ->aliasedName('Create new user'), 'update' => PostmanAction::fresh() ->aliasedName('Update existing user'), 'destroy' => PostmanAction::fresh() ->aliasedName('Delete existing user'), ]);
PostmanAction can use same functions as on simple Route to set settings and descriptions on resources.
This example will generate structure as described below:
Documentation will look like:
Markdown
Package implements MarkdownDocs class. That class can easily create markdown syntax with pretty functions structure,
like laravel Email class.
| Function | Explanation |
|---|---|
->heading('My heading', 'h1') |
Create heading element in markdown syntax. Second parameter is optional, by default, it equals to h1. You can set second parameter to: h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6. For example, h5 create heading with five ##### |
->line('My line', 'prefix here') |
Create simple paragraph element. Second parameter is optional. Second parameter accept prefix or the line. For example you want create a quote you can send > symbol into second parameter |
->quote(['First qoute', 'Second quote']) |
Create multiline quotes |
->numericList(['First plan line' => ['First sub plan', 'Second sub plan'], 'Second plan line']) |
Create multi-dimensional numeric list |
->unorderedList(['First plan line' => ['First sub plan', 'Second sub plan'], 'Second plan line']) |
Create multi-dimensional unordered list |
->block('php artisan tinker', 'bash') |
Create language block. First parameter can be used as new MarkdownDocs class instance. String conversion will work automatically |
->link('some_link_or_local_git_path', 'Here is a link') |
Insert link into markdown string |
->image('some_image_link_or_local_git_path', 'Here is an image') |
Insert image into markdown string |
->raw('Some raw markdown string or result of other Markdown class instance') |
Insert given string as is |
You can use ->raw functionality to insert result of another markdown class instance:
Markdown::raw(Markdown::new()->line('Some another configured line'));