capevace / cabinet
Cabinet is a turn-key file management solution for Laravel, that enables attaching files and folders to models, by integrating various file sources into a streamlined API and user interface.
Requires
- php: ^8.0
- ext-fileinfo: *
- illuminate/contracts: ^11.0 || ^10.0
- spatie/laravel-package-tools: ^1.15
README
Laravel Cabinet
Turn-key "Dropbox-like" file management, supporting multiple sources in the same folders
Made by Lukas Mateffy
Cabinet is a turn-key file management solution for Laravel, that enables uploading and managing files, as well as attaching files to models. It integrates various file sources into a streamlined API and user interface (including disks, spatie/media-library, custom database tables, external APIs and anything you can think of, basically).
Note
Cabinet is currently 0.x and considered "unstable". While it's API has not changed in months and is already used in production (domos.de), the API may still be subject to change. Planned release for version 1.0 and thus semver API stability is end of May 2024.
Screenshots
|
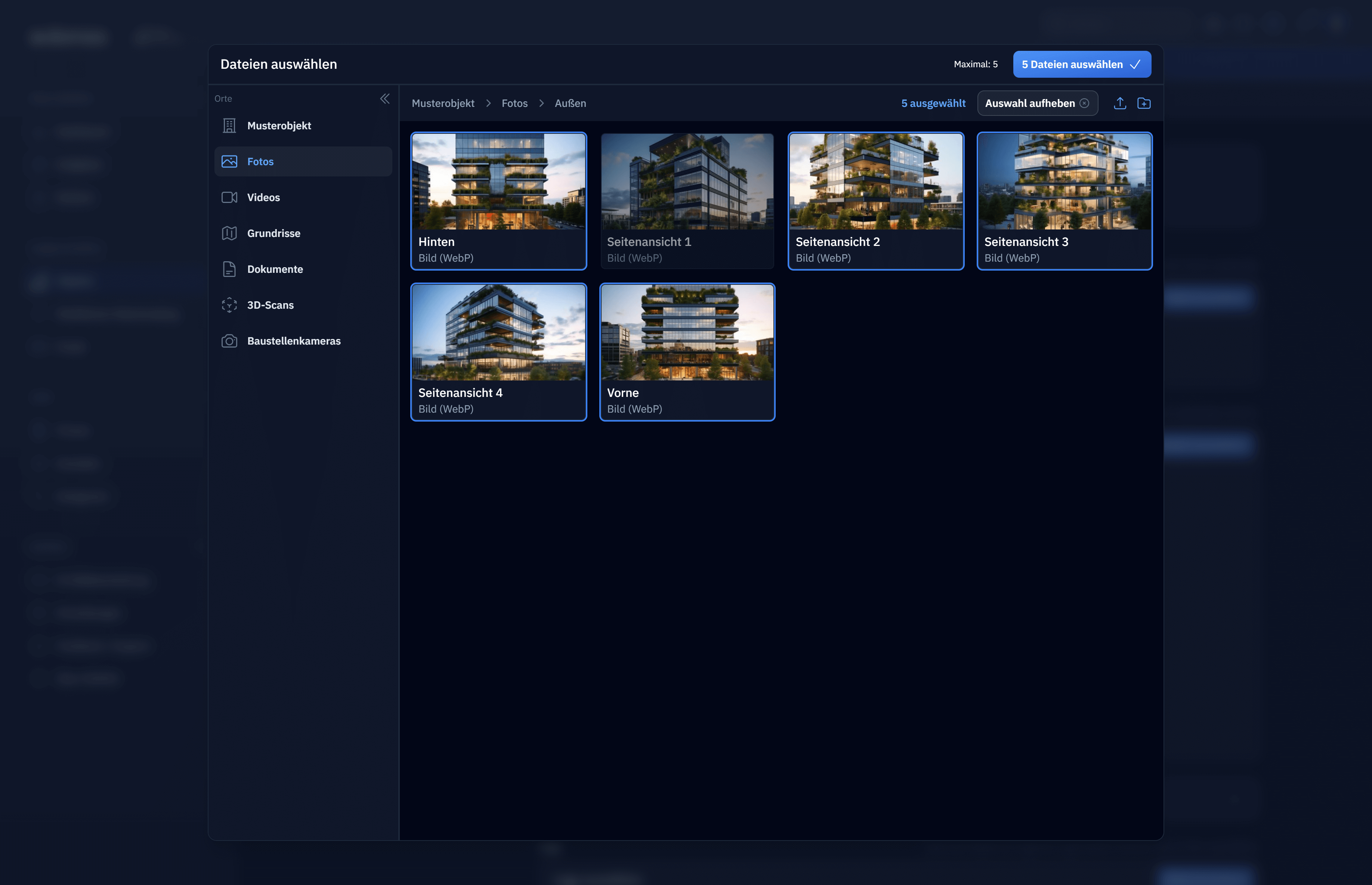
Finder popup to mamage and select filesYour application code just sets some parameters, like what file types are allowed, how many files are selected and what directory to open. |
|
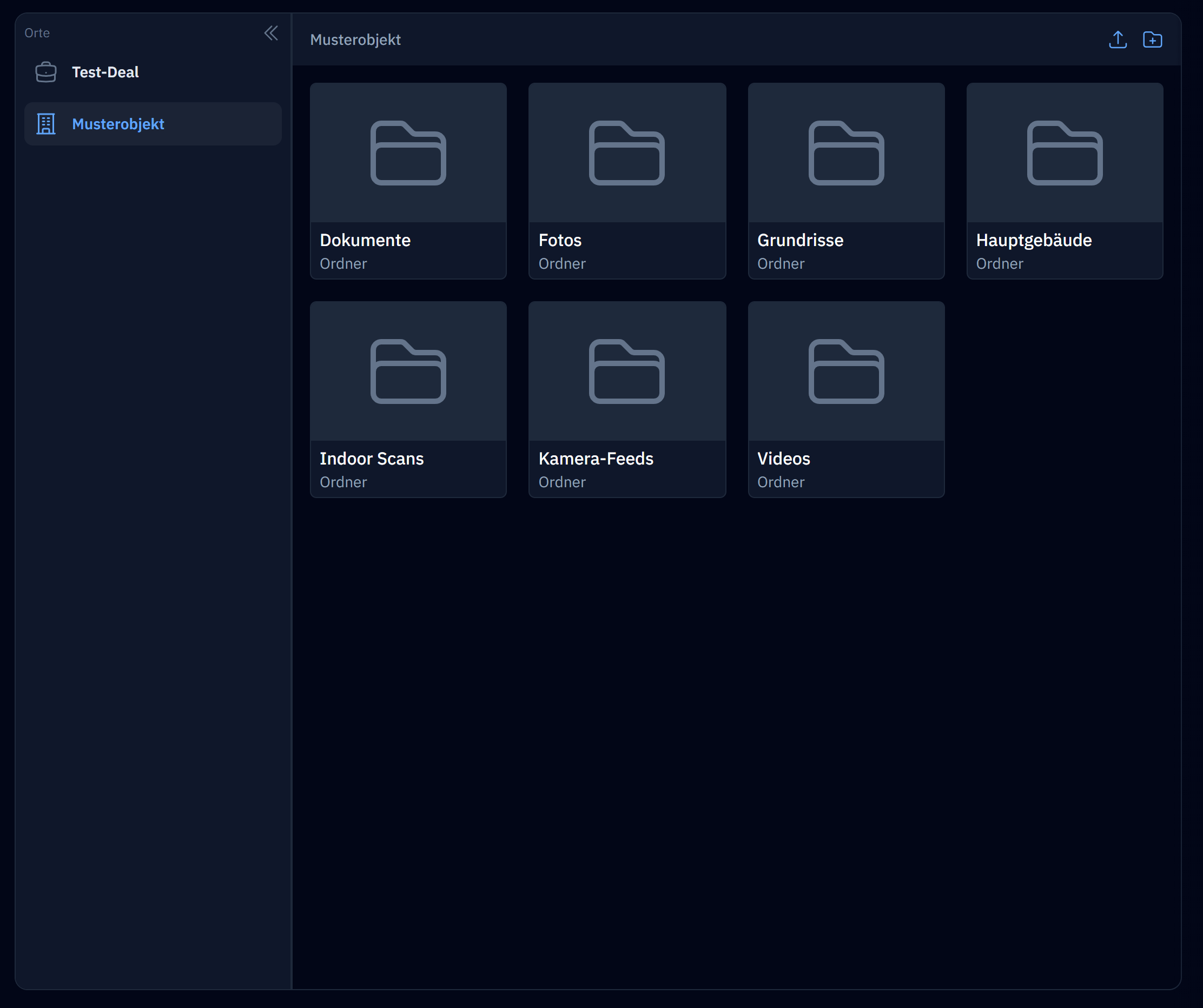
Supports creating and nesting folders and customizing the sidebar |
|
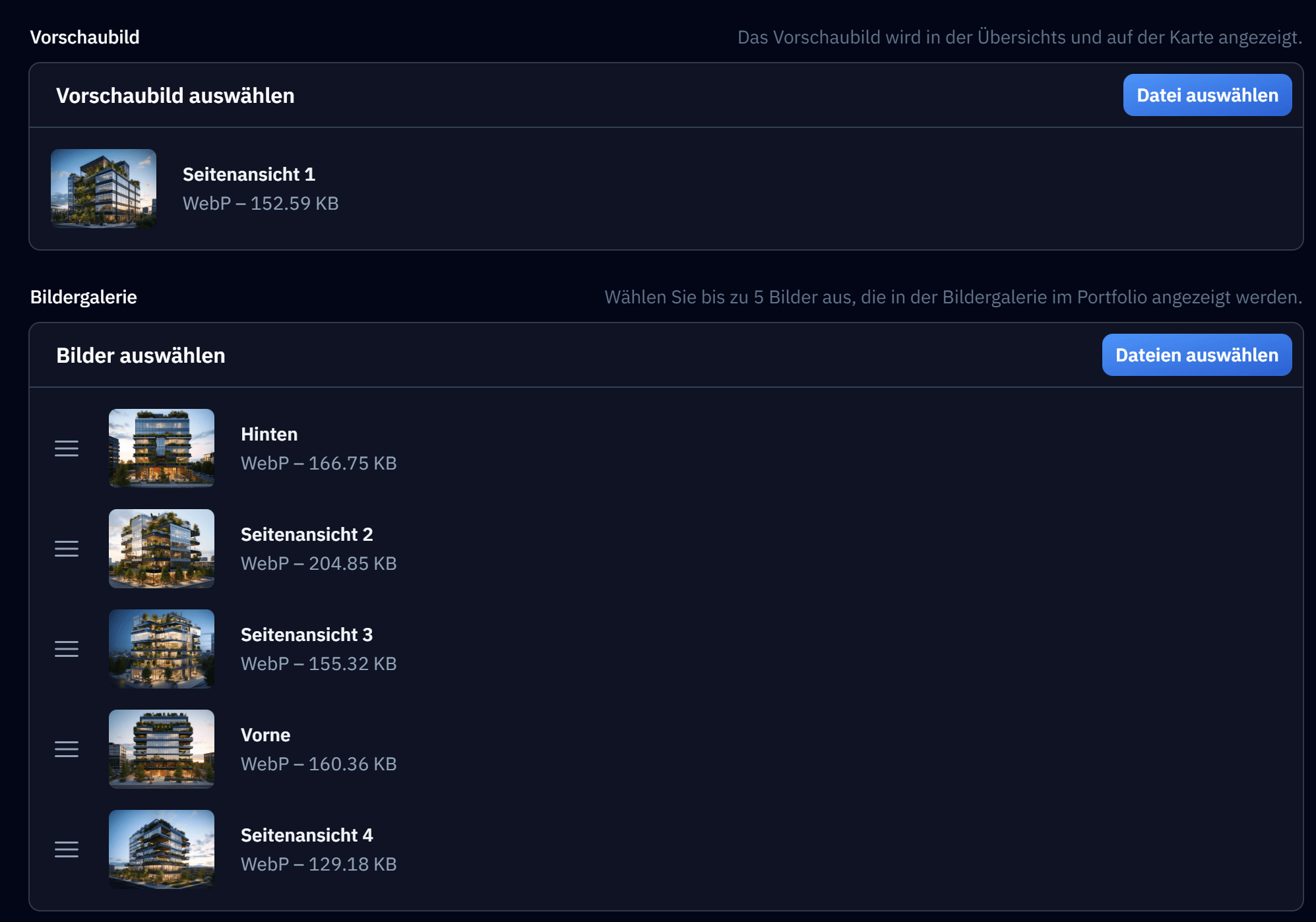
Pre-built file inputs for Filament Forms |
|
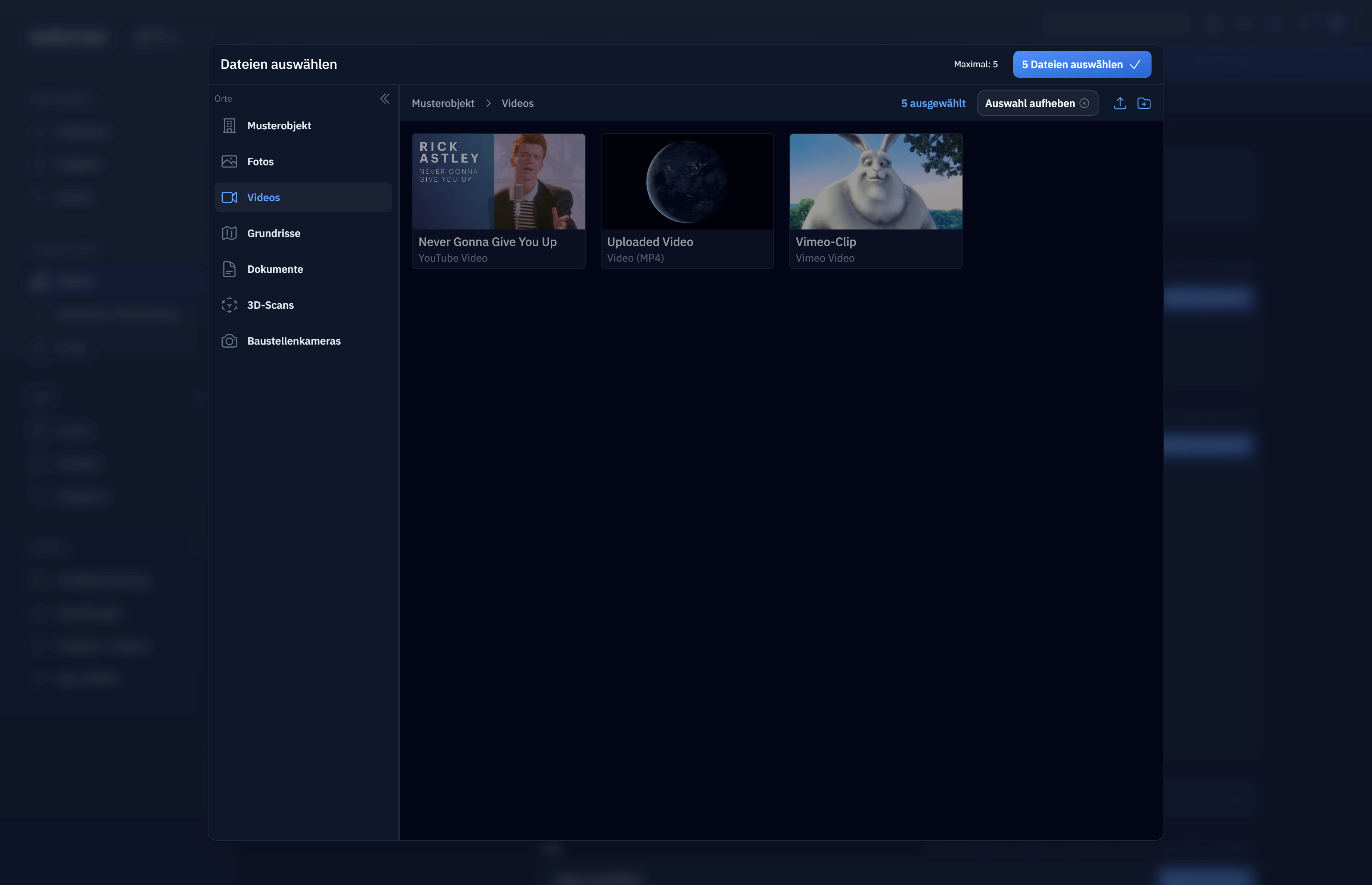
Supports showing multiple file types/sources in the same folder/viewIn this case, we can show an uploaded video (S3) right next to an "uploaded" YouTube/Vimeo video (added by URL). They share the combined file type |
|
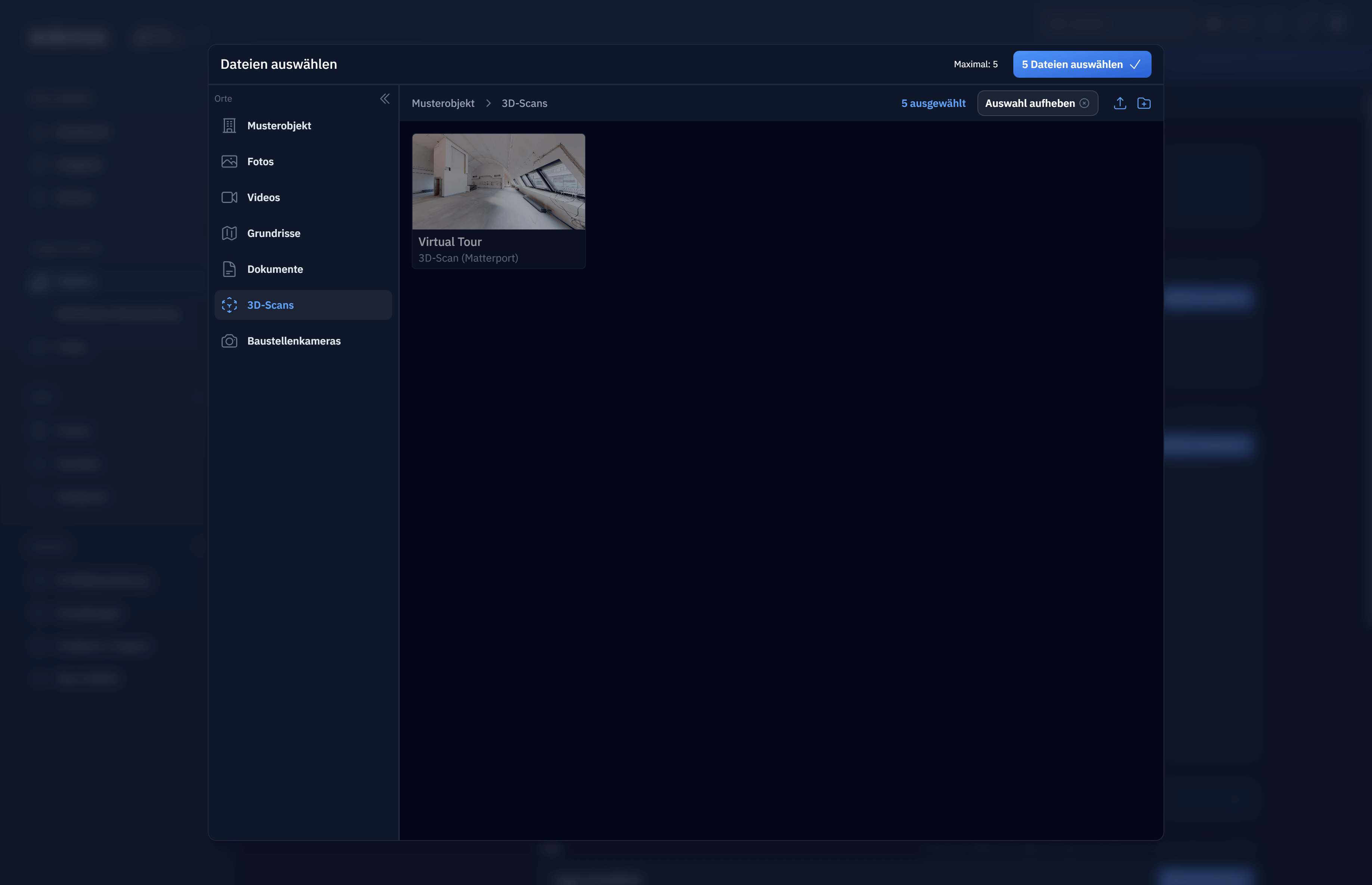
Supports real files and non-filesHere we use the Matterport API to add virtual scans/tours that only exist as an API resource, not singular files. In our application code however, we can just treat it as if it was a file. It has a custom (user-land) file type |
|
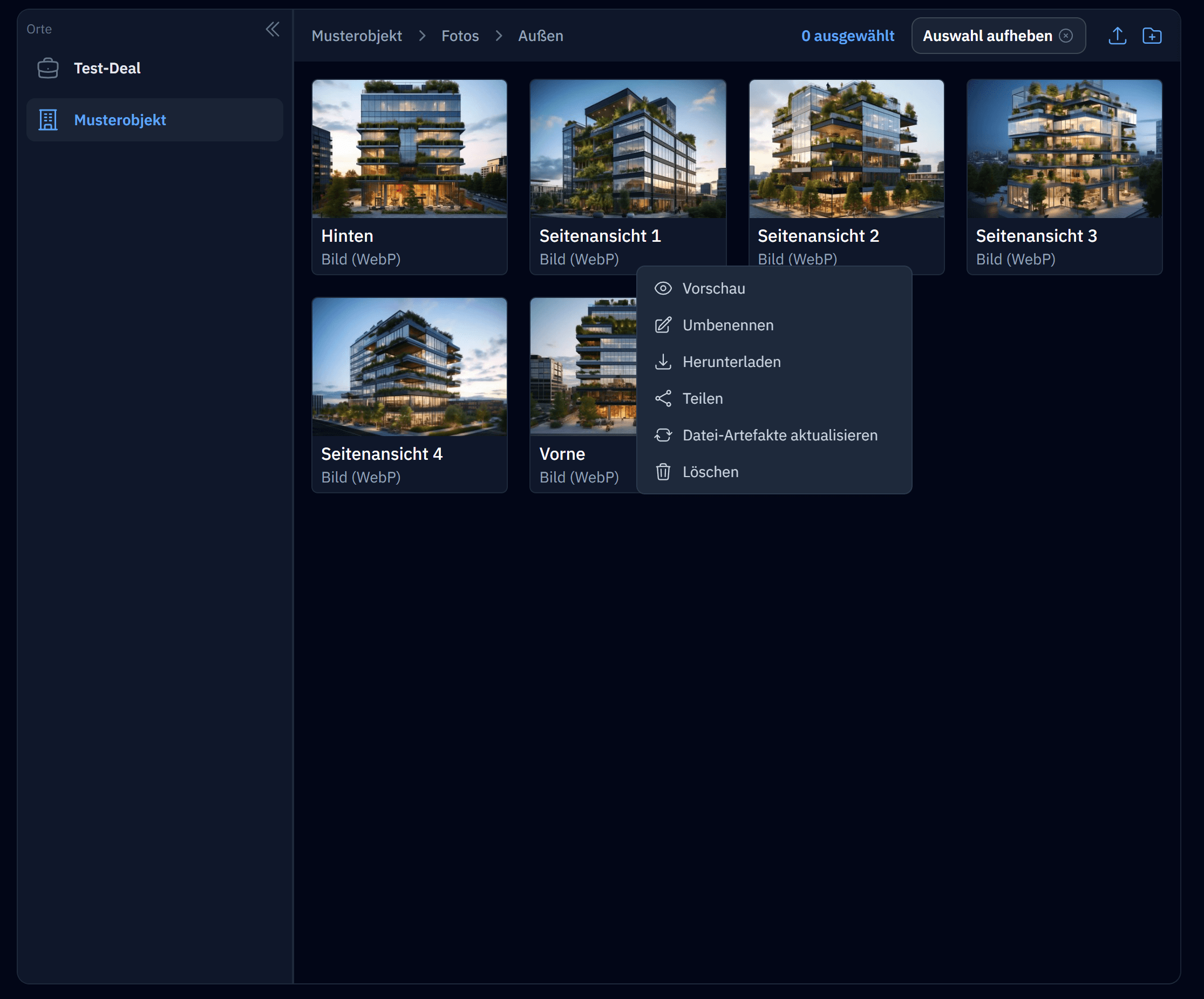
Supports a custom context menu |
|
Embeddable Finder Livewire componentBy assigning whole directories to your models, you can have encapsulated file management for single models. For example, manage contract documents for a Deal/Project CRM-like, media assets for CMS pages etc... |
Motivation
While building an application, I needed a solution to make uploaded files browsable and selectable inside a "Project"-like resource.
I needed a unified way to manage both uploadable files and "virtual files" that aren't files in the traditional sense, but still make sense to be selectable in a Finder-like view. For example it makes sense to be able to select a 3D-Scan of a building in the same way as a floor plan or its photo, even though the scan is only accessible via API and is only referenced via custom table in our app.
Cabinet is the solution I came up with that allows to manage files from different sources in a single, unified way.
How it works
File management is complicated! So in order to use Cabinet, it helps to have a basic understanding of how it works. Cabinet is built around the concept of sources, folders, files, file types and file references.
Sources
A source is a class that is responsible for listing and managing files. Sources will return a list of files for a given folder and can resolve file data for a given file identifier. Sources can read/write data from anywhere, from a disk, a database table, or an external API.
When querying files for a folder, Cabinet will query multiple sources and merge the results. This allows you to display many different types of files in a single view.
To create a source, Cabinet provides a Source interface that needs to be implemented. Sources can then support additional
features, such as uploading, deleting, etc. by implementing additional interfaces (AcceptsUploads, AcceptsData, etc.).
Learn more about creating sources.
Folders
Folders are a way to organize files. Folders can be nested and can contain files and other folders. Folders are
managed by Cabinet itself and are stored in the cabinet:directories database table, using the Directory model.
(We use "Directory" for the raw model / DB data and "Folder" throughout the rest of the code, in order to be able to
differentiate between the two).
Files
A File is a unified data structure that represents a file. It contains the file's metadata, such as its name, size,
and file type. It also contains everything required to resolve the file's data: its source the file's identifier.
These can be used to access a file's URL or its contents by calling the associated source through Cabinet.
File types
A FileType is a class that is responsible for determining the type of a file. Cabinet comes with a few built-in file
types, such as Image, Video, Audio, Document, etc. These file types unify many different file extensions and
mime types into a single type. For example, the Image file type will match all image files, such as .jpg, .png,
.gif, etc. and will also match the image/jpeg, image/png, image/gif mime types.
This makes it much easier to deal with files, as you don't have to worry about all the different file extensions and
mime types. You can simply check if a file is an Image and Cabinet will take care of the rest. However,
you can can still access the file's raw mime type and extension if you want to limit selection / uploads.
You can also create your own file types for your custom models by implementing the FileType interface.
Learn more about creating file types or look at some examples.
File references
A FileRef is a model that is used to reference a file from a model. It uses a polymorphic relationship to reference
the model to attach files to and stores the file's ID and source in order to retrieve it. This allows you to attach
files to any model in your application without needing pivot tables or other complex structures. However, FileRef's
have a UUID and nullable model columns, so you can also use your foreign key constraints if you want to create stronger
couplings.
It also stores the name of the relationship that is used to access the file. This allows you to attach multiple different files to a model, such as a thumbnail and a gallery, without having to worry about naming conflicts.
In addition, it also contains an order column, which allows saving multiple files in a specific order under a single relationship.
Installation
The following command will install the cabinet core package and the UI package. The pre-built UI is made with Filament and is technically optional, but recommended.
composer require capevace/cabinet capevace/cabinet-ui
If you want to completely build your own UI and just use Cabinet headlessly, you can omit the capevace/cabinet-ui package.
Run the install command to publish the config and migrations
Cabinet requires two tables to be present in your database. You can publish the migrations and config file using the following command:
php artisan cabinet:install
You're all done! You can now start using Cabinet.
Getting started
To demonstrate how Cabinet works, we'll build an example model that places a thumbnail and image gallery on a Post model.
1. Add HasFiles and InteractsWithFiles to your model
In order for a model to be able to have files attached to it, it needs to implement the HasFiles interface, which can be done by using the InteractsWithFiles trait.
use Capevace\Cabinet\Concerns\InteractsWithFiles; use Capevace\Cabinet\Contracts\HasFiles; class Post extends Model implements HasFiles { use InteractsWithFiles; // ... }
2. Define the file relationships
Next, we need to define the file relationships on the model. We'll add a thumbnail and gallery relationship to our Post model.
See Defining file relationships for more information.
use Capevace\Cabinet\Concerns\InteractsWithFiles; use Capevace\Cabinet\Contracts\HasFiles; class Post extends Model implements HasFiles { use InteractsWithFiles; public function thumbnail() { // Single file return $this->fileRef('thumbnail'); } public function gallery_images() { // Multiple files return $this->fileRefs('gallery_images'); } }
3. Uploading files to Cabinet
Now that we have our model set up, we can start uploading files to Cabinet. This can be done in two ways:
- Using the Cabinet UI
Findercomponent - Manually, using the
Cabinetfacade
Using the Cabinet UI
The Cabinet UI comes with a Finder component that can be used to upload manage files within Cabinet. This component can be included in any view using the x-cabinet-finder Blade component.
@props(['folderId' => null]) {{-- The folderId determines the folder that is opened and the "root" of this view --}} <x-cabinet::finder :folder-id="$folder->id" />
Manually, using the Cabinet facade
You can also upload files manually by specifying the file source and providing the required data.
For normal files (e.g. with spatie/media-library, etc.), this will be a TemporaryUploadedFile instance,
which Laravel provides when uploading files. For virtual files, this will be an array of data.
use \Cabinet\Facades\Cabinet; $folder = Cabinet::folder('<my-folder-uuid>'); $uploadedFile = request()->file('thumbnail'); // Upload a normal file $file = Cabinet::getSource('spatie-media') ->upload($folder, $uploadedFile); // Upload a virtual file $file = Cabinet::getSource('youtube-videos') ->add($folder, 'Rick Astley - Never Gonna Give You Up (Video)', [ 'id' => 'dQw4w9WgXcQ', ]);
4. Attach files to the model
Your models are now ready to have files attached to them. You can attach either attach files manually, or use the Cabinet UI to do so (this requires using Filament forms) .
Using the Cabinet UI
The Cabinet UI provides a FileInput Filament form component that can be used to attach
files to models. You can use this component by adding it to your form schema like so:
use \Livewire\Component; use \Livewire\Attributes\Computed; use \Filament\Forms\Contracts\HasForms; use \Filament\Forms\Form; use \Cabinet\Filament\Components\FileInput; class PostForm extends Component implements HasForms { public string $postId; #[Computed] public function post(): Post { return Post::findOrFail($this->postId); } public static function form(Form $form) { return $form ->model($this->post) ->schema([ // ... FileInput::make('thumbnail') ->label('Thumbnail') // The `relationship` method will automatically attach the file // to the model when saved ->relationship('thumbnail') // The amount of files that can be picked ->single() // This specifies the root folder that will be opened in the file picker ->root('<my-folder-uuid>'), FileInput::make('gallery_images') ->label('Gallery Images') // It is also possible to attach multiple files ->relationship('gallery_images') ->max(5) ->root('<my-folder-uuid>'), // ... ]); } public function save() { $data = $this->form->getState(); $this->post->update($data); // This will attach the files to the model $this->form->saveRelationships(); } }
Attaching files via code
If you're not using Filament in your app or you want to attach files in other places, you can also attach files manually using the Cabinet facade.
use \Cabinet\Facades\Cabinet; $post = Post::find(1); $file = Cabinet::file('spatie-media', '5'); // Attach a single file Cabinet::attach($file, to: $post, as: 'thumbnail'); // or directly via the relationship (we're "create"-ing a FileRef) $post->thumbnail()->create($file->getReferenceData()); // Attach multiple files Cabinet::attach($files, to: $post, as: 'gallery_images');
Concepts
Accessing Folders
$directory = Cabinet::directory($id); // -> Directory $folder = Cabinet::folder($id); // -> Folder // same as $directory->asFolder();
Referencing Files
$ref = Cabinet::reference($file); auth()->user()->update([ 'avatar_file_ref_id' => $ref->id, ]); Cabinet::attach($file, to: auth()->user(), as: 'avatar');
Accessing Files
$filesAndFolders = $folder->list(); // -> Collection<File|Folder> $files = $folder->files(); // -> Collection<File> $folders = $folder->folders(); // -> Collection<Folder> // Create a File DTO via source model ID $file = Cabinet::file('spatie-media', '5'); // -> Cabinet\File {#1618 // id: "5", // source: "spatie-media", // type: Cabinet\Types\Image {#1629}, // name: "yoda", // slug: "yoda.png", // mimeType: "image/png", // size: 6566715, // url: "https://v3.test/storage/5/yoda.png", // } // Create a File DTO via source path and disk $file = Cabinet::file($source, 'avatars/test.png', disk: 'local');
Renaming Files
// Will rename the file to "Hello there", the underlying file will be named 'hello-there-custom.png'. Cabinet::rename($file, 'Hello there'); // Will rename the file to "Hello there", the underlying file will be named 'hello-there-custom.png'. Cabinet::rename($file, 'Hello there', slug: 'hello-there-custom'); // Will only change the "virtual" filename, not the underlying file Cabinet::rename($file, 'Hello there', slug: false);
Moving Files
// You can pass either the Folder DTO Cabinet::move($file, $folder); // Or the Directory model Cabinet::move($file, $directory);
Delete Files
Cabinet::delete($file);
Uploading Files
use Illuminate\Http\UploadedFile; $uploadedFile = new UploadedFile(...); // Upload to a specific source $source = Cabinet::getSource('spatie-media') ->upload($directory || $folder, $uploadedFile); // or using shorthand syntax Cabinet::upload('spatie-media', $folder, $uploadedFile);
