zisunal / php-html
A package to render html directly from php
Requires
- php: >=8.0
- cerdic/css-tidy: ^2.2
- matthiasmullie/minify: ^1.3
- wongyip/html-beautify: ^1.1
README
- Don't need continuous
?>and<?phpanymore. - Use a more intuitive syntax for HTML generation.
- Create 🌀
reusable components🌀 easily with PHP. - Enjoy better code organization and readability.
- Use
Flutter-likewidget structure for your HTML. - Use
Zisunal\PhpHtmlto create your HTML output with ease. - Use with
Vanilla PHPor anyPHP frameworkfreely.
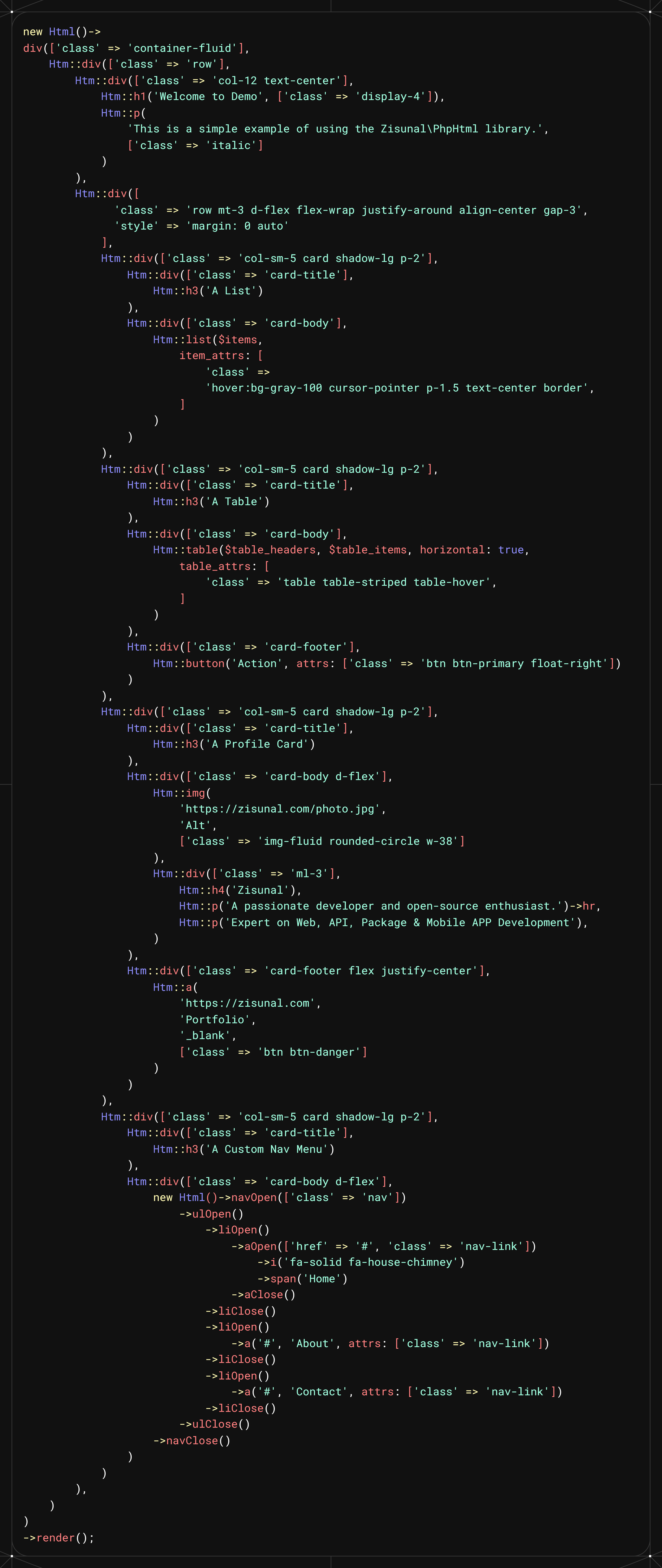
📑 See Some Examples
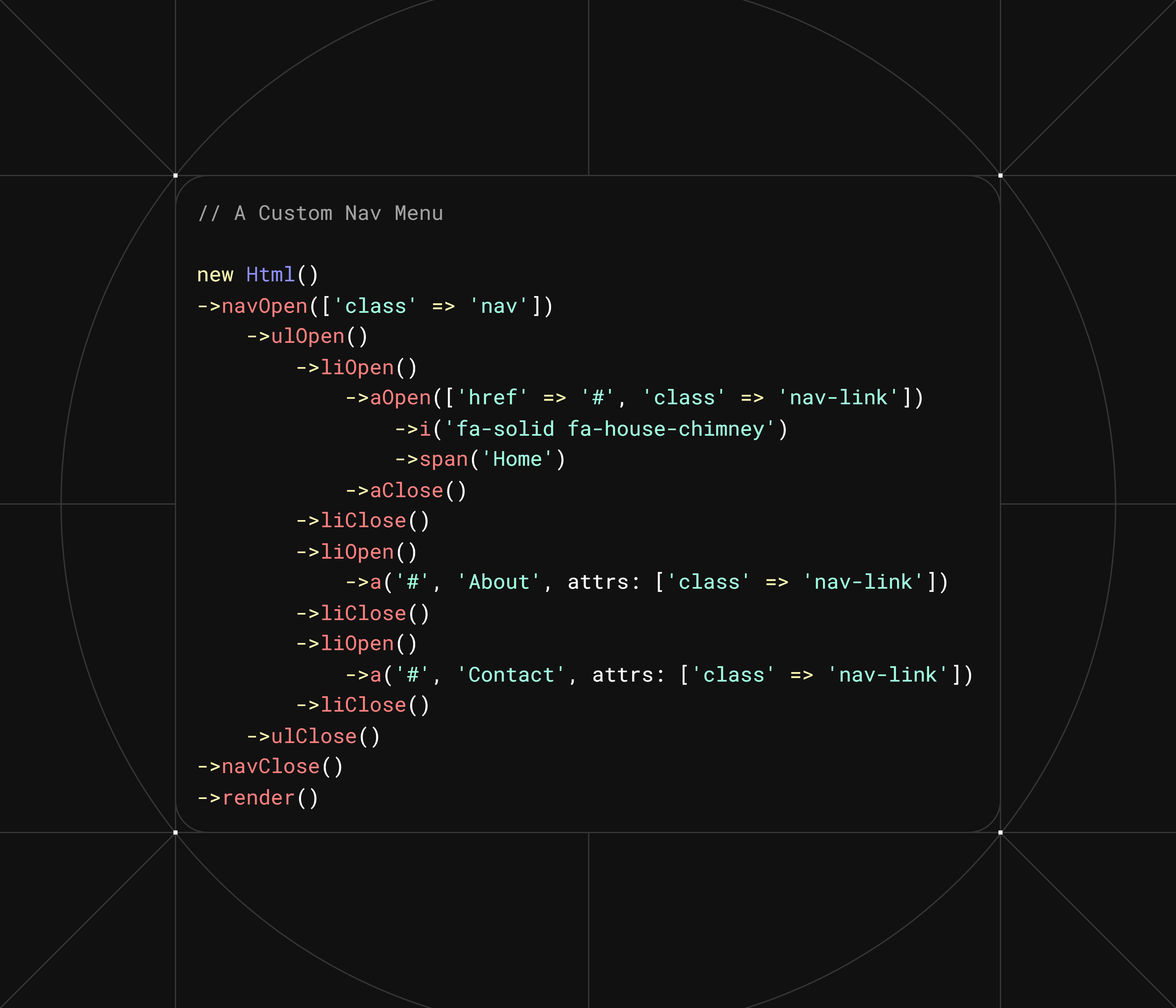
Custom Navigation Menu
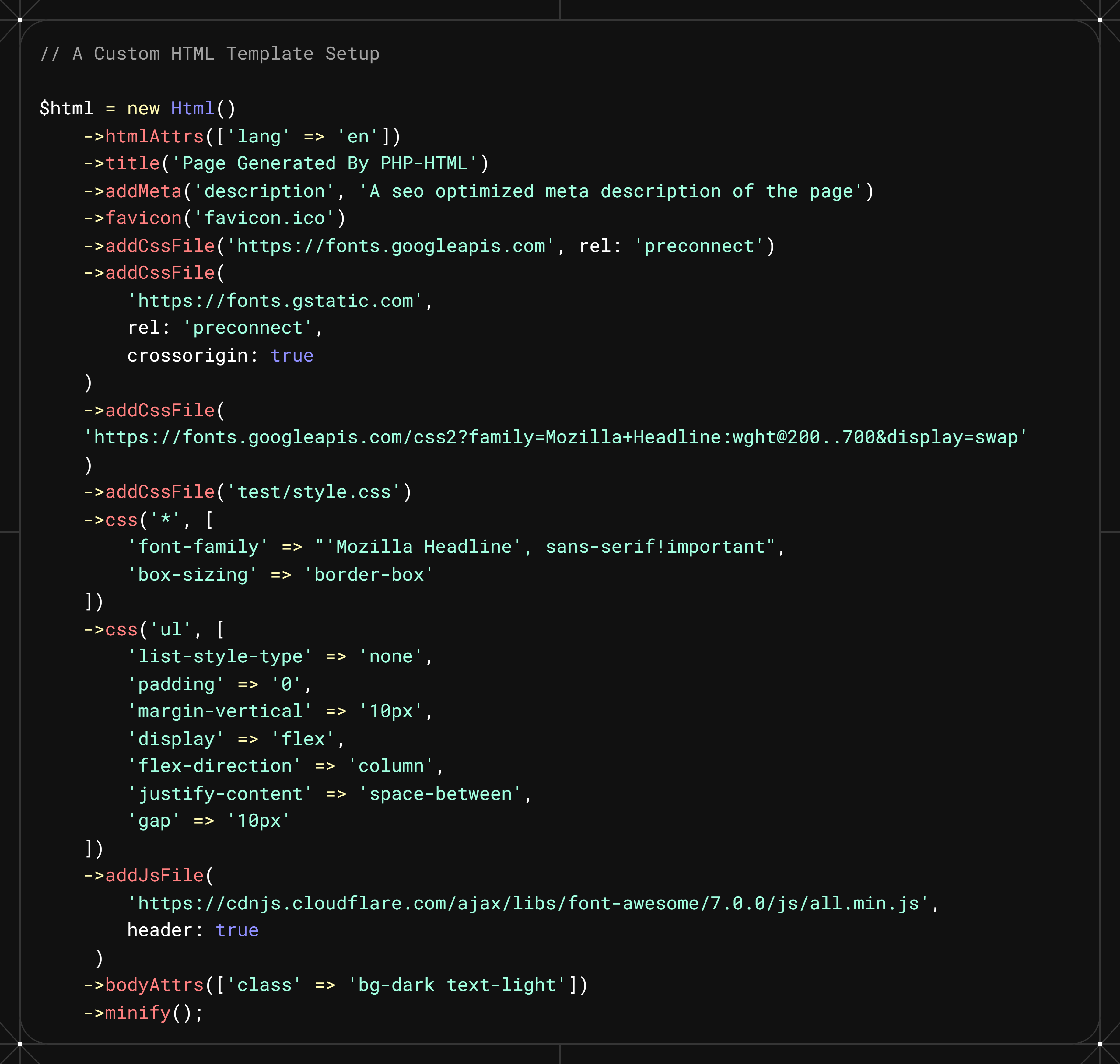
Custom Template
1. Let's Start with Installing Zisunal\PhpHtml
composer require zisunal/php-html
2. If you are not using frameworks like Laravel / Symfony / CodeIgniter, you need to include the autoloader in your project root:
require_once 'vendor/autoload.php';
3. Use Zisunal\PhpHtml\Html to Start:
use Zisunal\PhpHtml\Html;
4. For Static Html Methods, use Zisunal\PhpHtml\Htm instead:
use Zisunal\PhpHtml\Htm;
Note:
- This first one is
Htmland the second one isHtm. - No ending
lin the second one. Htmcan be used to create static HTML elements without the need for an instance.Htm::div(['class' => 'container'], Htm::h1('Hello World') ->hr(), Htm::p('This is a static paragraph.') );
- Most of the methods of
Htmlare also available inHtm, so you can use them interchangeably. - You can create an instance of
Htmllike this:$html = new Html();
- If you add any of the templating methods with a
Html, it will render a complete HTML document.// This code will generate a whole Html document starting from <!DOCTYPE html> to the ending </html> $html->title('My Page');
- If you only add the tags' methods for the body, it will only render the content as a component.
// This code will generate a div element with a class of "container" without the full Html document $html->divOpen(['class' => 'container']) ->h1Open() ->innerText('Hello World') ->h1Close() ->hr ->pOpen() ->innerText('This is a static paragraph.') ->pClose(); ->divClose() ->render(); // Notice that we can open and close almost all the container tags anywhere and add any content inside them.
- If you want
single divinstead ofdivOpenanddivClosein the previous code,$html->div(['class' => 'container'], $html->h1Open() ->innerText('Hello World') ->h1Close() ->hr ->pOpen() ->innerText('This is a static paragraph.') ->pClose(); )->render(); // Notice that, we are passing the attributes of <div> in the 1st argument and any number of Html/Htm in the 2nd, 3rd, ..... arguments
- If you want the
shorter versionof the previous code,$html->div(['class' => 'container'], $html->h1('Hello World')->hr->p('This is a static paragraph.') )->render(); // You can use shorter syntax for the most useful container tags and to all the self-closing tags
- If you want the previous code with
only static methods,Htm::div(['class' => 'container'], Htm::h1('Hello World'), Htm::hr(), Htm::p('This is a static paragraph.') )->render();
5. The Most Important info to know:
- You can call
render()method at the end of anyHtmlorHtmchain to get/print the final output. Remember, once you calledrender(), you can't add any more elements to the chain. - You can pass
trueas an argument torender()method to get the output as a string instead of printing it directly. - You can minify the whole Html, CSS, JS output by calling
minify()method anywhere beforerender().$html->title('My Title') ->p('My Paragraph') ->minify() ->render(); // If you view the page source, you will see the minified output.
-
The following static and non-static methods are equivalent (assuming
$html = new Html()). So, you can use any of them interchangeably:$html->hr=>$html->hr()=>Html::hr()=>Htm::hr()$html->br=>$html->br()=>Html::br()=>Htm::br()$html->wbr=>$html->wbr()=>Html::wbr()=>Htm::wbr()
- We will say📝
Single Tagsto refer toself-closing tagslike<br />,<hr />,<wbr />from now on. - We will say📝
Double Tagsto refer toopening and closing tagslike<div>,<h1>,<p>,<span>from now on.
- All the
Double Tagshave 2 methods:tagnameOpen()andtagnameClose().divOpen()anddivClose()for<div>tags.h1Open()andh1Close()for<h1>tags.pOpen()andpClose()for<p>tags.spanOpen()andspanClose()for<span>tags.aOpen()andaClose()for<a>tags.- And so on for all other double tags.
- Any other
Html tagor aninnerText()method can be called insideDouble Tagto customize the content as needed.$html->divOpen(['class' => 'container']) ->h1Open() ->innerText('Hello World') ->h1Close() ->hr() ->pOpen() ->innerText('This is a static paragraph.') ->pClose() ->divClose();
- All the
Single Tagscan be called directly without any Open and Close methods. It will accept attributes as an array.-
$html->input([ 'class' => 'img-fluid', 'name' => 'fullName', 'id' => 'fullName', 'placeholder' => 'Enter your full name', 'required' => true ]);
-
- Some
Single Tagscan also accept their required contents as arguments before the attributes array.-
$html->img('image.jpg', 'Alt Text', ['class' => 'img-fluid']);
-
- Some
Double Tagscan also accept their contents as arguments before the attributes array.$html->h1('Hello World', ['class' => 'title']); // Same as: $html->h1Open(['class' => 'title']) ->innerText('Hello World') ->h1Close();
📖 Methods Available to use:
- You can find the complete list of methods and documentations for
Htmlhere - You can find the complete list of methods and documentations for
Htmhere
❓ FAQ
Q: What is the difference between Html and Htm?
A: Html is the main class for generating HTML content, while Htm is a lightweight version that focuses on generating HTML snippets without the full document structure.
Q: Can I use Htm methods inside Html?
A: Yes, you can use Htm methods inside any Html methods as needed.
🔧 Adding more tags support
If you need any other standard Html tag support you can email me by clicking here
📝 Contributing
We welcome contributions to the Zisunal\PhpHtml package! If you'd like to contribute, please follow these steps:
-
Fork the repository: Create your own copy of the repository by forking it on GitHub.
-
Create a new branch: Before making changes, create a new branch for your feature or bug fix:
git checkout -b my-feature-branch -
Make your changes: Implement your feature or fix the bug in your local copy of the repository.
-
Write tests: If applicable, write tests to cover your changes. Ensure that all tests pass before submitting your pull request.
-
Submit a pull request: Once you're satisfied with your changes, push your branch to your forked repository and submit a pull request to the main repository.
-
Follow the code style: Please adhere to the existing code style and conventions used in the project.
Thank you for your contributions!