zidbih / laravel-deadlock
Make temporary Laravel workarounds expire and fail CI when ignored.
Installs: 873
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 94
Watchers: 0
Forks: 2
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/zidbih/laravel-deadlock
Requires
- php: ^8.2
- illuminate/console: ^10.0|^11.0|^12.0
- illuminate/http: ^10.0|^11.0|^12.0
- illuminate/support: ^10.0|^11.0|^12.0
- nikic/php-parser: ^5.0
Requires (Dev)
- laravel/pint: ^1.26
- orchestra/testbench: 9.0
- phpunit/phpunit: ^10.0
README
Laravel Deadlock
Have you ever shipped a temporary workaround and never came back to it?
Laravel Deadlock makes those workarounds explicit and time-boxed.
Annotate classes or methods with an expiration date, then enforce them in local development and CI without affecting production.
What it does
- Scans the codebase for
#[Workaround]attributes - Lists workarounds and their status
- Fails CI when a workaround has expired
- Blocks local execution of expired code
- Never enforces in production
Installation
composer require zidbih/laravel-deadlock
Requirements
- PHP: 8.2+
- Laravel: 10, 11, 12
Quick Start
Annotate a temporary workaround with a clear description and expiration date.
use Zidbih\Deadlock\Attributes\Workaround; #[Workaround( description: 'Temporary bypass for legacy payment gateway', expires: '2025-03-01' )] class PaymentService { // ... }
Supported targets
#[Workaround] can be applied to classes and methods.
Workarounds inside functions or other scopes are ignored.
What happens when it expires?
- Local Development: Execution is blocked with an exception
- CI/CD: Pipelines fail when running the check command
- Production: No effect
Enforcement Modes
Controllers (Automatic)
Controllers are discovered automatically and enforced at runtime.
Add the attribute; no additional calls are required.
namespace App\Http\Controllers; use Zidbih\Deadlock\Attributes\Workaround; #[Workaround(description: 'Legacy controller awaiting refactor', expires: '2025-06-01')] final class UserController extends Controller { #[Workaround(description: 'Temporary validation bypass', expires: '2025-02-01')] public function store() { // ... } }
Services, Jobs, Commands (Explicit)
For non-controller classes, enforcement is explicit by design to avoid hidden runtime behavior.
Class-Level Enforcement
namespace App\Services; use Zidbih\Deadlock\Attributes\Workaround; use Zidbih\Deadlock\Support\DeadlockGuard; #[Workaround(description: 'Temporary legacy pricing service', expires: '2025-01-01')] final class PricingService { public function __construct() { DeadlockGuard::check($this); } }
Method-Level Enforcement
namespace App\Services; use Zidbih\Deadlock\Attributes\Workaround; use Zidbih\Deadlock\Support\DeadlockGuard; final class PricingService { #[Workaround(description: 'Temporary calculation logic', expires: '2025-02-01')] public function calculate() { DeadlockGuard::check($this, __FUNCTION__); return 42; } }
Artisan Commands
List Workarounds
php artisan deadlock:list
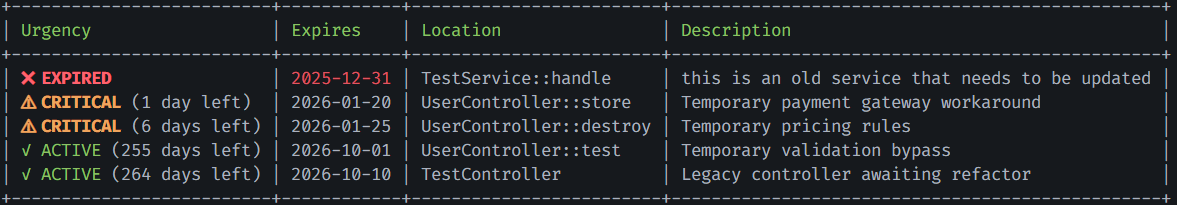
Example output:
Filters
Show only expired workarounds:
php artisan deadlock:list --expired
Show only active workarounds:
php artisan deadlock:list --active
Show workarounds expiring in 7 days or less:
php artisan deadlock:list --critical
CI/CD Enforcement
Run the check command in your pipeline:
php artisan deadlock:check
If an expired workaround is found, the command exits with code 1.
Example failure output:
Expired workarounds detected:
- Temporary payment gateway workaround | expires: 2025-02-10 | PaymentService::process
- Legacy admin controller | expires: 2025-01-31 | AdminController
CI example:
- name: Deadlock check run: php artisan deadlock:check
Runtime Enforcement (Local Only)
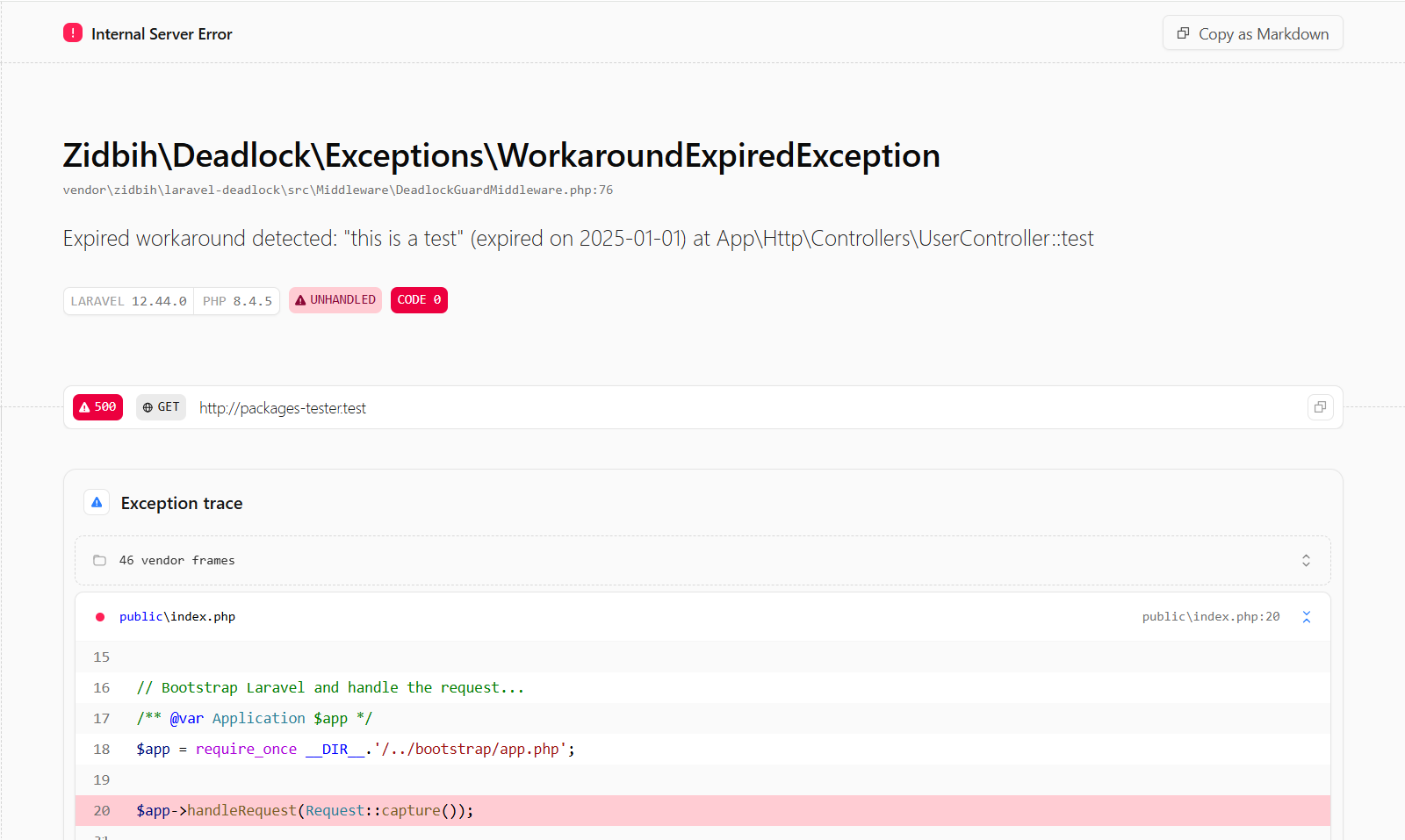
When an expired workaround is accessed locally, a WorkaroundExpiredException is thrown with:
- Description
- Expiration date
- Exact code location
Example exception output:
Production Safety
Laravel Deadlock never enforces debt in production.
- Runtime exceptions only occur in local environments
- CI blocks merges before debt reaches production
- Live users are never affected
Testing
The test suite uses PHPUnit and Orchestra Testbench for compatibility across supported Laravel versions.
License
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md