vgalvoso / phunctional
PHP functional framework
Installs: 20
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 1
Watchers: 1
Forks: 0
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/vgalvoso/phunctional
README
Functional PHP Framework
Introduction
PHunctional PHP is a functional PHP framework.
Today's development uses complicated or too much abstraction of codes, it doesn't have to be that way.
Doesn't it cool to easily know what the code does in one look?
Doesn't it cool to focus on the output rather than wasting your time on technical stuffs?
Doesn't it cool to use a framework immediately without overwhelming configurations and dependencies?
This is what PHunctional PHP is all about.
Structure
Here is the basic directory structure of PHunctional PHP.
api/
lib/
Database.php
DotEnv.php
Helper.php
Sql.php
public/
css/
js/
res/
routes/
api.php
view.php
view/
section/
header.php
footer.php
.env
.htaccess
index.php
README.md
Installation
Download the latest version and extract it on your web server's root folder.
Then rename the extracted root folder into your project's name.
Or use composer:
composer create-project vgalvoso/phunctional your_project_name
After extracting or creating your project, open a terminal in your project directory and run:
composer install
This will initialize Composer to let you add dependencies when needed.
Build Your First App
Hello World! Yes, let's create your first hello world using PHunctional PHP.
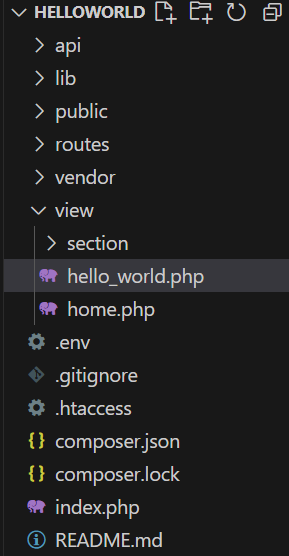
After you download and extract the latest version (see installation), create a PHP file inside the view folder and name it hello_world.php.
Let's assume you named your root folder "helloworld", this is what your project directory might look like.
Copy and paste this code inside hello_world.php:
<?php include "section/header.php"; ?> <h1>Hello World!</h1> <?php include "section/footer.php"; ?>
Open routes/web.php and add a new view route. Your routes/web.php should look something like this:
<?php view("", "home"); view("hello", "hello_world"); notFound();
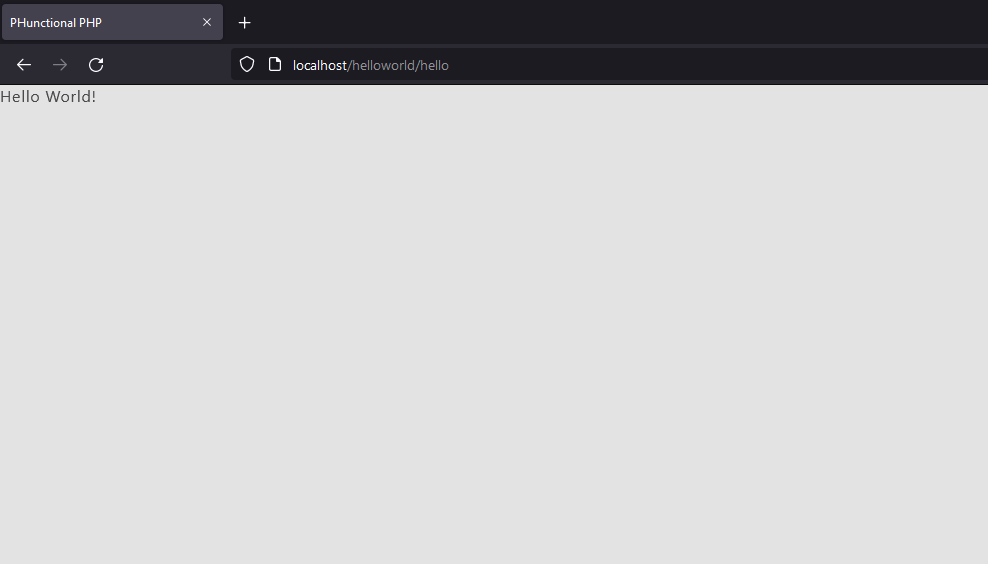
Now try to access this on your browser: http://localhost/helloworld/hello
It should look like this:
Congratulations! You created your first hello world using PHunctional PHP.
Routing
Define your routes inside routes/web.php for views and routes/api.php for API endpoints.
There are 4 functions for creating routes:
-
view(routeName, fileName)
Use this function to show views.[routeName]- Custom named route.[fileName]- File to call inside view folder.
-
post(routeName, fileName)
Use this function for POST requests.[routeName]- Custom named route.[fileName]- File to call inside api folder.
-
get(routeName, fileName)
Use this function for GET requests.[routeName]- Custom named route.[fileName]- File to call inside api folder.
-
put(routeName, fileName)
Use this function for PUT requests.[routeName]- Custom named route.[fileName]- File to call inside api folder.
Sample routes/web.php:
<?php view("", "home"); view("hello", "hello_world"); notFound();
Sample routes/api.php:
<?php post("validateLogin", "login"); get("getUsers", "users/all"); notFound();
The notFound() function should be placed at the end to handle unmatched routes.
Views
Place your views inside the view folder.
Let's create a view for our default route.
view/home.php
<?php include "section/header.php"; ?> <h1>Hello World!</h1> <?php include "section/footer.php"; ?>
Database Setup
PHunctional PHP uses a simple Database.php file for database connections. Configuration is managed via the .env file.
1. Configure .env
Add your database credentials to the .env file in your project root:
APP_ENV=development
DEFAULT_SERVER=localhost
DEFAULT_USER=root
DEFAULT_PASS=root
DEFAULT_DBNAME=helloworld_db
DEFAULT_DRIVER=mysql
DEFAULT_PORT=3306
2. Using Database.php
Here is a sample lib/Database.php file:
<?php $db = array( "default" => array( "server" => getenv('DEFAULT_SERVER'), "user" => getenv('DEFAULT_USER'), "pass" => getenv('DEFAULT_PASS'), "dbname" => getenv('DEFAULT_DBNAME'), "driver" => getenv('DEFAULT_DRIVER'), "port" => getenv('DEFAULT_PORT') ) );
This file loads the database credentials from environment variables and stores them in the $db array.
Creating an API
You can easily create API endpoints in PHunctional PHP by adding files inside the api folder and defining routes in routes/api.php.
1. Create a Sample Database
First, create a sample database and a users table. You can run the following SQL queries in your MySQL client:
-- 1. Create the database CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS myapp_db; -- 2. Use the newly created database USE myapp_db; -- 3. Create the users table CREATE TABLE users ( id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE, email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL UNIQUE, password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP );
2. Create api/add_user.php
Create a new file api/add_user.php with the following code to handle adding a user:
<?php $query = "INSERT INTO users (username, email, password) VALUES (:username, :email, :password)"; $inputs = [ "username" => $username, "email" => $email, "password" => password_hash($password, PASSWORD_DEFAULT), ]; if ($sql->exec($query, $inputs)) echo "User added successfully."; else echo "Error adding user: " . $sql->getError();
Note: In PHunctional PHP, POST payload keys are automatically converted into variables, so you can use
$username,$passworddirectly. No need to use$_POSTor$_GET.
Note: The
$sqlobject is automatically available and uses the "default" database configuration fromDatabase.php. If you want to use a different configuration, you can initialize it with$sql = new Sql('configname');.
3. Add the Route in routes/api.php
Open routes/api.php and add the following line:
post("users", "add_user");
Now you can send a POST request to /users with username, email, and password in the JSON body to add a new user.