vaened / laroute
An enhanced Laravel extension to export named routes to JavaScript, allowing you to use route names instead of URLs. Supports route grouping for modular applications.
Installs: 124 859
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 4
Watchers: 1
Forks: 0
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/vaened/laroute
Requires
- php: ^8.2
- lambdish/phunctional: ^2.1
- laravel/framework: ^v11.15|^12.0
- vaened/support: ^4.0
Requires (Dev)
- mockery/mockery: ^1.6
- orchestra/testbench: ^9|^10
- phpunit/phpunit: ^11
README
vaened\laroute is a PHP library inspired by aaronlord/laroute, designed to help Laravel developers
manage their application’s routes in JavaScript without the need to hardcode URLs. This library goes a step further by introducing
modular routing, allowing you to separate routes based on URL patterns into different modules. Each module generates its own routes file,
making it easier to manage and scale your application’s routing structure.
Installation
Laroute requires PHP 8.2. To get the latest version, simply require the project using Composer:
composer require vaened/laroute
Publish the configuration file.
php artisan vendor:publish --tag='laroute'
Now, generate the routes based on your configuration and export the JavaScript service.
php artisan laroute:generate
Usage
The library includes the necessary javascript service to interpret the exported routes, along with its corresponding d.ts type
definitions
for typescript.
The location of the service is configured in the library option within the configuration file.
Javascript / Typescript
Once the service is exported to the location defined in the configuration file, you can easily create a new file and export the service creation by passing the file containing the routes as a parameter.
import {RouteService} from "./laroute"; import routes from "./api-routes.json"; const apiRouteService = new RouteService({routes});
With this, you’re ready to start.
const response = await fetch(apiRouteService.generateFullURL('store.products.lists')) const data = response.json(); console.log(data)
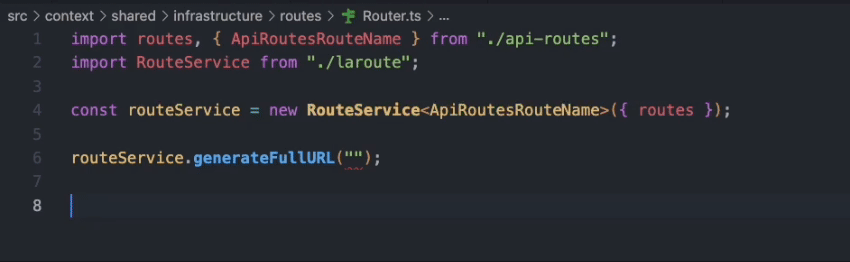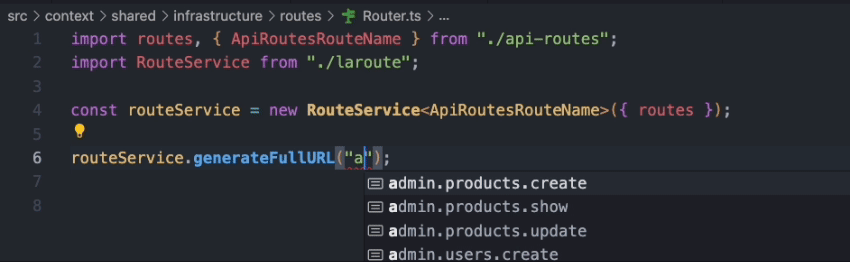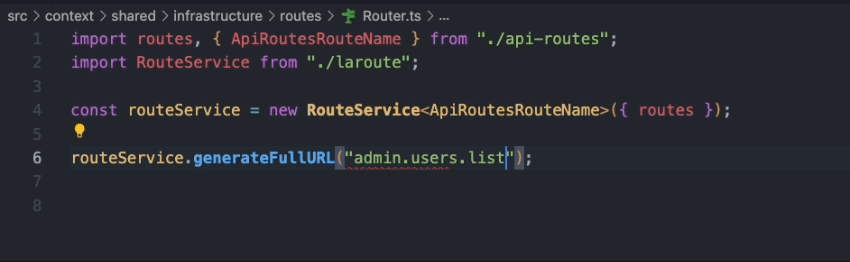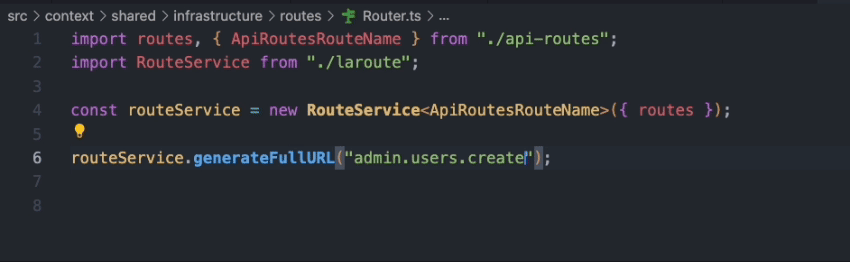
Additionally, you can export the routes as a TypeScript file to enable route autocompletion in your editor. To achieve this, simply modify
the output option in the configuration file.
Service
The route service provides three key methods to interact with the generated routes:
- generateFullURL(name, ?params): Generates a full URL, including any query string parameters.
apiRouteService.generateFullURL('admin.products.create', { id: '80768395-4208-4fd7-ac60-c429717014ab', name: 'Notebook' })
Returns
{host}/api/admin/products/80768395-4208-4fd7-ac60-c429717014ab?name=Notebook
- createURLWithoutQuery(name, ?params):Generates a full URL without any query string.
apiRouteService.createURLWithoutQuery('admin.products.update', { id: '80768395-4208-4fd7-ac60-c429717014ab', name: 'Notebook' })
Returns
{host}/api/admin/products/80768395-4208-4fd7-ac60-c429717014ab
- has(name): Checks if a specific route is defined within the service.
apiRouteService.has('admin.products.list')
Returns
trueif the route exists,falseotherwise.
Best Practices
To efficiently manage API calls, it’s advisable to create a dedicated file. You might name it Router.{ts, js}. In this file, you can
utilize fetch or a library like axios to streamline your API interactions. An example of what you might export could look like this:
import createRouteService, {Parameters} from "./laroute"; import axios, {AxiosRequestConfig, AxiosResponse} from "axios"; import api from "./api.json"; const apiRouteService = createRouteService(api); export const Router = { get(routeName: string, params: Parameters = {}, config: AxiosRequestConfig = {}) { return axios.get(apiRouteService.cleanURI(routeName, params), {params, ...config}); }, post(routeName: string, params: Parameters = {}, config: AxiosRequestConfig = {}) { return axios.post(apiRouteService.cleanURI(routeName, params), params, config); }, patch(routeName: string, params: Parameters = {}, config: AxiosRequestConfig = {}) { return axios.patch(apiRouteService.cleanURI(routeName, params), params, config); }, // ... };
Configuration
The default configuration should be sufficient for most projects, allowing you to simply export the routes and start working without any additional setup.
For customization options, refer to the comments in the configuration file laroute.php.
Advanced
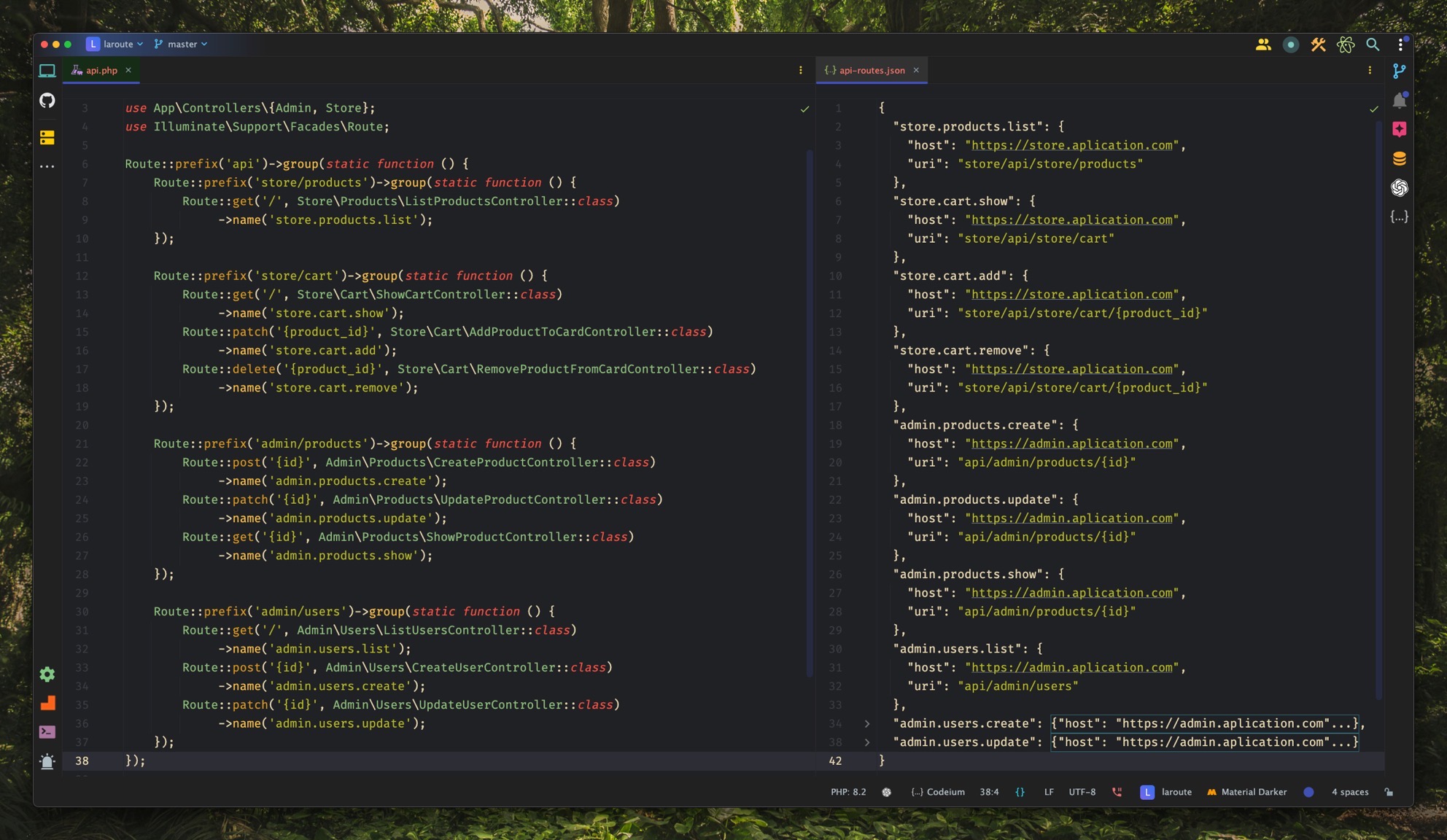
For larger projects, where different clients consume the API, you can configure the route export in a modular way. This allows you to create as many modules as needed, each corresponding to different URL segments.
For example, you could have a module for /api/store and another for /api/admin, which would generate two separate route files.
'modules' => [ [ 'match' => '/api/store', 'name' => 'store', 'rootUrl' => 'https://store.aplication.com', 'absolute' => true, 'path' => 'resources/routes', ], [ 'match' => '/api/admin', 'name' => 'admin', 'rootUrl' => 'https://admin.aplication.com', 'absolute' => true, 'path' => 'resources/routes', ], ]
Features
- Modular Routing: Define and separate routes by modules based on URL patterns (e.g., /api, /admin, /user), with each module generating a separate JSON file.
- Seamless Integration with Laravel: Automatically generate JavaScript routes from your Laravel routes, ensuring consistency across your application.
- TypeScript Support: Includes a TypeScript-compatible JavaScript file, allowing you to use strongly-typed route definitions in your front-end code.
- Customizable URLs: Generate absolute or relative URLs with customizable prefixes and root URLs, giving you full control over how URLs are constructed.
- Flexible Configuration: Easily configure modules and route matching criteria to fit the needs of your project, whether it’s a monolithic application or a modular one.
License
This library is licensed under the MIT License. For more information, please see the license file.
