symbioquine / farmos_wfs
WFS module for farmOS.
Installs: 630
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 8
Watchers: 1
Forks: 1
Open Issues: 0
Type:drupal-module
pkg:composer/symbioquine/farmos_wfs
Requires
- itamair/geophp: 1.6
README
farmOS_wfs provides a WFS module for farmOS. This makes FarmOS areas accessible as a Web Feature Service (WFS) which can be used in GIS software such as Quantum GIS (QGIS).
Limitations & Compatibility
- Only supports WFS 1.1.0 / GML 3.1.1 currently
- Only supports features with single geometries of the types; point, polygon, or line string
- Only supports querying/updating/deleting by simple filters on BBOX or feature id - more complex OGC Filter operations may be supported in the future
- Only supports the EPSG:4326 spatial reference system (SRS) which farmOS uses - QGIS and similar software generally supports reprojection of data sources into other SRS'
- Only supports PHP >= 7.4 - earlier versions will not work
- Only tested against the farmOS 4 - for farmOS 1.x see farmOS_wfs-7.x-1.x
- Only tested with QGIS 3.34 - earlier versions may work, but no promises
Getting Started
Use Composer and Drush to install farmOS_wfs in farmOS 4.x;
composer require drupal/farmos_wfs drush en farmos_wfs
Available released versions can be viewed at https://www.drupal.org/project/farmos_wfs/releases
QGIS Configuration
Configure OAuth2
- Name:
farmOS0-oauth2-resource-owner(Name as desired) - Grant Flow: Resource Owner
- Token URL:
https://path-to-your-farmOS-server.example.com/oauth/token - Client ID:
farm - Username:
your-farmOS-username - Password:
your-farmOS-username - Scope:
farm_manager
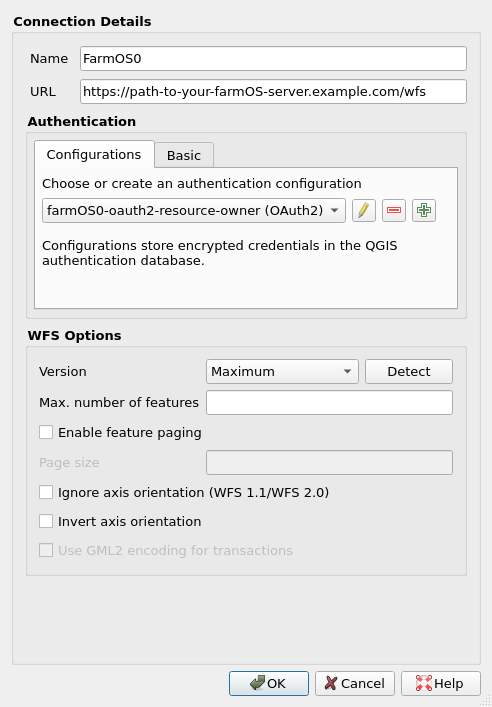
Configure WFS Server Connection
- Name:
FarmOS0(Name as desired) - URL:
https://path-to-your-farmOS-server.example.com/wfs - Authentication Config: Choose the OAuth2 configuration created above
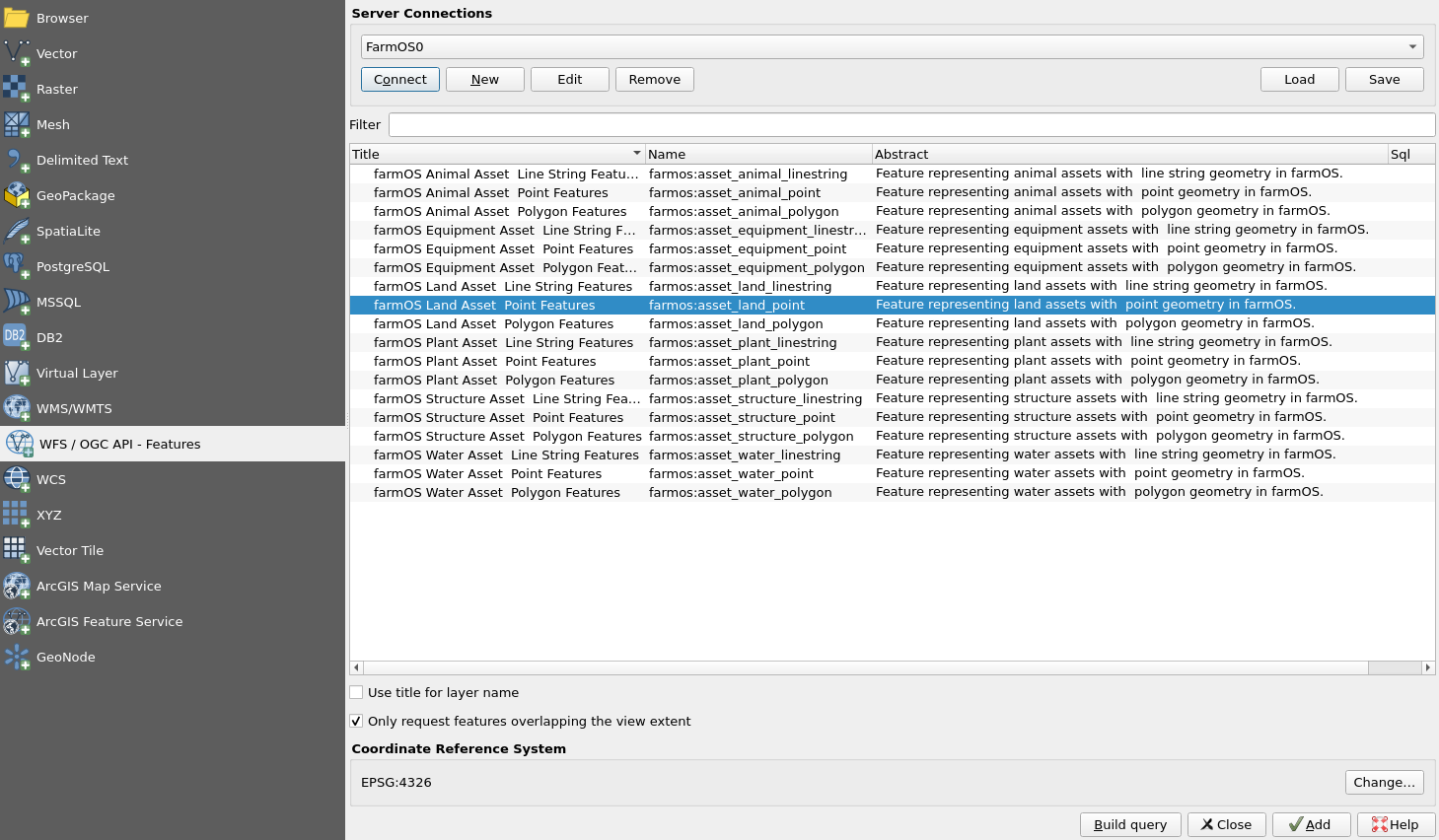
Add Layers
- Click 'Connect' and add the desired layers to your map!
FAQ
Why is this useful?
The farmOS_wfs module allows bidirectional integration between farmOS and GIS with farmOS as the "source of truth" for asset data. This means complex mapping/geospatial tasks can be accomplished using QGIS and always up-to-date data directly from farmOS. Without farmOS_wfs, doing something similar would involve importing/exporting data between farmOS/GIS formats which would make it hard to maintain a single authoritative data model.
Why are the different geometries surfaced as separate feature types (layers)?
farmOS allows any asset to have arbitrary geometry or even collections of geometries, however QGIS - and I believe most GIS tools - expect the geometry of features in a feature type to be homogeneous. The WFS specification does allow for features with geometry types like GeometryCollection or MultiGeometry, but then these wouldn't be easily viewable or editable. farmOS_wfs therefore makes the pragmatic choice of serving different geometry types as separate layers.
Why are some fields prefixed with two underscores (e.g. "__uuid")?
These are fields which farmOS/Drupal reports as read-only. Attempts to set values for such fields is not permitted through farmOS_wfs and will produce an error. Generally these fields are also populated automatically which means they may change as a result of committing changes via farmOS_wfs, but the new value will not appear until the feature is next fetched from farmOS.
Why can't I delete certain assets?
farmOS maintains the validity of asset references. Certain assets - especially non-fixed ones - will have movement/location logs referencing them. Those logs would need to be deleted before the asset could be deleted.
Possible Future Directions
- Surface the
locationfield - this needs more thought since the asset reference wouldn't be easily editable and a read-only name would be of limited utility - Use database transactions for committing changes to assets
- Support more complex OGC Filter queries
- Support additional WFS versions - most importantly WFS 2.0.0 to get full-featured pagination
- Detect when PostGIS spatial indices exist on the Geofield columns and switch to using PostGIS
ST_queries - relevant https://www.drupal.org/project/geofield/issues/2969564 & https://www.drupal.org/project/geofield_postgis - Consider adding support for MultiPoint, MultiLineString, and MultiPolygon feature layers
- Consider adding geometry agnostic feature layers only parameterized by the asset type
- Add tests for OpenLayers as a client
Development
Environment
In the docker/ directory of this repository run;
cp docker-compose.pgsql.yml docker-compose.yml docker-compose up -d
Once the command completes, farmOS should be running at http://localhost:80 with the farmOS_wfs module installed. The test site's username and password are 'root' and 'test' respectively.
Running Tests
In the docker/ directory with the above development environment started;
docker build -t qgis_test_harness qgis_test_harness docker run --rm -it --name qgis --network=docker_default -v $(pwd)'/qgis_tests:/tests_directory' qgis_test_harness:latest ./run_tests.sh
More Complex Test Filtering
Running a single test:
docker run --rm -it --name qgis --network=docker_default -v $(pwd)'/qgis_tests:/tests_directory' qgis_test_harness:latest ./run_tests.sh test_suite/test_cases/qgis_basic_crud_test.py::QgisBasicCrudTest::test_qgis_create_line_string_water_asset
Running all 'non-point' qgis tests:
docker run --rm -i --name qgis --network=docker_default -v $(pwd)'/qgis_tests:/tests_directory' qgis_test_harness:latest ./run_tests.sh -k 'qgis and not point'
Arguments are passed as-is to pytest. See https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/usage.html#specifying-tests-selecting-tests for more information.
Formatting tests
autopep8 --in-place --recursive docker/qgis_tests/
Procedure for pushing new versions
From the [development branch][development branch] of this repository:
# Create the commit git commit -m "Release version 4.0.1" # Tag the release git tag 4.0.1 # Push the 4.x branch and new tag git push --atomic origin HEAD:4.x 4.0.1