shopsys / deployment
Simplifies the deployment of the Shopsys Platform application in Kubernetes. It provides an intuitive set of tools and configurations, allowing you to seamlessly orchestrate and manage the deployment process.
- dev-main
- v5.0.0
- v4.6.1
- v4.6.0
- v4.5.2
- v4.5.1
- v4.5.0
- v4.4.0
- v4.3.0
- v4.2.0
- v4.1.1
- v4.1.0
- v4.0.11
- v4.0.10
- v4.0.9
- v4.0.8
- v4.0.7
- v4.0.6
- v4.0.5
- v4.0.4
- v4.0.3
- v4.0.2
- v4.0.1
- v4.0.0
- v3.3.4
- v3.3.3
- v3.3.2
- v3.3.1
- v3.3.0
- v3.2.9
- v3.2.8
- v3.2.7
- v3.2.6
- v3.2.5
- v3.2.4
- v3.2.3
- v3.2.2
- v3.2.1
- 3.2.0
- v3.1.0
- v3.0.4
- v3.0.3
- v3.0.2
- v3.0.1
- v3.0.0
- v2.1.2
- v2.1.1
- v2.1.0
- v2.0.1
- v2.0.0
- v1.1.0
- v1.0.3
- v1.0.2
- v1.0.1
- v1.0.0
- dev-rv/security-headers
- dev-rv/fix-img-resizer
- dev-TL/update-nginx
- dev-mg/gopay-notify-be-url
- dev-jg-refactor
- dev-jg-yq-upgrade
- dev-tl-enable-default-whitelist-ips
- dev-rv-language-locales
- dev-tl-ensure-friendly-url-resolver
- dev-mt-deploy-commands
- dev-vitek-rostislav-patch-1
- dev-jg-revert-verbose-logs
- dev-malyMiso-patch-1
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-03-11 16:07:35 UTC
README
How to install
-
Install package
composer require shopsys/deployment -
Copy deploy-project.sh into your project to
app/deploy/deploy-project.sh -
Create or copy htpasswd file with login credentials to
app/deploy/basicHttpAuthDefault login for basicHttpAuth is
username/passwordFor info about how change http auth credentials see Change HTTP auth -
Copy nginx.yaml into your project to
app/orchestration/kubernetes/configmap/nginx.yaml -
Update your
gitlab-ci.yml-
create new stage with name deploy:
stages: - build - test - review + - deploy - service -
Add new deploy template:
.deploy: &deploy image: name: shopsys/kubernetes-buildpack:2.0 stage: deploy tags: - docker rules: - if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "schedule"' when: never script: - docker create -ti --name image ${TAG} bash - docker cp image:/var/www/html/var/ ./ - mkdir -p /root/.kube/ && echo "${KUBE_CONFIG}" > /root/.kube/config - chmod +x ./deploy/deploy-project.sh && ./deploy/deploy-project.sh deploy
-
Add new jobs for deploy devel and production:
deploy:production: <<: *deploy resource_group: deploy_production variables: KUBE_CONFIG: ${KUBE_CONFIG_PROD} needs: - build rules: - if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "schedule"' when: never - if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "master" || $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH =~ /^master-.*$/' when: manual allow_failure: false environment: name: production url: https://${DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_1} deploy:devel: <<: *deploy resource_group: deploy_devel variables: KUBE_CONFIG: ${KUBE_CONFIG_DEVEL} needs: - build - test:standards - test:functional - test:acceptance rules: - if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "schedule"' when: never - if: '$CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "devel" || $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH =~ /^devel-.*$/' environment: name: devel url: https://${DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_1}
-
-
Set Environment variables to in Gitlab (Settings -> CI/CD -> Variables)
-
Push changes and have fun
Environment Variables
Environment variables can be set in Gitlab (Settings -> CI/CD -> Variables)
If you want to define your custom variables see Define custom variables section
| Name | Example | Description | Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEPLOY_REGISTER_USER | deploy | Credentials for downloading docker images *1) | All |
| DEPLOY_REGISTER_PASSWORD | ******* | Credentials for downloading docker images *1) | All |
| DISPLAY_FINAL_CONFIGURATION | 1 OR 0 | Display configurations after kubernetes scripts are prepared | All |
| RUNNING_PRODUCTION | 1 OR 0 | Enable/disable HTTP auth and mailer whitelist | production/devel |
| FIRST_DEPLOY | 1 OR 0 | Set to 1 if you are deploying project instance first time | production/devel |
| DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_* | example.com | Variable contains URL address for accessing website. See Add more or less domains | production/devel |
| ELASTICSEARCH_URL | username:password@elasticsearch | Elasticsearch login URL | All |
| POSTGRES_DATABASE_IP_ADDRESS | 127.0.0.1 | Postgres host IP address | production/devel |
| POSTGRES_DATABASE_PORT | 5432 | Postgres port | All |
| POSTGRES_DATABASE_PASSWORD | ******* | Postgres login password | production/devel |
| PROJECT_NAME | project-prod | Name of project (Used for namespace, prefixes and S3 bucket) - must be distinct for production/devel with prod/devel suffix | production/devel |
| S3_API_HOST | https://s3.vshosting.cloud | S3 API Host | All |
| S3_API_USERNAME | s3user | S3 API username | All |
| S3_API_PASSWORD | ******* | S3 API password | All |
| APP_SECRET | ******* | Used to add more entropy to security related operations | All |
| RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER | rabbitadmin | Default user used for RabbitMQ and the management service | All |
| RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS | ******* | Password for the default RabbitMQ user | All |
| RABBITMQ_IP_WHITELIST | 123.456.123.422, 423.534.223.234 | IP Addresses (separated by comma) for which is the RabbitMQ Management accessible | All |
| USING_CLOUDFLARE | 1 OR 0 | Set to 1 if your site is using Cloudflare (enables IP whitelisting) | production/devel |
*1) Credentials can be generated in Gitlab (Settings -> Repository -> Deploy Tokens) with read_registry scope only
You can add your custom variables. Do not forget to edit your deploy-project.sh file
Customize deployment
You can override Kubernetes manifests by placing your custom manifests into app/orchestration/kubernetes/ in your project.
You need to mirror folders to be able to override manifests
Create new cron instance
-
Create new Phing target that will run your cron:
<target name="cron-customers" description="...."> <exec executable="${path.php.executable}" passthru="true" checkreturn="true"> <arg value="${path.bin-console}" /> <arg value="shopsys:cron" /> <arg value="--instance-name=customers" /> </exec> </target>
-
Declare new cron to your deploy configuration file (
deploy-project.sh):As a key there is used phing target that you created in step 1. and value represents crontab timer
... declare -A CRON_INSTANCES=( ["cron"]='*/5 * * * *' + ["cron-customers"]='*/5 * * * *' ) ...
Add more or less domains
This example will work with 3 domains
-
Create environment variable for every domain:
Name Value DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_1 mydomain.prod.shopsys.cloud DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_2 sk.mydomain.prod.shopsys.cloud DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_3 en.mydomain.prod.shopsys.cloud -
Edit your
deploy-project.shfile:... function deploy() { DOMAINS=( DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_1 DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_2 + DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_3 ) ...
Define custom variables
- Create Environment variable
- Edit your
deploy-project.shfile:... declare -A ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLES=( ["DATABASE_HOST"]=${POSTGRES_DATABASE_IP_ADDRESS} ["DATABASE_NAME"]=${PROJECT_NAME} ["DATABASE_PORT"]=${POSTGRES_DATABASE_PORT} ) ...Left part is name of variable in application and right part is name of variable Gitlab.
Set custom Redis version
Add new variable to deploy-project.sh and specify your redis version
...
BASIC_AUTH_PATH="${BASE_PATH}/deploy/basicHttpAuth"
DEPLOY_TARGET_PATH="${BASE_PATH}/var/deployment/deploy"
+ REDIS_VERSION='redis:4.0-alpine'
function deploy() {
...
Enable Horizontal pod autoscaling
Add new variables to deploy-project.sh to enable pod autoscaling:
- Enable this functionality:
... function deploy() { DOMAINS=( DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_1 ... ) + ENABLE_AUTOSCALING=true ... - If you need more replicas, then you can adjust those variables (default values are set to 2):
MIN_PHP_FPM_REPLICASMAX_PHP_FPM_REPLICASMIN_STOREFRONT_REPLICASMAX_STOREFRONT_REPLICAS
How to launch only some domains
Add to deploy-project.sh new array FORCE_HTTP_AUTH_IN_PRODUCTION with domains which should be not accessible without HTTP auth:
...
)
+ # This setting has no effect when `RUNNING_PRODUCTION` is set to `0`
+ FORCE_HTTP_AUTH_IN_PRODUCTION=(
+ DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_2
+ )
declare -A ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLES=(
...
Change HTTP auth
- Generate new HTTP auth string (for example here), or by command
htpasswd -nb username password - Replace or add new HTTP auth string to
basicHttpAuth - Set new credentials to variable in
deploy-project.sh
...
function deploy() {
DOMAINS=(
DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_1
...
)
+ HTTP_AUTH_CREDENTIALS="username:password"
...
Whitelist IP addresses
There are two ways to set whitelisted IP addresses.
WHITELIST_IPS env variable on CI
You can set sensitive whitelisted IPs in your env variable like this:
WHITELIST_IPS="8.8.8.8, 217.23.44.23, 93.111.234.111"
DEFAULT_WHITELIST_IPS env variable in deploy-project.sh
For non-sensitive IPs, that you want to share between all environments you can use DEFAULT_WHITELIST_IPS in deploy-project.sh like this:
# Some IP Another IP Some service DEFAULT_WHITELIST_IPS="8.8.8.8, 217.23.44.23, 93.111.234.111"
Values from both variables (WHITELIST_IPS and DEFAULT_WHITELIST_IPS) will be merged and used in the final configuration.
Configure Cloudflare
If your site is using Cloudflare, you can restrict direct access and allow traffic only through Cloudflare:
- Enable Cloudflare protection by setting the environment variable
USING_CLOUDFLARE=1. - By default, ALL domains will be protected. If you need to exclude specific domains from Cloudflare protection (e.g., for direct access or testing), add them to the
CLOUDFLARE_EXCLUDED_DOMAINSarray:... + CLOUDFLARE_EXCLUDED_DOMAINS=( + DOMAIN_HOSTNAME_2 # This domain will not have Cloudflare IP restrictions + ) ...
This prevents users from bypassing Cloudflare by accessing your origin server directly.
Notify about deployment on Slack
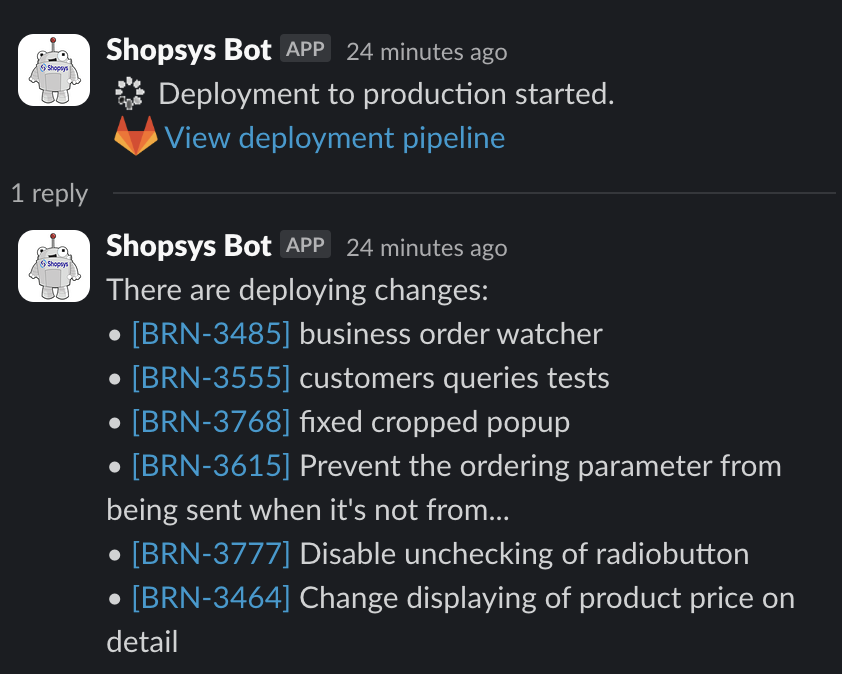
You can enable automatic notification of your deployment directly into Slack channel. It has some features:
- Notify about starting of deployment with a preview of features
Tip
If you are using Jira and you use [ABC-123] in the commit message, it will automatically create a link to the URL that is specified by JIRA_URL environment variable
Tip
Script will exclude commits that contain !ignore keyword
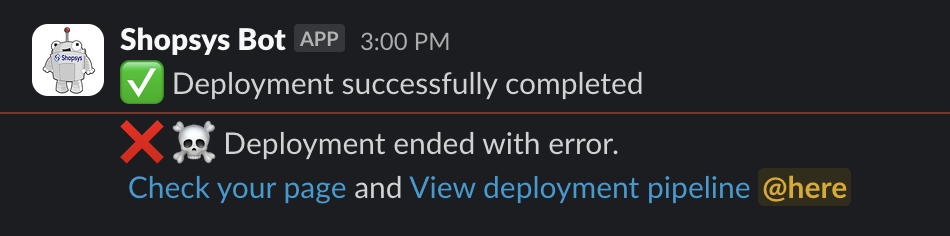
- Notify about the end of deployment. There are two possible alerts - Success and Error
This script works only with Gitlab and Slack, but you can override deploy/slack-notification.py if you want to change behavior. For Slack, you have to create some Slack App with permissions (chat:write, chat:write.public).
There has to be set some environment variables list in the table bellow:
| ENVIRONMENT VARIABLE | Additional information |
|---|---|
CI_API_V4_URL |
Automatic by Gitlab |
CI_PROJECT_ID |
Automatic by Gitlab |
CI_JOB_URL |
Automatic by Gitlab |
CI_COMMIT_SHA |
Automatic by Gitlab |
API_TOKEN |
Token for Gitlab API that has access to read deployments |
JIRA_URL |
Set URL for link Jira ID to Jira. |
SLACK_TOKEN |
Slack Bot User OAuth Token |
SLACK_CHANNEL |
Channel ID to post messages into. This variable should be set only for production Environment |
SLACK_DISABLE_CHANGES |
If set to true, no message with changes will be posted |
Run background jobs only on selected nodes
Backend pods such as RabbitMQ, Cron and Consumers can be run only on selected nodes. Those pods have already configured tolerations, so you can use taints to select nodes where those pods will be run.
Add taint to nodes where you want to run those pods
kubectl label nodes <node-name> workload=background kubectl taint nodes <node-name> workload=background:NoSchedule
Other pods will run on other nodes without this taint.