nickjbedford / laravel-transactions
Provides a simple class structure for building complicated transactions in Laravel project that handle failure.
Installs: 167
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 1
Watchers: 1
Forks: 0
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/nickjbedford/laravel-transactions
Requires
- php: >=7.4
- laravel/framework: >=5.8
Requires (Dev)
README
Laravel Transactions provides a class structure for building complicated transactions in Laravel project that handle failure.
By deriving from the YetAnother\Laravel\Transaction abstract
class and implementing the perform() and optional validate()
and cleanupAfterFailure() methods, you can write complicated
transactional actions that maintain integrity of state not
only within the database, but in external systems as well.
For example, when dealing with file uploads, your Transaction
subclass should maintain a list of successfully uploaded files
that should be deleted when the cleanupAfterFailure() method is
called by the base class in the case of an exception.
Brief Overview
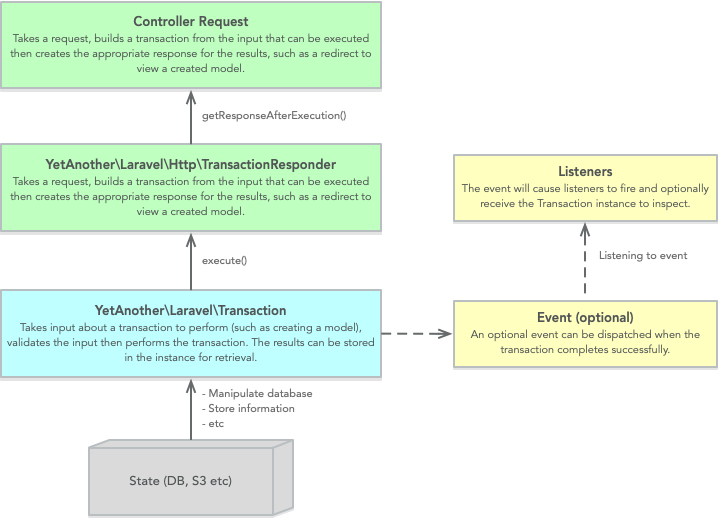
This library provides two abstract classes you can derive from to implement transactional database-related processes that may cause external side effects that require cleanup when errors occur, such as file uploads to a storage service.
These classes are:
// Used by business logic to perform transactional changes. abstract class YetAnother\Laravel\Transaction // Used by controllers to wrap [ request -> transaction -> response ] processes. abstract class YetAnother\Laravel\Http\TransactionResponder
It also provides two artisan commands to make new subclasses of these base classes.
php artisan make:transaction CustomTransaction php artisan make:responder CustomTransactionResponder
These generated classes are placed in the app/Transactions
and app/Http/Responders project directories.
Installation
To install Laravel Transactions into your Laravel project, bring up a terminal and run the following command:
composer require nickjbedford/laravel-transactions
This will add the package to your Composer package file and download the package to the projec's vendor folder.
Laravel Transactions Service Provider
To automatically register the package's artisan commands
make:transaction and make:responder, add the
YetAnother\Laravel\Providers\TransactionsServiceProvider
class to your project's config/app.php file in the providers array.
'providers' => [ // ... \YetAnother\Laravel\Providers\TransactionsServiceProvider::class, ],
Transaction Execution Process
When $transaction->execute() is called, a Laravel DB transaction context
is established that will catch any thrown exceptions and roll back
the changes to the database. External cleanup is handled as well,
if implemented correctly.
Exceptions should be thrown by both the subclass' implementations
of the validate() and perform() methods to rollback and cleanup
the transactions changes.
Optional methods have been added to allow for detailed processing of a
transaction's flow outside the DB transaction itself.
public function execute(): self { try { $this->lockTableIfNecessary(); $this->beforeTransaction(); DB::transaction(fn() => $this->validateAndPerform()); } catch(Throwable $exception) { $this->revertSideEffects(); $this->cleanupAfterFailure(); throw $exception; } finally { $this->afterTransaction(); $this->unlockTableIfNecessary(); $this->finally(); } $this->fireEvent(); return $this; }
Primary Virtual Methods
protected function validate() { }
This is an optional override and allows the transaction to separate validation checks before the actual work is performed.
If an action or parameter is not valid, an Throwable of any type
should be thrown for the execute() method to catch and handle roll
back and cleanup of the transaction.
protected abstract function perform()
This method must be overridden by subclasses to perform the changes
necessary. Database changes are committed or rolled back automatically,
however if an exception is thrown, external side effects must be cleaned
up by the cleanupAfterFailure() method.
Secondary Virtual Methods
protected function cleanupAfterFailure() { }
To handled cleanup of transaction side effects such as file uploads or changes to external services, this method should be overridden to do so. The subclass should maintain a list of reversible actions it may need to take, such as file paths to delete on failure.
protected function beforeTransaction/afterTransaction() { }
To perform custom processing before and after the transaction
regardless of success or failure, the beforeTransaction() and
afterTransaction() methods should be overriden.
protected function finally() { }
To perform code in the finally block after all other processing
regardless of success or failure, after all other methods,
override the finally() method.
Transaction Examples
The following is an example of a transaction that not only has to create a new record in the database, it must also upload a file to Amazon's S3 storage service.
In the case one or either processes fail, the database changes will automatically be rolled back by the base class, but it is up to the subclass to remove any external side effects, which in this case means to delete the file from S3 if the database fails to update.
use Illuminate\Http\UploadedFile; use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Storage; use YetAnother\Laravel\Transaction; use App\Models\Attachment; /** * Represents a transaction that must upload a file to a * storage destination and update the database. */ class UploadAttachmentTransaction extends Transaction { private ?string $uploadedFilePath = null; private UploadedFile $file; public ?Attachment $model = null; public function __construct(UploadedFile $file) { $this->file = $file; } /** * Validates the action before it is performed. * @throws Throwable */ protected function validate() : void { $extension = strtolower($this->file->getClientOriginalExtension()); if (!in_array($extension, [ 'png', 'jpg', 'jpeg', 'gif' ])) throw new InvalidArgumentException('Uploaded file is not a valid file type.'); } /** * Uploads the file to Amazon S3 then creates an * Attachment model in the database. * @throws Exception */ protected function perform() : void { $this->uploadFileToS3(); $this->createAttachment(); } protected function uploadFileToS3(): void { $path = 'some/path/to/' . $this->file->getClientOriginalName(); $s3 = Storage::disk('s3'); if ($s3->put($this->file, $path)) $this->uploadedFilePath = $path; } protected function createAttachment(): void { $this->model = Attachment::create([ 'disk' => 's3', 'path' => $this->uploadedFilePath ]); } /** * Deletes the file from S3 if any processes afterwards * failed. The database transaction has already been rolled * back at this time. */ public function cleanupAfterFailure() : void { parent::cleanupAfterFailure(); if ($this->uploadedFilePath) { $s3 = Storage::disk('s3'); $s3->delete($this->uploadedFilePath); } } }
Transaction Event Firing
Transactions can additionally fire an event when they complete successfully.
To specify the type of event class to fire, override the $event property
as follows. The event will be fired after the database transaction has
committed and no exceptions have been thrown.
Define Transaction Event
namespace App\Events; use Illuminate\Foundation\Events\Dispatchable; use Illuminate\Queue\SerializesModels; use YetAnother\Laravel\Transaction; /** * This event is fired after the transaction completes. */ class TransactionComplete { use Dispatchable, SerializesModels; public function __construct(Transaction $transaction) { // } }
Specify Event Class To Fire
use YetAnother\Laravel\Transaction; use App\Events\TransactionComplete; class EventFiringTransaction extends Transaction { protected ?string $event = TransactionComplete::class; protected function perform() : void { // } }
By default, this will try to pass the transaction instance to the
event's constructor if it accepts a parameter. If you wish to
create a custom event for dispatch, override the createEventInstance()
method as follows:
use YetAnother\Laravel\Transaction; use App\Events\TransactionComplete; class EventFiringTransaction extends Transaction { protected function perform() : void { // } /** * Create a custom event to dispatch. * @return mixed */ protected function createEvent() { return new TransactionComplete($this); } }
Transaction Responders
Due to Laravel's automatic response handling, it's possible
for a controller method to return an object and for the
request to be handled and transacted into a response
automically using the TransactionResponder base class.
Transaction Responders can almost be considered the "executing view" of a Transaction when used in the context of a controller action.
For example, a controller's store method can return a transaction responder designed to create a model from a request then provide the correct response.
use Illuminate\Contracts\Support\Responsable; use Illuminate\Http\Request; use Illuminate\Routing\Controller; class ModelController extends Controller { /** * Stores the model and redirects to the show action. * @param Request $request * @return Responsable */ public function store(Request $request): Responsable { return new CreateModelTransactionResponder(); } }
Laravel and the TransactionResponder class does the
rest by asking the responder for a transaction to execute.
Once the transaction is successful, the response is requested from the subclass. This could be a JSON response, a redirect or any other type of valid Laravel response.
use Illuminate\Http\Request; use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response; use YetAnother\Laravel\Http\TransactionResponder; use YetAnother\Laravel\Transaction; use App\Transactions\CreateModelTransaction; class CreateModelTransactionResponder extends TransactionResponder { /** * Creates the appropriate response for a successful transaction. * @param Transaction $transaction * @return Response */ protected function getResponseAfterExecution(Transaction $transaction): Response { /** @var CreateModelTransaction $transaction */ $redirectTo = route('model.show', [ 'model' => $transaction->model->id ]); return redirect($redirectTo); } /** * Creates the desired transaction from an incoming request. TransactionResponder * will execute this transaction. * @param Request $request * @return Transaction */ protected function createTransaction(Request $request): Transaction { $name = trim($request->name); $description = trim($request->description); return new CreateModelTransaction($name, $description); } /** * Overrides the response to return when a transaction fails with an exception. * By default, this throws the exception onto Laravel's handling mechanisms, but * this could be used to return a structured JSON response or other custom response. * @param Throwable $exception * @return Response */ protected function exceptionToResponse(Throwable $exception) : Response { return response()->json([ 'status' => false, 'error' => $exception->getMessage(), 'code' => $exception->getCode() ]); } }