madison-solutions / just-date
PHP library for dealing with dates without any time information
Installs: 4 706
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 0
Watchers: 1
Forks: 1
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/madison-solutions/just-date
Requires
- php: ^8.1
- ext-json: *
Requires (Dev)
- laravel/pint: ^1.17
- phpstan/phpstan: ^1.10
- phpunit/phpunit: ^10.3
README
PHP library for dealing with dates without any time information, and times without any date information
There are several excellent PHP libraries for working with DateTime objects. But sometimes you need to deal with only the date part, or only the time part of a DateTime object.
For example, a hotel booking system might care only about a guest's check-in date - and the exact time of arrival is unimportant. In those situations, all of the functionality relevant to the time of day just gets in the way, making things like comparisons and equality checks awkward. Added complications like timezones and daylight saving time further muddy the waters.
This library aims to make it simple to work with just the date part, or just the time part.
See below for a quick guide to the functionality, with some examples, or see the API reference here.
Note these instructions are for version 2 - see the migration guide for help migrating from version 1.
Install
composer require madison-solutions/just-date
JustDate
Represents a single date with no time information
Basic Use
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustDate; $date = JustDate::make(2019, 4, 21); (string) $date; // 2019-04-21 $date->format('D F jS Y'); // Sun April 21st 2019 $date->year; // 2019 $date->month; // 4 $date->day; // 21 $date->day_of_week; // DayOfWeek::Sunday $data->day_of_week->value; // 0 $date2 = JustDate::fromYmd('2019-04-22'); $date->isBefore($date2); // true
Time is ignored
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustDate; $t1 = new DateTime('2019-04-21 16:23:12', new DateTimeZone('Australia/Sydney')); $t1->format('r'); // Sun, 21 Apr 2019 16:23:12 +1000 $d1 - JustDate::fromDateTime($t1); $d1->format('r'); // Wed, 24 Apr 2019 00:00:00 +0000 // Different time, different timezone, but the date part is the same $t2 = new DateTime('2019-04-21 19:05:47', new DateTimeZone('Europe/London')); $d2 = JustDate::fromDateTime($t2); $d1->isSameAs($d2); // true
Today's date
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustDate; // The current date, in the local timezone $today = JustDate::today(); // What date is is right now in Denver? $today_in_denver = JustDate::today(new DateTimeZone('America/Denver'));
Traversing the calendar
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustDate; $d1 = JustDate::make(2019, 04, 21); $d2 = $d1->nextDay(); (string) $d2; // 2019-04-22
Note JustDate objects are immutable - nextDay() and all other similar methods return new instances of JustDate!
(string) $d1->prevDay(); // 2019-04-20 (string) $d1->addDays(3); // 2019-04-24 (string) $d1->startOfMonth(); // 2019-04-01 (string) $d1->endOfMonth(); // 2019-04-30 // What day was it on this day 2 years ago? JustDate::make($d1->year - 2, $d1->month, $d1->day)->format('l'); // Friday // Find the previous Wednesday $date = $d1; while (! $date->isWednesday()) { $date = $date->prevDay(); } $date->format('D F jS Y'); // Wed April 17th 2019 // How many days is it until the start of the next month? JustDate::difference($d1, $d1->endOfMonth()->nextDay()) // 10
Working days
// Add a certain number of 'working' days $holidays = new DateSet(...[ JustDate::make(2023, 12, 25), // Christmas JustDate::make(2023, 12, 26), // Boxing Day JustDate::make(2024, 1, 1), // New Year's Day ]); $order_date = JustDate::make(2023, 12, 28); // Delivery in 3 working days // 29th Dec is Friday (a working day), 30 & 31 are weekend, 1st is holiday, 2nd and 3rd are next 2 working days $delivery_date = $order_date->addWorkingDays(3, $holidays); // Wed 3rd Jan 2024
DateRange
Represents a range of dates between some start date and some end date (with no time information).
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\DateRange; use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustDate; $start = JustDate::make(2019, 04, 21); $end = $d1->addDays(4); $range = DateRange::make($start, $end); (string) $range; // 2019-04-21 to 2019-04-25 (string) $range->start; // 2019-04-21 (string) $range->end; // 2019-04-25 $range->includes(JustDate::make(2019, 04, 22)); // true // alternatively create from strings $range = DateRange::fromYmd('2019-04-21', '2019-04-25');
Note you can't create a range where $start is after $end
$illegal_range = DateRange::make(JustDate::fromYmd('2019-04-22'), JustDate::fromYmd('2019-04-20')); // Throws an \InvalidArgumentException
If you're not sure which of your 2 dates comes first, you can use eitherWayRound().
$range = DateRange::eitherWayRound(JustDate::fromYmd('2019-04-22'), JustDate::fromYmd('2019-04-20')); $range->start; // 2019-04-20 $range->end; // 2019-04-22
Intersection of 2 ranges
$range2 = DateRange::fromYmd('2019-04-18', '2019-04-23'); (string) DateRange::intersection($range, $range2); // 2019-04-21 to 2019-04-23 $range3 = DateRange::fromYmd('2019-04-18', '2019-04-19'); DateRange::intersection($range, $range3); // null - they don't intersect
Iterating over a range
foreach ($range->each() as $date) { echo $date->format('d') . ","; } // 21,22,23,24,25, foreach ($range->each(backwards: true) as $date) { echo $date->format('d') . ","; } // 25,24,23,22,21,
Length of a DateRange
Whenever you talk about the 'length' of a date range, there's an ambiguity about what this means.
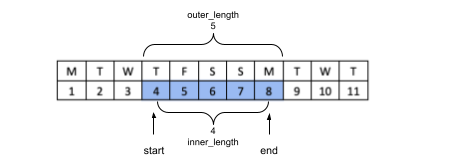
For example, if you have a DateRange where $start is Tuesday 4th, and $end is Monday 8th, as per the diagram below, then what should the 'length' of the range be?
There are 2 fairly reasonable, but different definitions.
You could count the number of days that are included in the range (inclusive of start and end dates). In the example above the answer would be 5. This could also be thought of as the length in days, measured from the first second of the start date to the last second of the end date. By this definition, the smallest possible DateRange, where start and end are the same day, would have length 1.
Alternatively you could define the length by subtracting the start date from the end date. In the example above, the answer would be 8 - 4 = 4. This could also be thought of as the length in days, measured from the middle of the start date to the middle of the end date, or as the number of nights that occur between the start and end date. By this definition, the smallest possible DateRange, where start and end are the same day, would have length 0.
The DateRange class provides both options - the first is accessed as $range->outer_length and the second is accessed as $range->inner_length.
$range = DateRange::fromYmd('2019-04-04', '2019-04-08'); $range->inner_length; // 4 $range->outer_length; // 5
JustTime
Represents a time without any date information.
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustTime; $time = JustTime::make(17, 45, 30); (string) $time; // 17:45:30 $time->format('g:ia'); // 5:45pm $time->hours; // 17 $time->minutes; // 45 $time->seconds; // 30 $time->since_midnight; // 63930 $time2 = JustTime::fromHis('17:55:00'); $time->isBefore($time2); // true $time3 = JustTime::fromSecondsSinceMidnight(125); // 00:02:05
Date info is ignored
The date part is removed, as well as the timezone. If date parameters are used in a format string, the date will be 1 Jan 1970 (unix epoch).
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustTime; $t1 = new DateTime('2019-04-21 16:23:12', new DateTimeZone('Australia/Sydney')); $t1->format('r'); // Sun, 21 Apr 2019 16:23:12 +1000 $time1 - JustTime::fromDateTime($t1); $time1->format('r'); // Thu, 01 Jan 1970 16:23:12 +0000 // Different date, different timezone, but the time part is the same $t2 = new DateTime('2018-10-06 16:23:12', new DateTimeZone('Europe/London')); $time2 = JustTime::fromDateTime($t2); $time1->isSameAs($time2); // true
The time now
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustTime; // The current time, in the local timezone $now = JustTime::now(); // What time is is right now in Denver? $time_now_in_denver = JustTime::now(new DateTimeZone('America/Denver'));
Traversing the clock
Note JustTime objects are immutable - addTime() returns new instances of JustTime!
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustTime; $t1 = JustTime::make(12, 0, 0); $t2 = $t1->addTime(2, 30, 10); (string) $t2; // '14:30:10' $t3 = $t1->addTime(14, 0, 0); (string) $t3; // '02:00:00' $t4 = $t1->addTime(0, 0, -1); (string) $t4; // '11:59:59'
Rounding to a certain interval
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\JustTime; $t1 = JustTime::make(12, 47, 10); // round to nearest minute $t2 = $t1->round(60); // 12:47:00 // round to nearest quarter of an hour $t3 = $t1->round(15 * 60); // 12:45:00
DateSet and MutableDateSet
Represent a set of dates (not necessarily a continuous range). MutableDateSet can have dates added or removed, DateSet cannot be changed after it is created.
use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\DateSet; use MadisonSolutions\JustDate\MutuableDateSet; // Create a DateSet from any number of JustDate or DateRange objects (or other DateSet objects) $set = new DateSet(JustDate::fromYmd('2023-11-17'), DateRange::fromYmd('2023-10-01', '2023-10-10'), JustDate::fromYmd('2023-10-05')); // Dates in the sets are automatically de-duplicated and sorted (string) $set; // '2023-10-01 to 2023-10-10, 2023-11-17' $set->includes('2023-10-11'); // false $mset = new MutableDateSet(); $mset->isEmpty(); // true $mset->add(JustDate::fromYmd('2023-11-17')); (string) $mset; // '2023-11-17' $mset->add(DateRange::fromYmd('2023-10-01', '2023-10-10')); (string) $mset; // '2023-10-01 to 2023-10-10, 2023-11-17'
Combining / Comparing DateSets
$a = new DateSet(DateRange::fromYmd('2023-11-05', '2023-11-09')); $b = new DateSet(DateRange::fromYmd('2023-11-08', '2023-11-12')); DateSet::union($a, $b); // 2023-11-05 to 2023-11-12 DateSet::intersection($a, $b); // 2023-11-08 to 2023-11-09 $a->subtract($b); // 2023-11-05 to 2023-11-07 $b->subtract($a); // 2023-11-10 to 2023-11-12
The contains($other) method of DateSet and MutableDateSet can be used to compare with other objects to test whether they contain all of the dates in the other object. The other object does not have to be the same type, it can be a JustDate, DateRange, DateSet or MutableDateSet (or anything else implementing the DateRangeList interface).
$jan_and_march = new DateSet(DateRange::fromYmd('2024-01-01',' 2024-01-31'), DateRange::fromYmd('2024-03-01', '2024-03-31')); $jan_and_march->contains(DateRange::fromYmd('2024-01-10', '2024-01-20')); // true $jan_and_march->contains(DateSet::fromString('2024-01-01, 2024-01-17, 2024-03-05')); // true $jan_and_march->contains(JustDate::fromYmd('2024-02-10')); // false
The isSameAs($other) method of DateSet and MutableDateSet can be used to compare with other objects to test whether they contain the exact same set of dates. Again the other object does not have to be the same type.
$set = new DateSet(JustDate::fromYmd('2024-08-01'), JustDate::fromYmd('2024-08-02'), JustDate::fromYmd('2024-08-03')); $set->isSameAs(DateRange::fromYmd('2024-08-01', '2024-08-03')); // true - $set contains the exact same 3 dates that are in the DateRange
Iterating over a DateSet
You can choose to iterate over the continuous ranges in the set, or over the individual dates.
$set = new DateSet(JustDate::fromYmd('2023-10-17'), DateRange::fromYmd('2023-10-20', '2023-10-25')); foreach ($range->eachRange() as $range) { echo $range->start->format('d') . '-' . $range->end->format('d') . ", "; } // 17-17, 20-25, foreach ($range->eachDate() as $date) { echo $date->format('d') . ","; } // 17,20,21,22,23,24,25,