lxlang / rdp
Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm for polyline simplification
Installs: 4 053
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 0
Watchers: 0
Forks: 7
pkg:composer/lxlang/rdp
Requires
- php: >=8.0
Requires (Dev)
- phpunit/phpunit: ^11.0
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-01-27 16:59:40 UTC
README
PHP implementation of the Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm for polyline simplification.
License: Public Domain
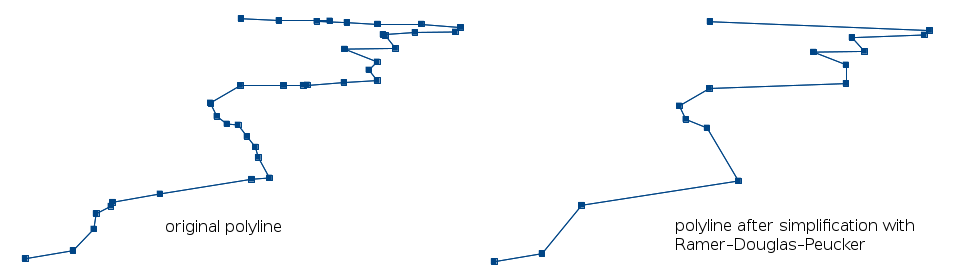
Example simplified polyline
Installation
composer require david-r-edgar/rdp
Example usage
use davidredgar\polyline\RDP;
$line = array(
array(150, 10),
array(200, 100),
array(360, 170),
array(500, 280));
$rdpResult = RDP::RamerDouglasPeucker2d($line, 30);
$rdpResult will contain a resulting array with the reduced number of points. For this example:
$rdpResult == array(
array(150, 10),
array(200, 100),
array(500, 280));
The second parameter to RamerDouglasPeucker2d() is epsilon, the maximum perpendicular distance for any point from the line between two adjacent points. Try replacing it with, say, 10 or 50 and observe the results.
Use for geographic purposes
I originally implemented this in order to simplify a complex route on a map. Because I was doing this in Great Britain with OSGB36 coordinates, this worked.
However, be careful if you want to want to attempt this with other coordinate systems. The algorithm assumes cartesian coordinates on a 2D plane. Attempting to use latitudes and longitudes on the surface of a sphere will result in incorrect results. For approximate polyline simplification, the results may still be acceptable. As you approach the poles, errors will become more and more apparent: put simply, the degrees of longitude will become much closer to one another than the degrees of latitude, and so incorrect points will be chosen to be removed from the polyline.