kegi / php-error-handler
Requires
- php: >=7.0
- filp/whoops: ^2.1
- psr/log: ^1.0
This package is not auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-03-01 04:04:07 UTC
README
PHP7; Object oriented error handler. This is an alpha version.
#Introduction
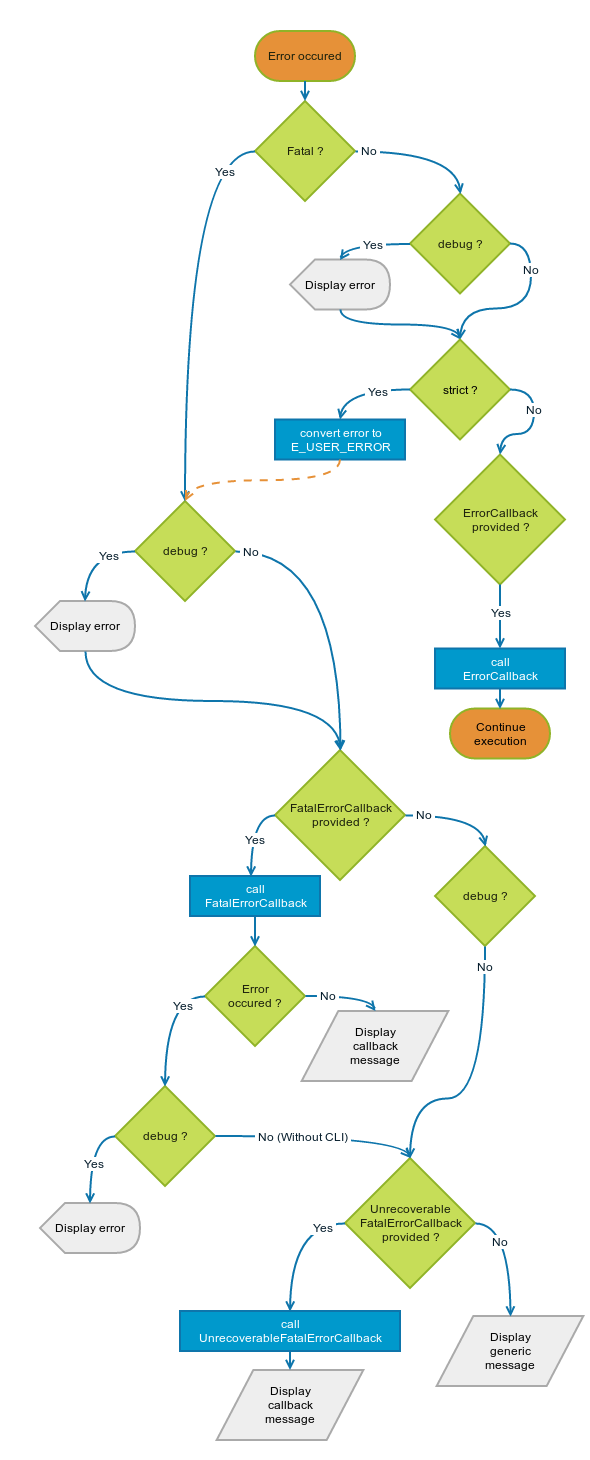
This error handler detects PHP errors, convert them into exceptions and let you handle them easilly. Aditionnaly, this library handle the output buffering to avoid uncompleted body response. This library optionnaly log errors (accepts PSR Interface).
Installation
Install this library with Composer
composer require kegi/php-error-handler
Debug mode
disabled by default
- With debug enabled, errors are displayed normally (you are still notifided).
- With debug disabled, all errors are hidden, you are notified and it's your job to return an error message.
Strict mode
disabled by default
Strict mode will convert all non-fatal errors into fatal errors.
Complexe error handling runtime
You can execute complexe code if a fatal error is detected. (eg. you can call your errorController, build a response from a template according to the user's language settings...)
If an other fatal error occured while handling this fatal error... (eg. a fatal error on the core of your app), you'll be notified that an unrecoverable error occured and you'll be able to return an error message (eg. return the content of a static error html page).
#How to implement it on your project
-
you instanciate PhpErrorHandler at the very beggining of your project.
-
you provided a callable function for the wanted error level (non-fatal, fatal and unrecoverable).
-
the uncaught exception of your project will naturally go on your fatal error method. You don't need to handle them differently anymore.
#Example
<?php namespace Your\Project\Bootstrap; use KeGi\PhpErrorHandler\PhpErrorHandler; use KeGi\PhpErrorHandler\PhpFatalErrorException; class App { public function __construct() { /*instanciate the error handler*/ (new PhpErrorHandler()) ->setDebug(false) //prod #->setErrorCallback([$this, 'handleError']) //most projects don't need this ->setFatalErrorCallback([$this, 'handleFatalError']) ->setUnrecoverableErrorCallback([$this, 'handleUnrecoverableError']); } public function run() { //run your application... throw new \Exception('Uncaught exception'); //or... trigger_error('Uncaught error', E_USER_ERROR); } public function handleFatalError(PhpFatalErrorException $phpFatalErrorException) { // you can check the php error like this : if($phpFatalErrorException->getCode() === E_PARSE){ //parse error occured... } // you would normally call your router and emit a response return 'A fatal occured occured...'; } public function handleUnrecoverableError() { //you could include a static error page //eg. return include '/static/server-error.html'; return 'A very bad error occured'; } }
#Command line (CLI)
The errors on command line will also be handled.
- In case of a fatal error, the output buffer won't be clear in CLI. (There is no output buffer)
- In case of a second level fatal error, the unrecoverable callback won't be used in CLI.
#Unit testing coming soon
#Output buffering It's a good practice to build a response object and to emit it when ready, most php router do that. If your project generate content directly (eg. echo, print, var_dump...), this will also be handled.
If a fatal error occured with debug mode disabled, the content already generated will be dismiss so only our error response is visible.
On the error callbacks, you can echo directly your message or return a string.
#Parameters ##Constructor If you don't want the library to changed php errors settings (ini_set and error_reporting), set $setErrorDisplay to false on the constructor.
__construct(
bool $debug = false,
bool $strict = false,
$errorCallback = null,
$fatalErrorCallback = null,
$unrecoverableErrorCallback = null,
$errorLogger = null,
bool $setDisplayErrors = true
)
##Debug mode Set/unset debug mode. (default: false)
setDebug(bool $debug)
hasDebug() : bool
##Strict mode Set/unset strict mode. With strict mode enabled, non-fatal php error (such as E_NOTICE) are converted into fatal error. (default: false)
setStrict(bool $strict)
isStrict() : bool
##Error callback Set/unset error callback. This will be call for every single php (non-fatal) error. Most project don't need this.
setErrorCallback([mixed $callable])
getErrorCallback() : mixed
##Fatal error callback Set/unset fatal error callback. This will be call in case of a fatal error. You can print or return your input.
setFatalErrorCallback([mixed $callable])
getFatalErrorCallback() : mixed
##Unrecoverable error callback Set/unset fatal error callback. This will be call in case of a fatal error from "fatalErrorCallback" or if don't have a fatal error callback defined. You can print or return your input.
setUnrecoverableErrorCallback([mixed $callable])
getUnrecoverableErrorCallback() : mixed
##Error logger Set/unset error logger. ErrorLogger need to implement PSR Logger interface. Note: Logs are enabled with or without debug mode.
setErrorLogger([LoggerInterface $errorLogger])
getErrorLogger() : mixed
##Cancel This will cancel the error handler. Once its cancelled, you can't re-enabled it. You'll still be able to read values of the handler (getters). Trying to edit value of the handler (setters) will throw an exception.
cancel()
isCancelled() : bool