jeromesiau / filament-multilang
Multi-language input component for Filament 3
Installs: 195
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 0
Watchers: 1
Forks: 0
Open Issues: 0
pkg:composer/jeromesiau/filament-multilang
Requires
- php: ^8.1
- filament/filament: ^3.0
- spatie/laravel-translatable: ^6.0
README
A component for managing multilingual fields in Filament 3, integrated with Spatie Laravel Translatable.
Why This Plugin?
This plugin was created to offer a focused, input-level approach to multilingual content in Filament forms, unlike other solutions that implement translations at the page or fieldset level.
Key features:
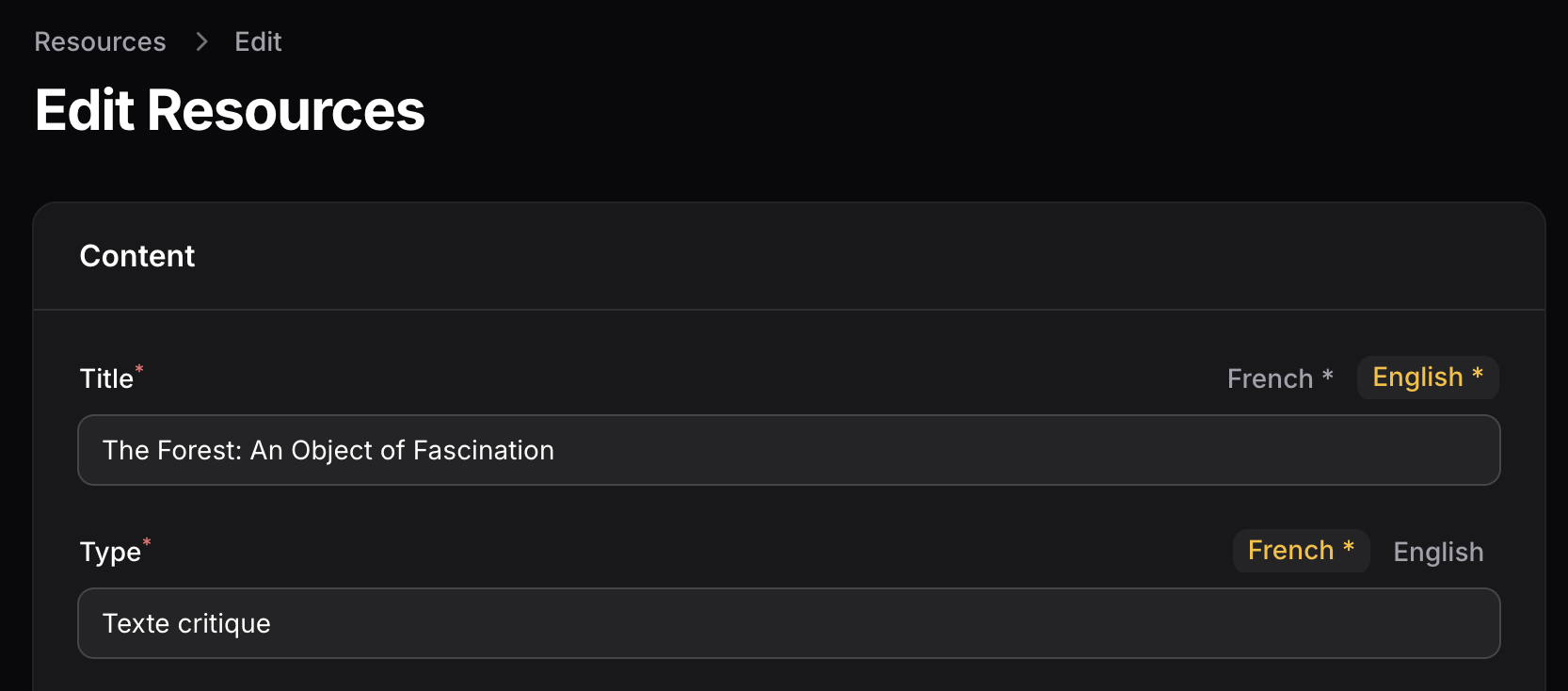
- Input-level language tabs: Each translatable field has its own compact set of language tabs directly on the input
- Flexible validation: Define which languages are required on a per-field basis
- Multiple input types: Works seamlessly with both standard text inputs and rich text editors
The goal is to provide a streamlined editing experience for multilingual content that feels natural and integrated with Filament's design philosophy.
Installation
You can install the package via composer:
composer require jeromesiau/filament-multilang
This package automatically integrates Spatie Laravel Translatable to efficiently manage translations storage.
To configure available languages, you can publish the configuration file:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag="filament-multilang-config"
The published configuration file will look like this:
return [ 'locales' => [ 'fr' => ['name' => 'French'], 'en' => ['name' => 'English'], ], ];
Simply modify the locales array to add, remove, or change the available languages for your application. Each language requires a key (language code) and a name that will be displayed in the language tabs.
By default, when displaying values in Filament tables, the component will use the translation that corresponds to your application's current locale (APP_LOCALE environment variable by defaut). This ensures a consistent display in listings while still maintaining full multilingual capabilities in forms.
Model Configuration
To use the component with your models, make sure they use Spatie's HasTranslations trait:
use Spatie\Translatable\HasTranslations; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model; class Page extends Model { use HasTranslations; public $translatable = ['title', 'content']; }
Important: Spatie Translatable recommends that translatable database fields should be defined as json type (or text if JSON is not available in your database). Make sure your migration reflects this:
Schema::create('pages', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->json('title'); $table->json('content'); $table->timestamps(); });
Usage
use JeromeSiau\FilamentMultilang\Components\MultiLangInput; // In your Filament form MultiLangInput::make('title') ->required() // All languages will be required // For rich text fields MultiLangInput::make('content') ->type('rich') ->required() // To make only specific languages required MultiLangInput::make('title') ->required() ->requiredLocales(['fr']) // Customize available languages MultiLangInput::make('title') ->locales([ 'fr' => ['name' => 'French'], 'en' => ['name' => 'English'], 'es' => ['name' => 'Spanish'], ]) // Customize rich editor toolbar buttons MultiLangInput::make('content') ->type('rich') ->toolbarButtons([ 'bold', 'italic', 'link', ]) // Set editor height MultiLangInput::make('content') ->type('rich') ->editorHeight('300px')
Data Transformation
You can transform data before it's stored:
MultiLangInput::make('content') ->type('rich') ->transform( function ($value) { // Transform value before storing return clean($value); }, function ($value) { // Transform value when retrieved return $value; } )
Data Structure
Data is stored as an associative array with language codes as keys:
[
'fr' => 'French content',
'en' => 'English content',
]
With Spatie Laravel Translatable, this array is automatically stored in a JSON field in your database, which greatly simplifies translation management.
Styling
The component comes with default styling that places language tabs neatly at the top-right of each input field. You can customize the appearance by targeting the .fi-multilang-input CSS class in your own stylesheets.
Credits
License
MIT