halpdesk / perform
Requires
- php: ^7.2
- ext-json: *
- illuminate/support: ^6.0
Requires (Dev)
- halpdesk/helpers: ^0.9
- illuminate/validation: ^6.0
- phpunit/phpunit: ^7.0
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-03-07 22:10:40 UTC
README
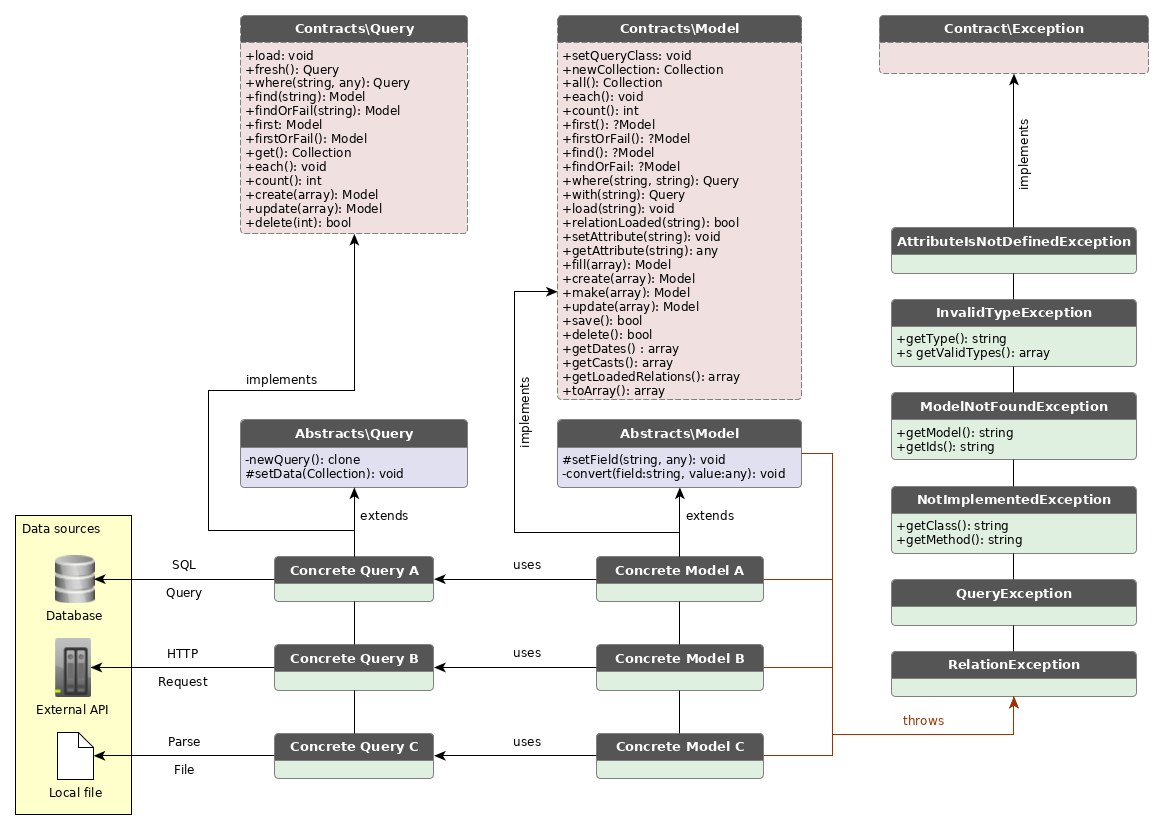
Perform is a swiss army repository adapter. It provides functions such as find, get, all for your Model. It is built for systems with a lot of integrations where data comes from different sources. The package provides two classes which both needs to be implemented in order to set up one entity; a model class and a query class.
The library is build with Eloquent in mind. The model class mimics the Eloquent model and the query class mimics the Eloquent builder.
WIP
The library is a work in progres. See tests for implementation. A short example is given below:
Example
An example with two classes, the Person class and the PersonQuery class. In this example, the person data is located in a person.json.
Model class
use Halpdesk\Perform\Abstracts\Model; use Halpdesk\Perform\Contracts\Model as ModelContract; class Person extends Model implements ModelContract { static public $query = PersonQuery::class; protected $fields = [ 'id', 'name', 'age', 'birthDate', ]; protected $casts = [ 'name' => 'string', 'age' => 'integer', 'birthDate' => 'datetime', ]; protected $dates = [ 'birthDate', ]; public $dateFormat = 'Y-m-d'; }
Query class
use Halpdesk\Perform\Abstracts\Query; use Halpdesk\Perform\Contracts\Query as QueryContract; class PersonQuery extends Query implements QueryContract { protected $model = Person::class; public function load() : void { /* * Use any method to set the data: read from file, make HTTP call, query database, etc. * In this example, we use a json file which contains all person data */ $data = json_file_to_array('./person.json'); $this->setData(collect($data)); } /* * create(), update() and delete() must be implemented * in this class in order to actually use those functions * * it will not be covered in this simple example (yet). */ }
Data source (person.json)
[
{ "id": 1, "name": "Adam", "age": 37, "birthDate": "1982-11-02" },
{ "id": 2, "name": "Billy", "age": 26, "birthDate": "1993-05-28" },
{ "id": 3, "name": "Charlie", "age": 31, "birthDate": "1988-10-05" },
{ "id": 4, "name": "David", "age": 33, "birthDate": "1986-03-14" }
{ "id": 5, "name": "Billy", "age": 22, "birthDate": "1997-02-09" }
]
Method examples
Below is a few examples of what you can do with the model class. The query class is mostly abstracted/hidden (just as the Builder class in Laravel Eloquent).
// Constructs a Person with data associated with id:1 from person.json $person = Person::find(1); // Return a collection with Persons named Billy from person.json $persons = Person::where("name", "Billy")->get(); // Return a full collection with Persons constructed from person.json $all = Person::all(); // Throws a ModelNotFoundException (since id:7 does not exist in the person loaded) $person = Person::findOrFail(7); // Convert the Person class to an array $personArray = Person::findOrFail(2)->toArray(); // Create a new person -- this method calls the query class to attempt store the person in the data source (i.e. person.json) // But the create method must be implemented in the query class; if it is not, an `NotImplementedException` will be thrown $newPerson = Person::create([ "name" => "Ester", "age" => 55, "birthDate" => "1964-07-02" ]); // Same as above, but creates a temporary object which is not meant to be stored in the data source $tempNewPerson = Person::make([ "name" => "Ester", "age" => 55, "birthDate" => "1964-07-02" ]); // Other methods that needs to be implemented to work, or otherwise throw an `NotImplementedException` $person->save(); $person->update(); $person->delete();
Tests
Run tests with PHPUnit