franzip / serp-scraper
A library to extract, serialize and store data scraped on Search Engine result pages.
Installs: 67
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 18
Watchers: 2
Forks: 8
Open Issues: 2
pkg:composer/franzip/serp-scraper
Requires
- php: >=5.4.0
- franzip/serp-fetcher: 0.2.*@dev
- franzip/serp-page-serializer: 0.2.*@dev
- franzip/throttler: 0.2.*@dev
Requires (Dev)
- phpunit/phpunit: 4.0.*
- satooshi/php-coveralls: dev-master
- seld/jsonlint: dev-master
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-13 22:17:02 UTC
README
SerpScraper
A library to extract, serialize and store data scraped on Search Engine result pages.
Installing via Composer (recommended)
Install composer in your project:
curl -s http://getcomposer.org/installer | php
Create a composer.json file in your project root:
{
"require": {
"franzip/serp-scraper": "0.1.*@dev"
}
}
Install via composer
php composer.phar install
Supported Search Engines
- Bing
- Ask
- Yahoo
Supported Serialization format
- JSON
- XML
- YAML
Legal Disclaimer
Under no circumstances I shall be considered liable to any user for direct, indirect, incidental, consequential, special, or exemplary damages, arising from or relating to userʹs use or misuse of this software. Consult the following Terms of Service before using SerpScraper:
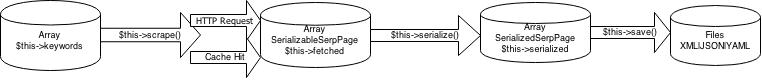
How it works in a nutshell
Description
Scraping legal status seems to be quite disputed. Anyway, this library tries to avoid unnecessary HTTP overhead by using three strategies:
-
Throttling: an internal object takes care of capping the amount of allowed HTTP requests to a default of 15 per hour. Once that limit has been reached, it will not be possible to scrape more content until the timeframe expires.
-
Caching: the library used to retrieve data caches every fetched page. The default cache expiration is set to 24 hours.
-
Delaying: a simple and quite naive approach is used here. Multiple HTTP requests will be spaced out by a default 0,5 sec delay.
Constructor details
This is the abstract constructor, used by all the concrete implementations:
SerpScraper($keywords, $outDir = 'out', $fetcherCacheDir = 'fetcher_cache', $serializerCacheDir = 'serializer_cache', $cacheTTL = 24, $requestDelay = 500);
$keywords- array- The keywords you want to scrape. Cannot be an empty array.
$outDir- string- Path to the folder to be used to store serialized pages.
$fetcherCacheDir- string- Path to the folder to be used to store SerpFetcher cache.
$serializerCacheDir- string- Path to the folder to be used to store SerpPageSerializer cache.
$cacheTTL- integer- Time expiration of the SerpFetcher cache expressed in hours.
$requestDelay- integer- Delay to use between multiple HTTP requests, expressed in microseconds.
Building a Scraper (using Factory)
Specify the vendor as first argument. You can specify custom settings using an array as second argument (see the SerpScraper constructor above).
use Franzip\SerpScraper\SerpScraperBuilder; $googleScraper = SerpScraperBuilder::create('Google', array(array('keyword1', 'keyword2', ...))); $askScraper = SerpScraperBuilder::create('Ask', array(array('key1', 'key2'))); $bingScraper = SerpScraperBuilder::create('Bing', array(array('baz', 'foo'))); ...
Building a Scraper (with explicit constructors)
use Franzip\SerpScraper\Scrapers\GoogleScraper; use Franzip\SerpScraper\Scrapers\AskScraper; use Franzip\SerpScraper\Scrapers\BingScraper; use Franzip\SerpScraper\Scrapers\YahooScraper; $googleScraper = new GoogleScraper($keywords = array('foo', 'bar'), $outDir = 'google_results'); $askScraper = new AskScraper($keywords = array('foo', bar), $outDir = 'ask_results'); ...
scrape() and scrapeAll()
You can scrape a single tracked keyword with scrape(), or scrape all the
tracked keywords using scrapeAll().
scrape() signature:
$serpScraper->scrape($keyword, $pagesToScrape = 1, $toRemove = false, $timezone = 'UTC', $throttling = true);
Usage example:
// Scrape the first 5 pages for the keyword 'foo', remove it from the tracked // keyword, use the Los Angeles timezone and don't use throttling. $serpScraper->scrape('foo', 5, true, 'America/Los Angeles', false);
scrapeAll() signature:
$serpScraper->scrapeAll($pagesToScrape = 1, $toRemove = false, $timezone = 'UTC', $throttling = true);
Usage example:
// Scrape the first 5 pages for all the tracked keywords, remove them all from // tracked keywords, use the Berlin timezone and don't use throttling. $serpScraper->scrapeAll(5, true, 'Europe/Berlin', false); // keywords array has been emptied var_dump($serpScraper->getKeywords()); // array()
serialize() and getFetchedPages()
Serialize all the results fetched so far. Supported formats are: JSON, XML and
YAML.
You can access the fetched array by calling getFetchedPages().
serialize() signature:
$serpScraper->serialize($format, $toRemove = false);
Usage example:
$serpScraper->serialize($format, $toRemove = false); // serialize to JSON the stuff retrieved so far $serpScraper->serialize('json'); // serialize to XML the stuff retrieved so far $serpScraper->serialize('xml'); // fetched pages are still there var_dump($serpScraper->getFetchedPages()); // array( // object(Franzip\SerpPageSerializer\Models\SerializableSerpPage) (1), // ... // ) // now serialize to YAML the stuff retrieved so far and empty the fetched data $serpScraper->serialize('yml', true); // fetched array is now empty var_dump($serpScraper->getFetchedPages()); // array()
save() and getSerializedPages()
Write to files the serialized results so far. The format used as filename is the following: vendor_keyword_pagenumber_time.format | google_foo_3_12032015.json
save() signature:
$serpScraper->save($toRemove = false)
Usage example:
// write serialized results so far to the specified output folder $serpScraper->save(); // serialized pages are still there var_dump($serpScraper->getSerializedPages()); // array( // object(Franzip\SerpPageSerializer\Models\SerializedSerpPage) (1), // ... // ) // write serialized results so far to the specified output folder and remove // them from the serialized array $serpScraper->save(true); // serialized array is now empty var_dump($serpScraper->getSerializedPages()); // array()
Adding/Removing keywords.
$serpScraper->addKeyword('bar'); $serpScraper->addKeywords(array('foo', 'bar', ...)); $serpScraper->removeKeyword('bar');
Cache flushing
You can call flushCache() anytime. This will remove all the cached files
used by the SerpFetcher component and will also remove all the entries
from the fetched and serialized arrays.
$serpScraper->flushCache(); var_dump($serpScraper->getFetchedPages()); // array() var_dump($serpScraper->getSerializedPages()); // array()
Basic usage
use Franzip\SerpScraper\SerpScraperBuilder; $googleScraper = SerpScraperBuilder::create('Google', array(array('keyword1', 'keyword2', 'keyword3'))); // scrape the first page for 'keyword1' $googleScraper->scrape('keyword1'); // scrape the first 5 page for 'keyword2' $googleScraper->scrape('keyword2', 5); // serialize to JSON what has been scraped so far $googleScraper->serialize('json'); // ...
Using multiple output folders
You can use different output folders as you see fit. In this case, the same
keywords will be scraped once but the results will be written to different folders,
based on their serialization format.
Since the results are cached, the serialize() method will use the same
data over and over again.
use Franzip\SerpScraper\SerpScraperBuilder; $googleScraper = SerpScraperBuilder::create('Google', array(array('foo', 'baz', ...))); // output folders $xmlDir = 'google_results/xml'; $jsonDir = 'google_results/json'; $yamlDir = 'google_results/yaml'; ... // scraping action happens here... // write xml results first $googleScraper->serialize('xml'); $googleScraper->setOutDir($xmlDir); $googleScraper->save(); // now json $googleScraper->serialize('json'); $googleScraper->setOutDir($jsonDir); $googleScraper->save(); // write yaml results, we can now remove the serialized array $googleScraper->serialize('yml', true); $googleScraper->setOutDir($yamlDir); $googleScraper->save();
TODOs
- Avoid request delay on cache hit.
- Validate YAML results in the tests (couldn't find a suitable library so far).
- Improve docs with better organization and more examples.
- Refactoring messy tests.
License
MIT Public License.