codewiser / polyglot
Translation strings parser and web editor for Laravel applications
Requires
- php: ^8.1
- ext-gettext: *
- ext-json: *
- laravel/framework: >=10.0
- sepia/po-parser: ^6.0
Requires (Dev)
- phpunit/phpunit: ^9.0
- dev-main
- 2.1.2
- 2.1.1
- 2.1.0
- 2.0.9
- 2.0.8
- 2.0.7
- 2.0.6
- 2.0.5
- 2.0.4
- 2.0.3
- 2.0.2
- 2.0.1
- 2.0.0
- 1.1.2
- 1.1.1
- 1.1.0
- 1.0.11
- 1.0.10
- 1.0.9
- 1.0.8
- 1.0.7
- 1.0.6
- 1.0.5
- 1.0.4
- 1.0.3
- 1.0.2
- 1.0.1
- 1.0.0
- 0.7.5
- v0.7.4
- v0.7.3
- 0.7.2
- 0.7.1
- 0.7.0
- 0.6.4
- 0.6.3
- 0.6.2
- 0.6.1
- 0.6.0
- 0.5.5
- 0.5.4
- 0.5.3
- 0.5.2
- 0.5.1
- 0.5.0
- 0.4.3
- 0.4.2
- 0.4.1
- 0.4.0
- 0.3.7
- 0.3.6
- 0.3.5
- 0.3.4
- 0.3.3
- 0.3.2
- 0.3.1
- 0.3.0
- 0.2.16
- 0.2.15
- 0.2.14
- 0.2.13
- 0.2.12
- 0.2.11
- 0.2.10
- 0.2.9
- 0.2.8
- 0.2.7
- 0.2.6
- 0.2.5
- 0.2.2
- 0.2.0
- 0.1.2
- 0.1.1
- 0.1.0
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-19 09:55:25 UTC
README
- Introduction
- Installation
- Configuration
- Upgrading Polyglot
- Web Editor
- Strings Collector
- Gettext Translator
- Vue|JavaScript Support
Introduction
Polyglot provides a beautiful translation editor and can extract translations strings from the application source codes.
With Polyglot you may be sure, that you application is fully localized.
Installation
Install Gettext on your server and make sure, that php has ext-gettext extension enabled.
Now you are ready to install Polyglot into your project using the Composer package manager:
composer require codewiser/polyglot
After installing Polyglot, publish its assets using the polyglot:install Artisan command:
php artisan polyglot:install
Configuration
After publishing Polyglot's assets, its primary configuration file will be located at config/polyglot.php. This configuration file allows you to configure Polyglot working mode. Each configuration option includes a description of its purpose, so be sure to thoroughly explore this file.
Upgrading Polyglot
When upgrading to any new Polyglot version, you should re-publish Polyglot's assets:
php artisan polyglot:publish
To keep the assets up-to-date and avoid issues in future updates, you may add the polyglot:publish command to the post-update-cmd scripts in your application's composer.json file:
{
"scripts": {
"post-update-cmd": [
"@php artisan polyglot:publish --ansi"
]
}
}
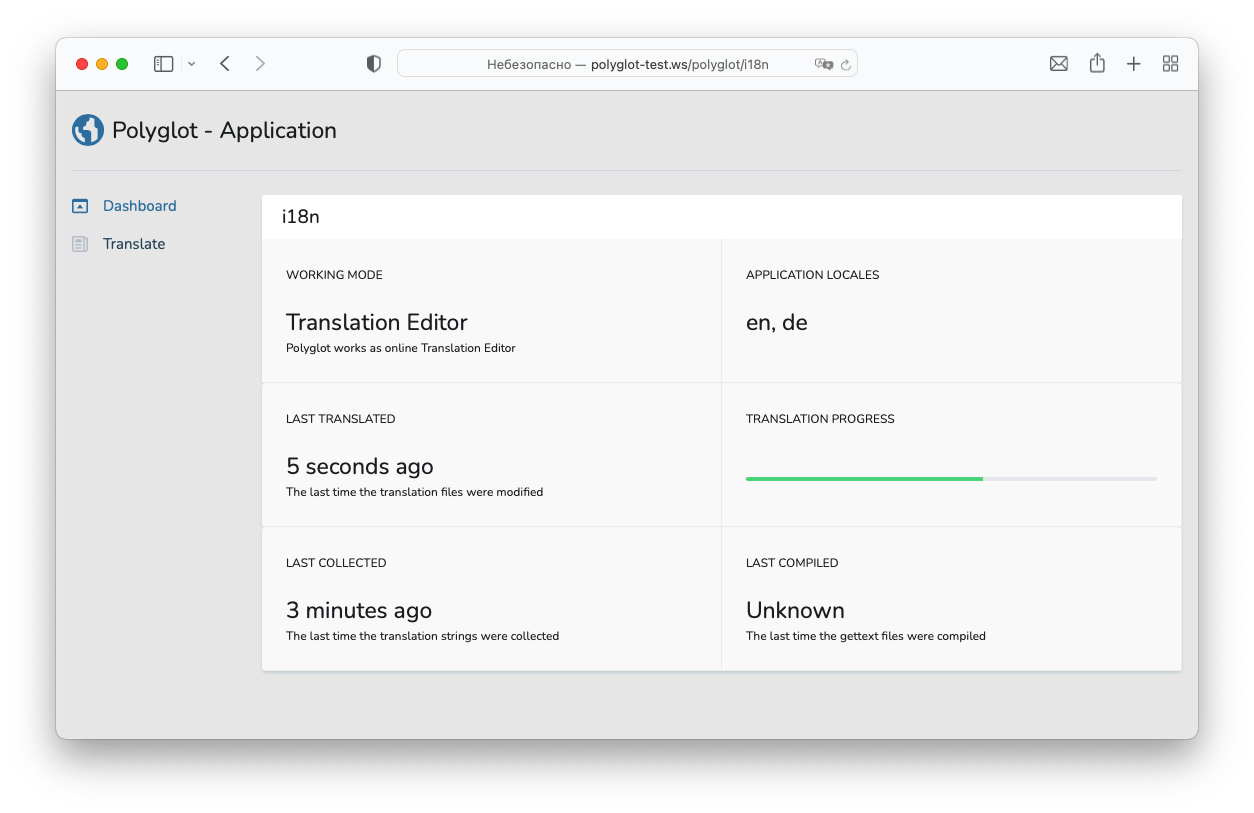
Web editor
Configuration
Dashboard Authorization
Polyglot exposes a dashboard at the /polyglot URI. By default, you will only be able to access this dashboard in the local environment.
It is not recommended to use Polyglot in non-local environments, as Polyglot modifies files in
resources/lang.
However, within your app/Providers/PolyglotServiceProvider.php file, there is an authorization gate definition. This authorization gate controls access to Polyglot in non-local environments. You are free to modify this gate as needed to restrict access to your Polyglot installation.
/** * Register the Polyglot gate. * * This gate determines who can access Polyglot in non-local environments. * * @return void */ protected function gate() { Gate::define('viewPolyglot', function ($user) { return in_array($user->email, [ 'username@example.com', ]); }); }
Alternative Authentication Strategies
Remember that Laravel automatically injects the authenticated user into the gate closure. If your application is providing Polyglot security via another method, such as IP restrictions, then your Polyglot users may not need to "login". Therefore, you will need to change function ($user) closure signature above to function ($user = null) in order to force Laravel to not require authentication.
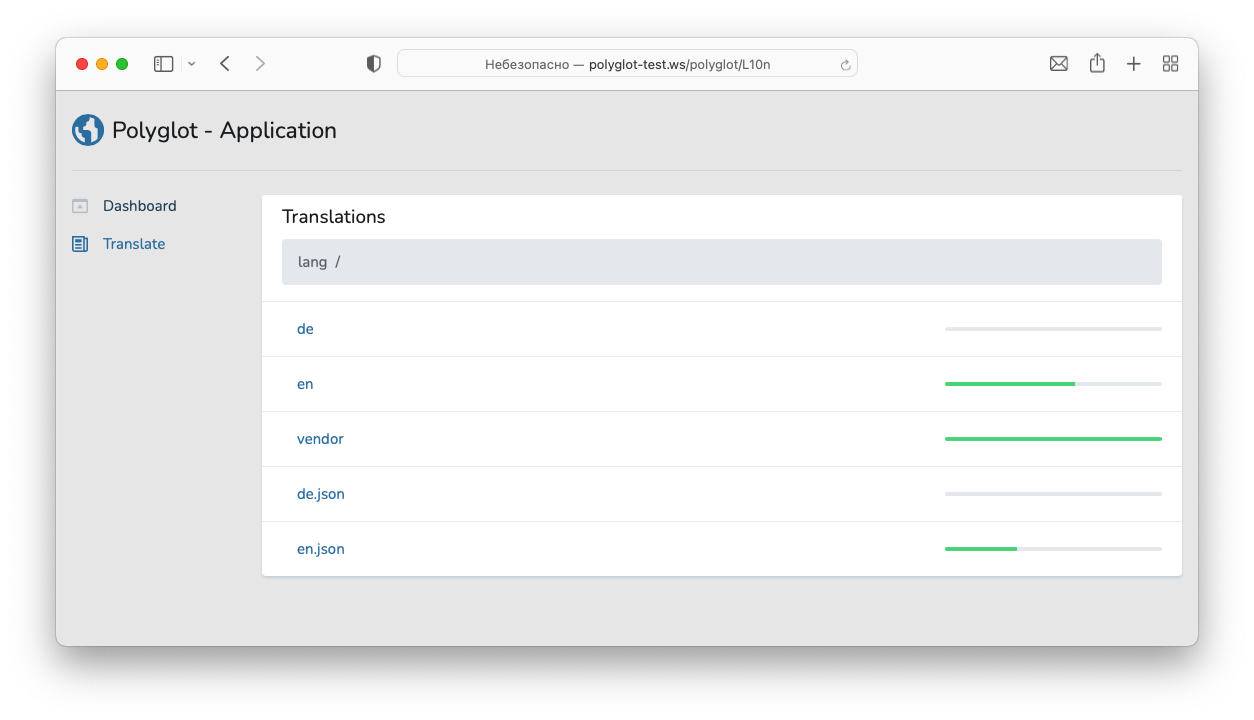
Strings Collector
Configuration
Define at least one group of source files to collect strings from.
'sources' => [ [ 'include' => [ app_path(), resource_path('views') ], 'exclude' => [], ] ],
Application locales
Gettext depends on server support of locales.
For example, your application provides Italian language (it).
And your server supports following locales:
> locale -a | grep it it_CH it_CH.utf8 it_IT it_IT@euro it_IT.utf8
Then you should list system locales in order of preference. Read more at https://www.php.net/manual/en/function.setlocale.php
'locales' => [ 'en' => ['en_US', 'en_US.utf8', 'en_US.UTF-8'] 'it' => ['it_IT', 'it_IT.utf8', 'it_IT.UTF-8'], 'es' => ['es_ES', 'es_ES.utf8', 'es_ES.UTF-8'], ],
After collecting strings, Polyglot will populate collected strings through every configured locale.
Collecting strings
Once you have configured sources in your application's config/polyglot.php configuration file, you may collect strings using the polyglot Artisan command. This single command will collect all translation strings from the configured sources:
php artisan polyglot:collect
Polyglot uses sources to collect translation strings, understanding trans, trans_choice, @trans and other Laravel specific directives.
After collecting strings your application's resourse/lang folder may look like:
resources/
lang/
es/
auth.php
passwords.php
en/
auth.php
passwords.php
it/
auth.php
passwords.php
es.json
en.json
it.json
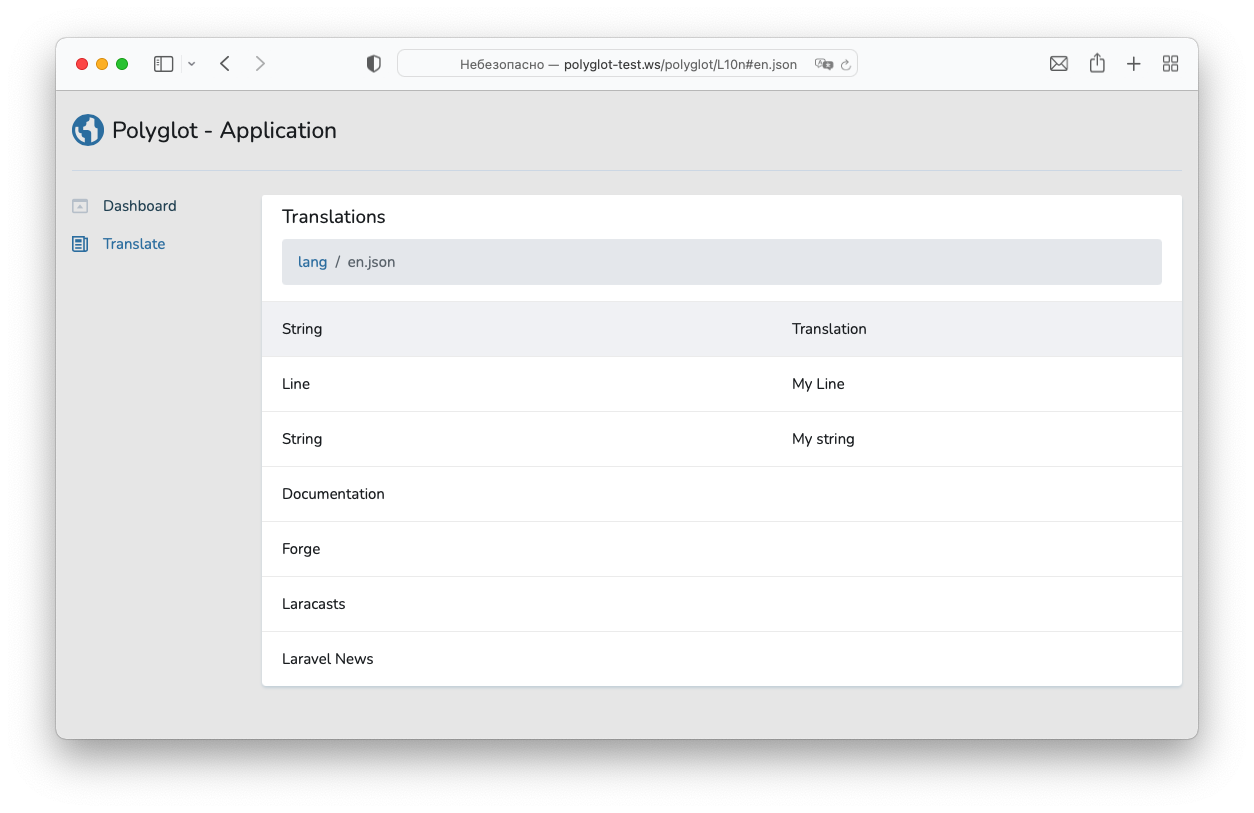
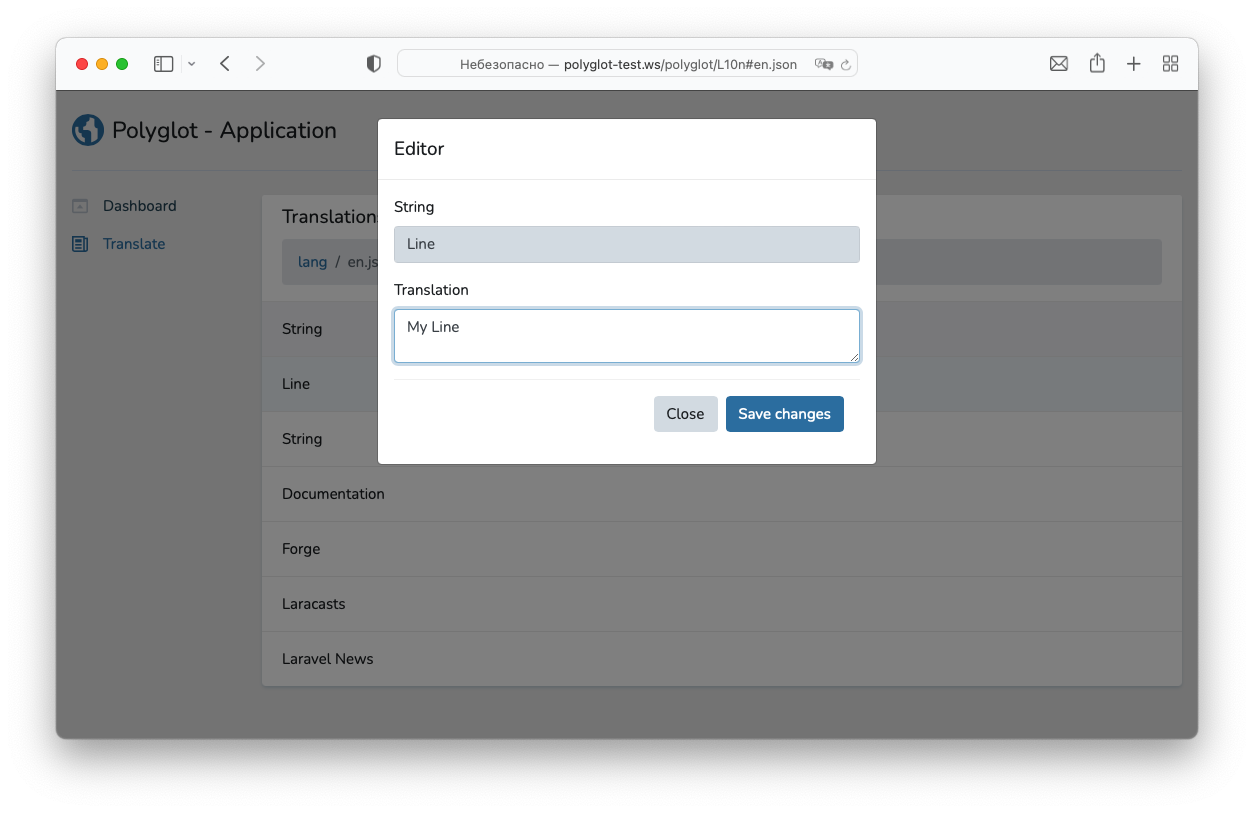
You only left to translate files.
Loading Strings
Polyglot provides AcceptLanguage middleware that may help to set proper locale to the application.
class AcceptLanguage { public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next) { app()->setLocale($request->getPreferredLanguage(Polyglot::getLocales())); return $next($request); } }
Gettext Translator
Before reading, you should familiarize yourself with Gettext.
Configuration
Set POLYGLOT_GETTEXT=true environment variable to use Gettext to localize your application.
'enabled' => env('POLYGLOT_GETTEXT', true),
Text Domains
You may configure additional group of source files that way:
'sources' => [ [ 'text_domain' => 'frontend', 'include' => [ app_path(), resource_path('views'), ], 'exclude' => resource_path('views/admin'), ], [ 'text_domain' => 'backend', 'include' => [ resource_path('views/admin'), ], 'exclude' => [], ], ],
Default value for
text_domainis stringmessages.
Collecting strings
After you run polyglot:collect Artisan command, your application's resourse/lang folder may look like:
resources/
lang/
es/
LC_MESSAGES/
backend.po
frontend.po
en/
LC_MESSAGES/
backend.po
frontend.po
it/
LC_MESSAGES/
backend.po
frontend.po
Compiling strings
Generated files contains collected string, that you might want to translate. After you have finished translation you should compile all po files to mo format, that is understandable by Gettext. Use Artisan command to compile.
php artisan polyglot:compile
Beside every po file will appear mo file.
Do remember, that php caches contents of
mofiles. So, after compiling, be sure, you have restarted the web server.
Backward Compatability
Even using Gettext driver, you may continue to use Laravel translator directives, such as trans and trans_choice.
Meanwhile, you may use Gettext directives, such as gettext, ngettext and others.
They are all understandable by Polyglot.
Loading Text Domain
By default, Polyglot will load into php memory the first configured text domain.
If you configure few text domains, you may load next text domain by accessing Laravel's Lang facade:
Lang::setTextDomain('frontend');
Supported Directives
Polyglot supports the following Gettext directives.
Lookup a message in the current text domain:
gettext(string $message): string
Plural version of gettext:
ngettext(string $singular, string $plural, int $count): string
Particular version of gettext allows to define context:
pgettext(string $context, string $message): string
Particular version of ngettext.
npgettext(string $context, string $singular, string $plural, int $count): string
Other directives, that allows to override current text domain and category are also supported.
The Power of Gettext
Gettext can be very helpful for the translator. Use following recipes to get localization done well.
References
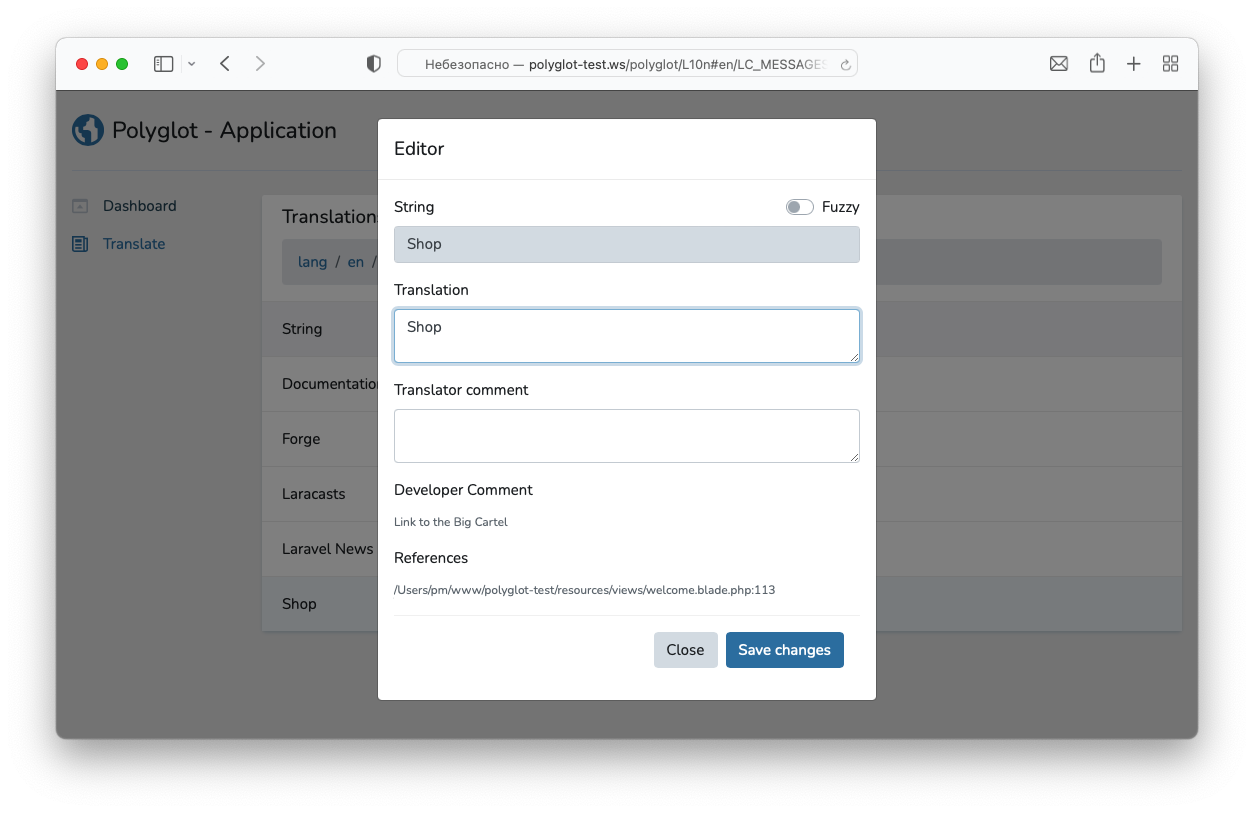
Gettext extracts references of the string, so translator may suppose the context.
#: /sources/php/second.php:3 /sources/js/first.js:1
msgid "Short message"
msgstr ""
Developer comments
Gettext may extract developer comment, that might be helpful for translator.
#. The message will be shown at test page only.
msgid "Hello world"
msgstr ""
That was originated from such source code:
// The message will be shown at test page only. echo gettext('Hello world');
Message context
The developer may explicitly define the message context.
gettext('May');
pgettext('Month', 'May');
Here we have two messages with equal msgid but with different msgctxt that is actually a part of string key.
msgid "May"
msgstr ""
msgctxt "Month"
msgid "May"
msgstr ""
Translator comments
While editing strings, translator may left one or many comments. This comments may be helpful for future translators.
# They say it was about posibilities...
msgid "May"
msgstr ""
Fuzzy strings
Both Gettext (while parsing source codes) and a translator may mark string as fuzzy. It means that a string, previously situated on that place, was changed, so current translation might no longer be appropriate.
#, fuzzy
msgid "May"
msgstr ""
Vue and JavaScript Support
Vue and JavaScript sources supported as well.
Compiling Strings
Artisan polyglot:compile command will compile every translation file into json format and put them into storage folder. After compiling storage/lang may look like:
storage/
lang/
es/
frontend.json
en/
frontend.json
it/
frontend.json
You may use these files to localize the frontend.
Polyglot provides translations.js that your application may use as mixin. Polyglot dashboard localized that way.