clarifynl / responsive-pics
Responsive Pics is a Wordpress tool for resizing images on the fly.
Installs: 17 956
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 83
Watchers: 5
Forks: 4
Open Issues: 6
Type:wordpress-plugin
pkg:composer/clarifynl/responsive-pics
Requires
- php: >=5.5.0
- composer/installers: ^1.0|^2.0
Requires (Dev)
- slowprog/composer-copy-file: ~0.3
- woocommerce/action-scheduler: ^3.5
- wpackio/enqueue: ^3.5
- dev-main
- 1.9.4
- 1.9.3
- 1.9.2
- 1.9.1
- 1.9.0
- 1.8.4
- 1.8.3
- 1.8.2
- 1.8.1
- 1.8.0
- 1.7.8
- 1.7.7
- 1.7.6
- 1.7.5
- 1.7.4
- 1.7.3
- 1.7.2
- 1.7.1
- 1.7.0
- 1.6.4
- 1.6.3
- 1.6.2
- 1.6.1
- 1.6.0
- 1.5.2
- 1.5.1
- 1.5.0
- 1.4.5
- 1.4.4
- 1.4.3
- 1.4.2
- 1.4.1
- 1.4.0
- 1.3.5
- 1.3.4
- 1.3.3
- 1.3.2
- 1.3.1
- 1.3.0
- 1.2.3
- 1.2.2
- 1.2.1
- 1.2.0
- 1.1.3
- 1.1.2
- 1.1.1
- 1.1.0
- 1.0.1
- 1.0.0
- 1.0.0-rc.4
- 1.0.0-rc.3
- 1.0.0-rc.2
- 1.0.0-rc.1
- 0.7.2
- 0.7.1
- 0.7
- 0.6.6
- 0.6.5
- 0.6.4
- 0.6.3
- 0.6.2
- 0.6.1
- 0.6
- 0.5.5
- 0.5.4
- 0.5.3
- 0.5.2
- 0.5.1
- 0.5.0
- 0.4.5
- 0.4.4
- 0.4.3
- 0.4.2
- dev-dependabot/npm_and_yarn/multi-acd8535d99
- dev-dependabot/npm_and_yarn/qs-6.14.2
- dev-dependabot/composer/lib/action-scheduler/phpunit/phpunit-8.5.52
- dev-dependabot/npm_and_yarn/lodash-4.17.23
- dev-dependabot/npm_and_yarn/lib/action-scheduler/lodash-4.17.23
- dev-dev
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-02-28 03:50:39 UTC
README
ResponsivePics is a WordPress plugin that enables WordPress theme authors to automatically resize images* in responsive layouts.
- Saves bandwidth and lets your site load faster
- No need anymore for defining custom image sizes
- Adds retina support to your theme images
- Supports art-directed responsive images
- Supports image srcset & sizes attributes
- Supports focal point based crops
- Supports aspect ratio based crops
- Supports WebP images (requires Wordpress 5.8 or higher)
- Supports LQIP (low quality image placeholder)
- Supports lazyloading
- Supports intrinsic ratio boxes
- Supports offloading media to S3 storage with WP Offload Media (Lite)
- Supports WP REST API
- Uses background processing for resize- and crop tasks
*ReponsivePics does not handle images in the WordPress wysiwig editor, it’s only useful for theme authors that use images or photos in their themes. It automatically handles retina or hdpi images via media queries.
Documentation
For full documentation and examples visit: responsive.pics
Table of contents
Requirements
| Prerequisite | How to check |
|---|---|
| PHP >= 5.6.x | php -v |
| Wordpress >= 3.5.x | wp core version |
| WP-Cron enabled or a real cron job set up | test WP-Cron |
Installation
You can install this plugin via the command-line or the WordPress admin panel.
via Command-line
If you're using Composer to manage WordPress, add ResponsivePics to your project's dependencies.
composer require toinekamps/responsive-pics
Then activate the plugin via wp-cli.
wp plugin activate responsive-pics
via WordPress Admin Panel
- Download the latest zip of this repo.
- In your WordPress admin panel, navigate to Plugins->Add New
- Click Upload Plugin
- Upload the zip file that you downloaded.
- Activate the plugin after installation.
Browser Support
Currently the <picture> element and srcset and sizes attributes on the <img> element are supported in all modern browsers except Internet Explorer 11.
In order to enable support for the picture element and associated features in browsers that do not yet support them, you can use a polyfill. We recommend using Picturefill.
To install Picturefill in your wordpress theme as a node module, run the following command from your theme directory:
npm
npm install --save picturefill
Yarn
yarn add picturefill
And import the package in your theme’s global javascript file:
import 'picturefill';
Configuration
ResponsivePics uses the following default variables:
| Variable | Type | Default | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
$columns |
number | 12 |
The amount of columns your grid layout uses |
$gutter |
number | 30 |
The gutter width in pixels (space between grid columns) |
$breakpoints |
array | ['xs' => 0, 'sm' => 576, 'md' => 768, 'lg' => 992, 'xl' => 1200, 'xxl' => 1400] |
The media query breakpoints ResponsivePics will use for creating and serving your image sources |
$grid_widths |
array | ['xs' => 576, 'sm' => 540, 'md' => 720, 'lg' => 960, 'xl' => 1140, 'xxl' => 1320] |
The maximum widths of your layout in pixels ResponsivePics will use for resizing your images |
$max_width_factor |
number | 2 |
The maximum factor of the width to use for resizing and cropping the height of an image source |
$lazyload_class |
string | lazyload |
The css class to be added on the img tag when lazyload is enabled |
$lqip_width |
number | 100 |
The image width to be used for the LQIP (low quality image placeholder) |
$lqip_class |
string | blur-up |
The css class to be added on the img tag when LQIP (low quality image placeholder) is enabled |
$image_quality |
number | 90 |
The image compression quality in percentage used in the WP_Image_Editor when resizing images |
$wp_rest_cache |
boolean | false |
Wether to enable cache in the WP Rest API response headers |
$wp_rest_cache_duration |
number | 3600 |
The cache duration (max-age) in seconds of the WP Rest API Cache-Control header |
By default, ResponsivePics will use the Bootstrap 4 SCSS variables for defining:
The amount of grid columns: $grid-columns: 12;
The grid gutter width in pixels: $grid-gutter-width: 30px;
The grid breakpoints in pixels:
$grid-breakpoints: ( xs: 0, sm: 576px, md: 768px, lg: 992px, xl: 1200px, xxl: 1400px );
And the maximum widths of the containers in pixels:
$container-max-widths: ( sm: 540px, md: 720px, lg: 960px, xl: 1140px, xxl: 1320px );
Note: ResponsivePics will add the xs container max width for you (= 576), based upon the default sm grid breakpoint (= 576px).
If you have customized the bootstrap defaults or if you’re using a different grid system (Foundation, Materialize etc.), or even if you want to add extra breakpoints & container widths, you can pass your own grid variables to the ResponsivePics library.
Add these lines to your theme’s functions.php and make sure to check if the ResponsivePics class exists:
/* * Set ResponsivePics variables */ if (class_exists('ResponsivePics')) { ResponsivePics::setColumns(12); ResponsivePics::setGutter(30); ResponsivePics::setBreakPoints([ 'xs' => 0, 'sm' => 576, 'md' => 768, 'lg' => 992, 'xl' => 1200, 'xxl' => 1400, 'xxxl' => 1600, 'xxxxl' => 1920 ]); ResponsivePics::setGridWidths([ 'xs' => 576, 'sm' => 768, 'md' => 992, 'lg' => 1200, 'xl' => 1400, 'xxl' => 1600, 'xxxl' => 1920 ]); ResponsivePics::setMaxWidthFactor(4); ResponsivePics::setLazyLoadClass('lozad'); ResponsivePics::setLqipWidth(200); ResponsivePics::setLqipClass('blurred'); ResponsivePics::setImageQuality(85); ResponsivePics::setRestApiCache(true); ResponsivePics::setRestApiCacheDuration(86400); }
Helper Functions
You can retrieve any variables used in ResponsivePics by running one of these helper functions:
ResponsivePics::getColumns(); // Will return $columns ResponsivePics::getGutter(); // Will return $gutter ResponsivePics::getBreakpoints(); // Will return $breakpoints ResponsivePics::getGridWidths(); // Will return $grid_widths ResponsivePics::getMaxWidthFactor(); // Will return $max_width_factor ResponsivePics::getLqipWidth(); // Will return $max_width_factor ResponsivePics::getLazyLoadClass(); // Will return $lazyload_class ResponsivePics::getLqipWidth(); // Will return $lqip_width ResponsivePics::getLqipClass(); // Will return $lqip_class ResponsivePics::getImageQuality(); // Will return $image_quality ResponsivePics::getRestApiCache(); // Will return $wp_rest_cache ResponsivePics::getRestApiCacheDuration(); // Will return $wp_rest_cache_duration
Usage
Image Element
For inserting a responsive <img> element in your template, use the get_image function or the responsive-pics/v1/image API endpoint with the available parameters.
PHP
ResponsivePics::get_image(id, sizes, crop, classes, lazyload, lqip, decorative);
REST API
GET /wp-json/responsive-pics/v1/image/<id>?sizes=<sizes>&crop=<crop>&classes=<classes>&lazyload=<lazyload>&lqip=<lqip>&decorative=<decorative>
Image Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | number | yes | The WordPress image id (e.g. 1). | |
| sizes | string | yes | A comma-separated string of preferred image sizes (e.g. 'xs-12, sm-6, md-4, lg-3'). See the Sizes section for more information. |
|
| crop | number/string | optional | false |
A crop-factor of the width for the desired height within the default range of 0-2 (e.g. 0.75) with (optional) crop positions (e.g. 0.75|c t). See the Cropping section for more information. |
| classes | string | optional | null |
A comma-separated string of additional CSS classes you want to add to the img element (e.g. 'my_img_class' or 'my_img_class, my_second_img_class'). |
| lazyload | boolean/string | optional | false |
When true enables lazyload classes and data-srcset attributes. When native enables native loading="lazy" attribute. See the Lazyloading section for more information. |
| lqip | boolean | optional | false |
When true enables LQIP classes and src attribute. See the LQIP section for more information. |
| decorative | boolean | optional | false |
When true the image will be treated as a decorative image and an empty alt attribute will always be added. |
Image Data
For retrieving the responsive <img> data in your theme, you can use the get_image_data function or the responsive-pics/v1/image-data API endpoint with the available parameters id, sizes, crop, classes, lazyload, lqip and decorative.
PHP
ResponsivePics::get_image_data(id, sizes, crop, classes, lazyload, lqip, decorative);
REST API
GET /wp-json/responsive-pics/v1/image-data/<id>?sizes=<sizes>&crop=<crop>&classes=<classes>&lazyload=<lazyload>&lqip=<lqip>&decorative=<decorative>
This will return an array containing the available image sources per breakpoint, alt text, mime type, boolean values for alpha channel, lazyload and decorative, an url for the lqip image and an array for the css picture classes.
[ 'alpha' => (bool) $alpha, 'alt' => (string) $alt, 'classes' => (array) $classes, 'decorative' => (bool) $decorative, 'lazyload' => (bool) $lazyload, 'lqip' => (string) $lqip, 'mimetype' => (string) $mime_type, 'sources' => (array) $sources ];
Picture Element
For inserting a responsive <picture> element in your template, use the get_picture function or the responsive-pics/v1/picture API endpoint with the available parameters.
PHP
ResponsivePics::get_picture(id, sizes, classes, lazyload, intrinsic, img_classes);
REST API
GET /wp-json/responsive-pics/v1/picture/<id>?sizes=<sizes>&classes=<classes>&lazyload=<lazyload>&intrinsic=<intrinsic>&img_classes=<img_classes>
Picture Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | number | yes | The WordPress image id (e.g. 1). | |
| sizes | string | yes | A comma-separated string of preferred image sizes (e.g. 'xs-12, sm-6, md-4, lg-3'). See the Sizes section for more information. |
|
| classes | string/array | optional | null |
A comma-separated string or array of additional CSS classes you want to add to the picture element (e.g. 'my_picture_class' or 'my_picture_class, my_second_picture_class'). |
| lazyload | boolean/string | optional | false |
When true enables lazyload classes and data-srcset attributes. When native enables native loading="lazy" attribute. See the Lazyloading section for more information. |
| intrinsic | boolean | optional | false |
When true enables intrinsic classes and data-aspectratio attributes. See the Intrinsic Aspectratio section for more information. |
| img_classes | string/array | optional | null |
A comma-separated string or array of additional CSS classes you want to add to the picture's img element (e.g. 'my_image_class' or 'my_image_class, my_second_image_class'). |
Picture Data
For retrieving the responsive <picture> data in your theme, you can use the get_picture_data function or the responsive-pics/v1/picture-data API endpoint with the available parameters id, sizes, classes, lazyload, intrinsic and img_classes.
PHP
ResponsivePics::get_picture_data(id, sizes, classes, lazyload, intrinsic, img_classes);
REST API
GET /wp-json/responsive-pics/v1/picture-data/<id>?sizes=<sizes>&classes=<classes>&lazyload=<lazyload>&intrinsic=<intrinsic>&img_classes=<img_classes>
This will return an array containing the available picture sources per breakpoint, alt text, mime type, boolean values for alpha channel, animated, lazyload and intrinsic, an array for the picture css classes and an array for the img css classes.
[ 'alpha' => (bool) $alpha, 'alt' => (string) $alt, 'animated' => (bool) $animated, 'mimetype' => (string) $mime_type, 'sources' => (array) $sources, 'lazyload' => (bool) $lazyload, 'intrinsic' => (bool) $intrinsic, 'picture_classes' => (array) $picture_classes, 'image_classes' => (array) $image_classes ];
Background Image
For inserting a responsive background image in your template, use the get_background function or the responsive-pics/v1/background API endpoint with the available parameters.
PHP
ResponsivePics::get_background(id, sizes, classes);
REST API
GET /wp-json/responsive-pics/v1/background/<id>?sizes=<sizes>&classes=<classes>
Background Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | number | yes | The WordPress image id (e.g. 1). | |
| sizes | string | yes | A comma-separated string of preferred image sizes (e.g. 'xs-12, sm-6, md-4, lg-3'). See the Sizes section for more information. |
|
| classes | string | optional | null |
A comma-separated string of additional CSS classes you want to add to the background element (e.g. 'my_bg_class' or 'my_bg_class, my_second_bg_class'). |
Background Data
For retrieving the responsive background image data in your theme, you can use the get_background_data function or the responsive-pics/v1/background-data API endpoint with the available parameters id, sizes and classes.
PHP
ResponsivePics::get_background_data(id, sizes, classes);
REST API
GET /wp-json/responsive-pics/v1/background-data/<id>?sizes=<sizes>&classes=<classes>
This will return an array containing the available background image sources per breakpoint, alt text, mime type, a boolean value if the image has an alpha channel, an id for the background and an array for the background css classes.
[ 'sources' => (array) $sources, 'alt' => (string) $alt, 'mimetype' => (string) $mime_type, 'alpha' => (bool) $alpha, 'id' => (string) $id, 'classes' => (array) $classes ];
Supported image formats
The following image file formats are supported:
| File format | MIME Type | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| jp(e)g | image/jpeg | |
| webp | image/webp | Requires Wordpress version 5.8 or higher. |
| png | image/png | When the png contains an alpha channel, an extra 'has-alpha' class will be added to the picture image element for additional styling. |
| gif | image/gif | When the gif is animated (it will check for multiple header frames), no image resizing or cropping will be done to prevent discarding the animation. |
Any other image formats, will not be resizes or cropped.
Sizes
Image sizes
The following syntax is available for each image size in the sizes parameter:
breakpoint:width
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| breakpoint | number or string | yes | If undefined, and width is a number, breakpoint will be the same as the width. If undefined, and width is a column definition, breakpoint will be the corresponding breakpoint (e.g. if width is 'xs-8', breakpoint will be 'xs'). |
|
| width | number or string | yes | A column definition is a key in $grid_widths plus a dash and a column span number (e.g. 'xs-8').If the column span number is suffixed with -full (e.g. 'xs-8-full'), the column width is calculated as a percentage of the $grid_width, but as the next matching $breakpoint width (like in a .container-fluid).You can also use full as span number (e.g. 'xs-full') for full width size based upon next matching $breakpoint width. |
Picture & background sizes
Since the <picture> element and background images support art directed images, the following full syntax is available for each image size in the sizes parameter:
breakpoint:width [/factor|height]|crop_x crop_y
The following parameters are available in the sizes syntax:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| breakpoint | number or string | yes | If undefined, and width is a number, breakpoint will be the same as the width. If undefined, and width is a column definition, breakpoint will be the corresponding breakpoint (e.g. if width is 'xs-8', breakpoint will be 'xs'). |
|
| width | number or string | yes | The desired (max) width of the image (e.g. 800). A column definition is a key in $grid_widths plus a dash and a column span number (e.g. 'xs-8').If the column span number is suffixed with -full (e.g. 'xs-8-full'), the column width is calculated as a percentage of the $grid_width, but as the next matching $breakpoint width (like in a .container-fluid).You can also use full as span number (e.g. 'xs-full') for full width size based upon next matching $breakpoint width. |
|
| height | number | optional | The desired (max) height of the image (e.g. 500). |
|
| factor | number | optional | A crop-factor of the width for the desired height within the default range of 0-2 (e.g. 0.75). |
|
| crop_x | number or string | optional | c | Crop position in horizontal direction (e.g. c). See the Cropping section for more information. |
| crop_y | number or string | optional | c | Crop position in vertical direction (e.g. b). See the Cropping section for more information. |
Cropping
The following options are available as valid crop positions:
Crop position shorthands
You can use the following crop position shorthands in horizontal direction (x):
l: leftc: centerr: rightf: focal point (See the Focal Point section for more information)
And in vertical direction (y):
t: topc: centerb: bottom
If the vertical direction is not set, the horizontal direction x will be treated as a shortcut:
c: center centert: top centerr: right centerb: center bottoml: left centerf: focal point (See the Focal Point section for more information)
Crop position percentages
You can also use percentages as valid crop position syntax:
75 10: 75% from left, 10% from top25 80: 25% from left, 80% from top50 100: 50% from left, 100% from top (equalscenter bottom)
In this case both the coordinates x and y need to be passed.
Focal Point
When you want to crop an image but keep a certain area of the image in view, you can use the f(ocal) shorthand feature. In order to set this focal area of an image, we added a focal point picker interface to several views of the Wordpress media framework.
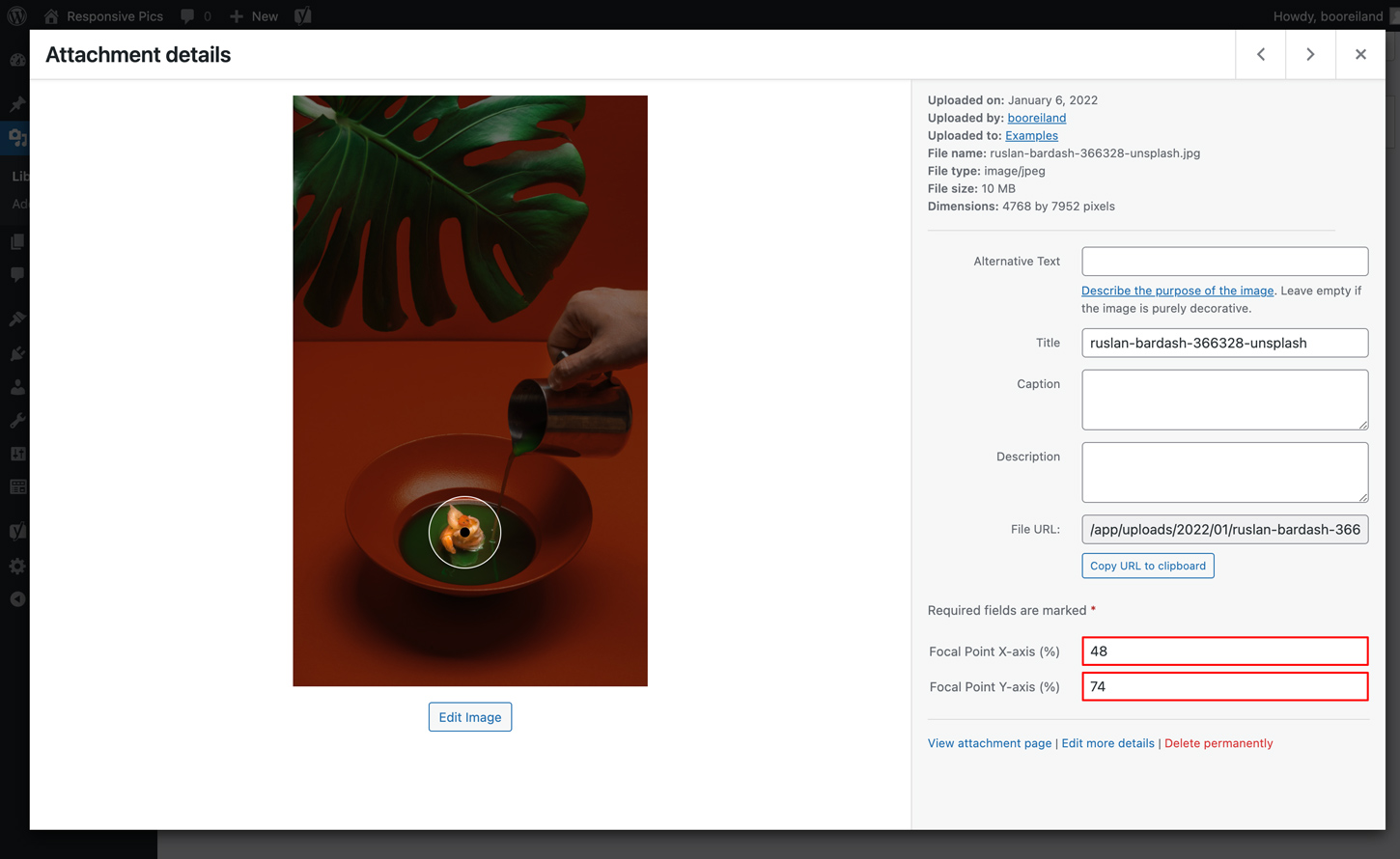
Attachment Details
When clicking on a thumbnail from the Wordpress Media Library grid view, you will see the Attachment details modal. This will be the most accurate view to select your focal point:
Featured Image
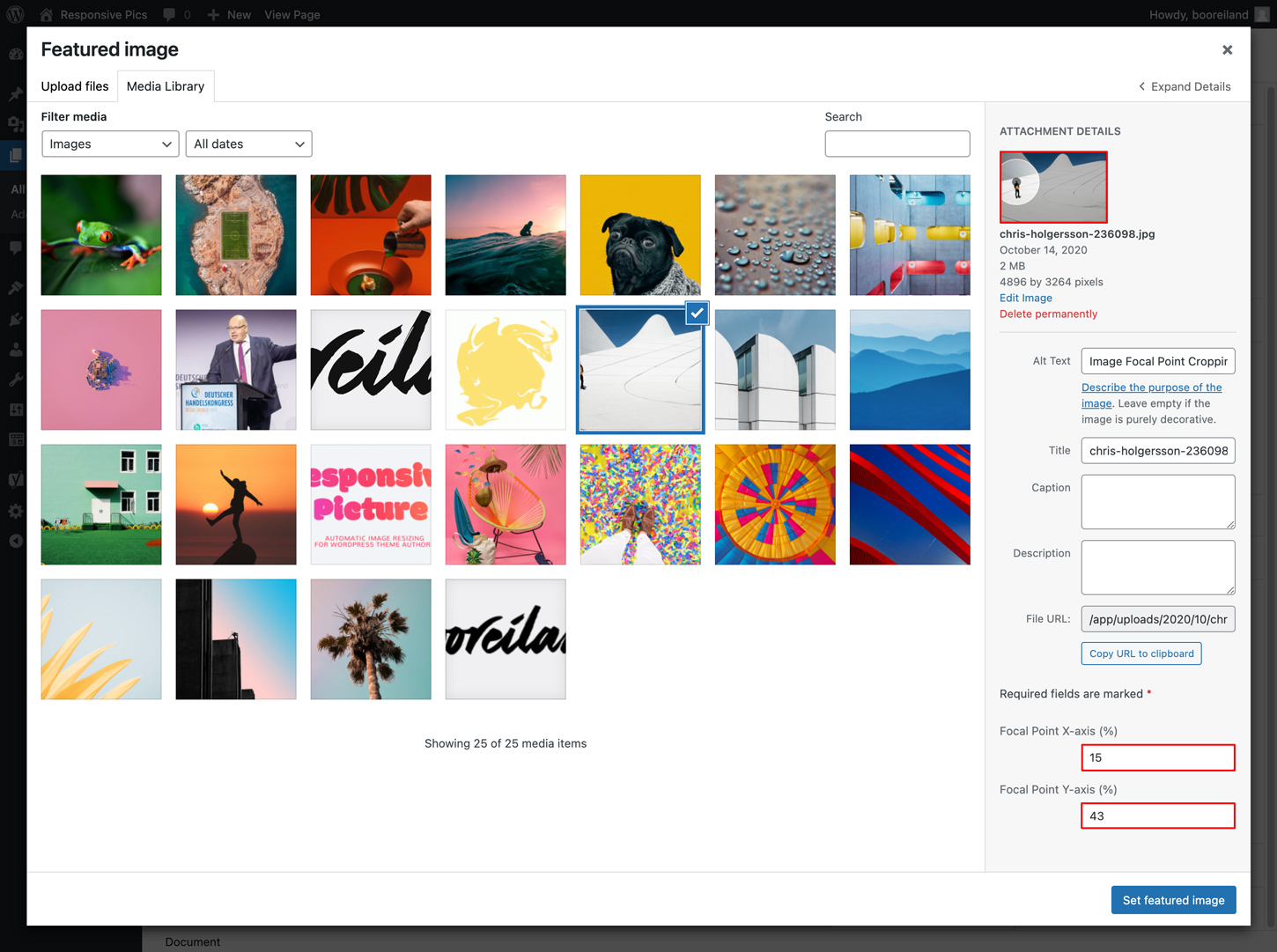
When setting or replacing an featured image in a page or post, you will see the Featured image modal. In this view you can select your focal point in the thumbnail at the top of the right sidebar:
Edit Image
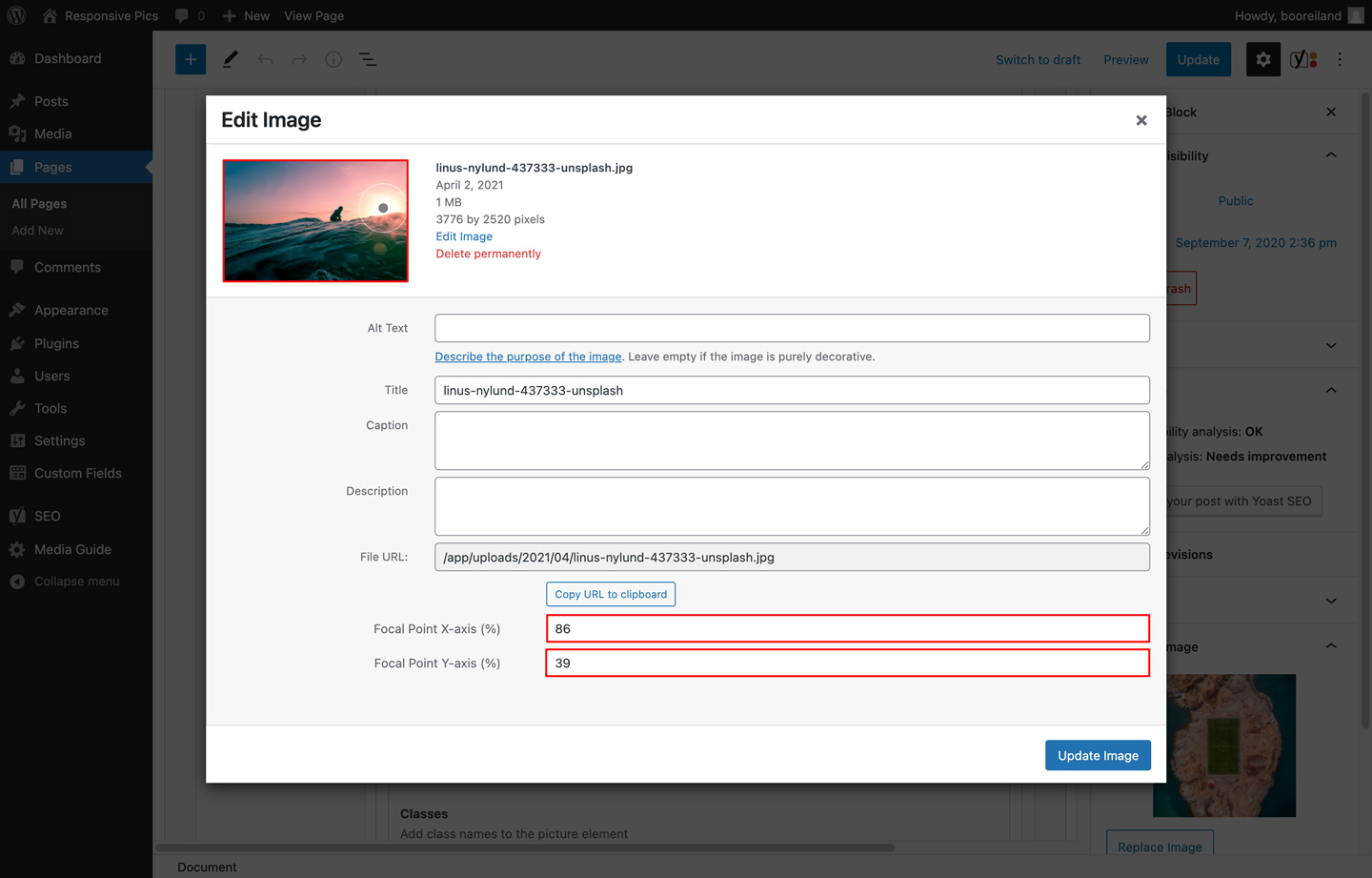
When uploading or editing an image in the WYSIWYG editor or meta field in a page or post, you will see the Edit image modal. In this view you can select your focal point in the thumbnail at the top left:
There are 3 ways you can set the focal point of an image with the interface:
- By directly clicking on the desired focal point in the image.
- By dragging and dropping the focal point circle element on the image.
- By entering the Focal Point X & Y-axis values as percentages directly in the attachment input fields.
By using one of these options a post meta key named responsive_pics_focal_point will be added or updated to the attachment with an array value containing the x & y coordinates as percentages:
[ 'x' => '86', 'y' => '39' ]
To use this value elsewhere in your theme, you can retrieve it by calling:
$focal_point = get_post_meta($attachment_id, 'responsive_pics_focal_point', true);
Process
- When visiting a front-end page and a
ResponsivePicsfunction call is made, this library will add the resize and/or crop image task as a job to the background process queue using Action Scheduler. - On every page load or on the next cron interval, Action Scheduler will run the next batch of jobs in the background process queue. See the Cron section for more information.
- When a job is up next in the queue and ready to be processed it will execute the resize and/or crop task and save the image in the same location as the original image when successful and it will remove the job from the queue.
- Once the image variation is created, it will skip the process of that variation on the next page load.
- When you change one of the image size parameters, it will automatically try and create the new image variation on the next page load.
- When the original image does not meet the dimension requirements of the requested image size, it will skip that image size variation and proceed to the next image size.
- Alt text will automatically be added on the picture img element if the original image in the media library has one.
- When deleting an attachment from the library, it will also delete all the resized images created by this plugin.
Background Processing
The background processing library Action Scheduler has a built in administration screen for monitoring, debugging and manually triggering scheduled image resize jobs. The administration interface is accesible via:
Tools > Scheduled Actions
Every resize job will be grouped by it's wordpress image id
Cron
When you are using the built-in WP-Cron, the background process queue will only process any tasks on every page load.
If you have disabled WP-Cron in your setup and you are using your own cron job on your server, Action Scheduler will use the interval set in that cron job to process the next batch of jobs.
define('DISABLE_WP_CRON', true);
If you're using Trellis like us ❤️, the default cron interval is set to every 15 mins.
You can override this to for example 1 mins with setting the cron_interval (or cron_interval_multisite for multisite) variable per wordpress site to */1:
In for example trellis/group_vars/development/wordpress_sites.yml:
wordpress_sites: example.com: site_hosts: - canonical: example.test redirects: - www.example.test local_path: ../site # path targeting local Bedrock site directory (relative to Ansible root) admin_email: admin@example.test multisite: enabled: false ssl: enabled: false provider: self-signed cache: enabled: false cron_interval: '*/1'
Don't forget to re-provision your server after changing this value.
Error handling
If an error occurs during the resizing process or if there's invalid syntax, ResponsivePics will display or return an error.
PHP
ResponsivePics errors - breakpoint xxs is neither defined nor a number
REST API
{
"code": "responsive_pics_invalid",
"message": "breakpoint xxs is neither defined nor a number",
"data": {
"xs": 0,
"sm": 576,
"md": 768,
"lg": 992,
"xl": 1200,
"xxl": 1400
}
}
Hooks
The following actions allow you to hook into the image resizing process timeline. You can place them in your theme's functions.php file.
responsive_pics_request_scheduled
This action fires when ResponsivePics has scheduled a new image resize request to the ActionScheduler queue.
do_action('responsive_pics_request_scheduled', (int) $post_id, (array) $resize_request);
Parameters
-
$post_id
(integer) The attachment ID -
$resize_request
(array) The resize request parameters:
[ 'id' => (int) The attachment ID, 'quality' => (int) The requested image quality, 'width' => (int) The requested image width, 'height' => (int) The requested image height, 'crop' => (array) The requested image crop positions, 'ratio' => (float) The requested image ratio, 'path' => (string) The requested image file path, 'rest_route' => (string) The requested rest api route ]
responsive_pics_request_processed
This action fires when the ActionScheduler has processed an image resize request in the queue.
do_action('responsive_pics_request_processed', (int) $post_id, (int) $quality, (int) $width, (int) $height, (array) $crop, (float) $ratio, (string) $resize_path, (string) $rest_route);
Parameters
-
$post_id
(int) The attachment ID -
$quality
(int) The requested image quality -
$width
(int) The requested image width -
$height
(int) The requested image height -
$crop
(array) The requested image crop positions in percentages:
[
'x' => (int) The horizontal crop position as percentage,
'y' => (int) The vertical crop position as percentage
]
-
$ratio
(float) The requested image ratio -
$resize_path
(string) The requested image file path
responsive_pics_file_saved_local
This action fires when ResponsivePics has successfully saved a resized image file locally.
do_action('responsive_pics_file_saved_local', (int) $post_id, (array) $file);
Parameters
-
$post_id
(int) The attachment ID -
$file
(array) The saved file containing:
[
'path' => (string) The saved image filepath,
'file' => (string) The saved image filename,
'width' => (int) The saved image file width,
'height' => (int) The saved image file height,
'mime-type' => (string) The saved image file mime-type,
'filesize' => (int) The saved image filesize
]
responsive_pics_file_s3_uploaded
This action fires when WP Offload Media has uploaded the resized image file to your S3 storage.
do_action('responsive_pics_file_s3_uploaded', (int) $post_id, (array) $file);
Parameters
-
$post_id
(int) The attachment ID -
$file
(array) The S3 uploaded file containing:
[
'path' => (string) The uploaded image filepath,
'file' => (string) The uploaded image filename,
'width' => (int) The uploaded image file width,
'height' => (int) The uploaded image file height,
'mime-type' => (string) The uploaded image file mime-type,
'filesize' => (int) The uploaded image filesize
]
responsive_pics_file_deleted_local
This action fires when ResponsivePics has successfully deleted a resized image file locally.
do_action('responsive_pics_file_deleted_local', (int) $post_id, (string) $file);
Parameters
-
$post_id
(int) The attachment ID -
$file
(string) The deleted image file path
responsive_pics_file_s3_deleted
This action fires when WP Offload Media has deleted a resized image file in your S3 storage.
do_action('responsive_pics_file_s3_deleted', (int) $post_id, (array) $file_paths);
Parameters
-
$post_id
(int) The attachment ID -
$file_paths
(array) The deleted resized file paths in your S3 storage.
Features
S3 Offload
When you installed and activated the WP Offload Media (Lite) plugin, this library automatically:
- Will offload any resized/cropped image generated by this plugin to your configured S3 storage provider.
- Will delete any resized/cropped image generated by this plugin in your configured S3 storage provider when deleting an attachment.
NOTE
When the Remove Files From Server option is activated in the Offload Media Lite settings, this plugin will NOT remove any resized/cropped image generated by this plugin!
Lazyloading
When enabling the lazyload option in the get_picture or get_image functions or API endpoints with a boolean value true, this library automatically:
- adds a
lazyloadclass to the<img>element. - swaps the
srcsetwithdata-srcsetattribute on the picture<source>or the<img>elements.
This will enable you to use a lazy loading plugin such as Lazysizes.
You can also set your own lazyload class by passing it to ResponsivePics library in your theme’s functions.php:
if (class_exists('ResponsivePics')) { ResponsivePics::setLazyLoadClass('lazy'); }
To install Lazysizes in your wordpress theme as a node module, run the following command from your theme directory:
npm
npm install --save lazysizes
Yarn
yarn add lazysizes
And import the package in your theme’s global javascript file:
import 'lazysizes';
When enabling lazyload with a string value native, this library automatically:
- adds the native
loading="lazy"attribute to the<img>element.
LQIP (Low Quality Image Placeholder)
When enabling the lqip option in the get_image function or /responsive-pics/v1/image API endpoint, this library automatically:
- adds a
blur-upclass to the<img>element. - adds a fallback
srcattribute on the<img>element with a low quality placeholder image with a default width of 100px.
This will enable you to style your placeholder image before the actual high quality image is loaded.
You can also set your own lqip class by passing it to ResponsivePics library in your theme’s functions.php:
if (class_exists('ResponsivePics')) { ResponsivePics::setLqipClass('blurred'); }
Intrinsic Aspectratio
When enabling the intrinsic option in the get_picture function or /responsive-pics/v1/picture API endpoint, this library automatically:
- adds a intrinsic class to the
<picture>element and aintrinsic__itemclass to the picture<img>element. - adds
data-aspectratioattributes on the picture<source>and<img>elements with the calculated source image ratio.
This will enable you to pre-occupy the space needed for an image by calculating the height from the image width or the width from the height with an intrinsic plugin such as the lazysizes aspectratio extension.
To use the Lazysizes aspectratio extension in your wordpress theme, first install lazysizes as a node module as described in the Lazyloading section and import the extension in your theme’s global javascript file:
import 'lazysizes/plugins/aspectratio/ls.aspectratio.js';
Issues
Please submit any issues you experience with the ResponsivePics library over at Github.
Todo's
- Add Application Password Authentication to REST API endpoints.
- Add Gutenberg Blocks support.
- Add WPML (Media) support for focal point.
- Add multiple background images syntax support.
- Add bulk image delete functionality.
Maintainers
ResponsivePics is developed and maintained by:
@twansparant (creator)
Copyright
Code and documentation copyright 2017-2025 by Toine Kamps & Clarify.
Code released under the MIT License.
Docs released under Creative Commons.
